SYSTEMATIC RANDOM SAMPLING
TLDRThis video script introduces systematic sampling, a probability sampling method where every nth element from a population list is selected for the sample. It emphasizes the precision and ease of this method, akin to simple random sampling, with a key feature of selecting elements at regular intervals. An example is provided, demonstrating how to determine the interval and select respondents from a target population of 300 to achieve a sample size of 60. The process is further illustrated with a practical application involving high school students.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses probability sampling, specifically focusing on systematic sampling as presented by Dr. Amadeo Cristobal.
- 🔢 Systematic sampling involves selecting every nth element from a population after determining the sample size.
- 📈 The process starts with listing all elements of the population, which is then used to systematically choose elements at regular intervals.
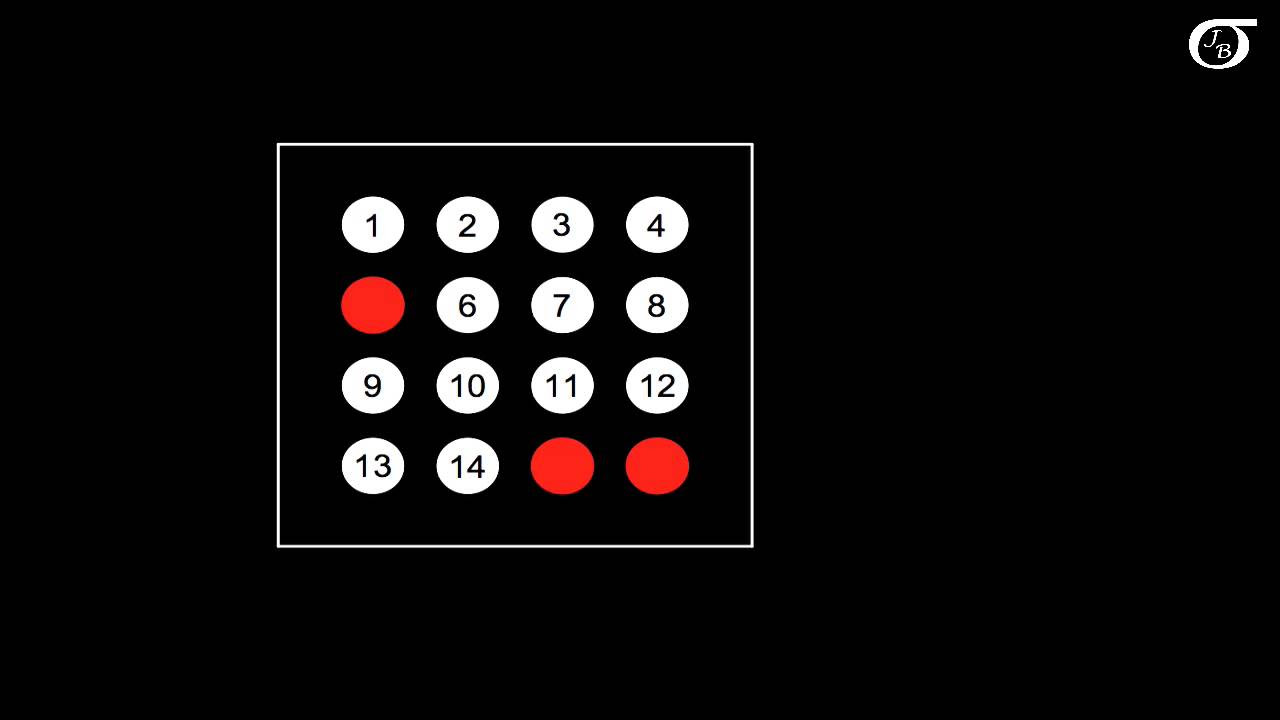
- 🎯 An example is given where a target population of 300 is divided by a desired sample size of 60, resulting in an interval of 5.
- 🔹 The nth element (in this case, 5) is used to start the selection, and every 5th element thereafter is included in the sample.
- 🌟 Systematic sampling is noted to be as precise as simple random sampling but with the added feature of a predictable pattern.
- 📝 Another example is provided where a list of 1000 high school students is used, and every 10th student is selected for the sample.
- 🎲 The use of a random number generator, such as strips of paper with numbers 0-9, is suggested for selecting the starting point in the sampling process.
- 🎥 The video is part of a series on sampling methods, with a previous video discussing simple random sampling.
- 👥 The target audience for this content appears to be researchers, students, or individuals interested in statistical sampling methods.
- 📊 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding sampling techniques for accurate data collection and analysis.
- 👋 The video ends with a call to action for viewers to join the next video in the series for further discussion on sampling methods.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is systematic sampling, a method under probability sampling.
Who are the researchers mentioned in the script?
-The researchers mentioned in the script are Dr. Amadeo Cristobal and Tanda and Ditos.
How is systematic sampling defined in the video script?
-Systematic sampling is defined as a method of selecting every nth element of the population after the size of the sample has been determined.
What is the formula used to determine the nth element in systematic sampling?
-The formula used to determine the nth element in systematic sampling is the total population size divided by the desired sample size.
Can you provide an example of how to calculate the sampling interval in systematic sampling?
-For example, if you have a target population of 300 and a desired sample size of 60, you would divide 300 by 60 to get an interval of 5. Every 5th element in the population list would then be selected for the sample.
What is the purpose of listing all elements of the population in systematic sampling?
-Listing all elements of the population in systematic sampling allows for a structured and systematic selection process, ensuring that each member of the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample.
How does systematic sampling differ from simple random sampling?
-Systematic sampling differs from simple random sampling in that it involves selecting elements at a fixed interval after a random starting point, whereas simple random sampling does not follow a fixed pattern and each selection is independent.
What is the advantage of using systematic sampling over other probability sampling methods?
-The advantage of systematic sampling is that it is precise and efficient, especially when dealing with large populations. It also reduces the potential for bias and simplifies the sampling process.
How does the video script illustrate the selection process in systematic sampling?
-The video script illustrates the selection process by using an example where a list of the entire population is created, and then every nth element is selected according to the calculated interval.
What is the significance of the 'nth element' in systematic sampling?
-The 'nth element' in systematic sampling is significant as it determines the regular interval at which elements are selected from the population list. This ensures a systematic and structured approach to sampling.
How can researchers ensure that their sampling method is representative of the population?
-Researchers can ensure that their sampling method is representative by using probability sampling techniques like systematic sampling, which gives each member of the population an equal chance of being selected.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Probability Sampling
This paragraph introduces the topic of probability sampling, specifically focusing on simple random sampling. It mentions a previous discussion about the basics of sampling and introduces the concept of systematic sampling as explained by Dr. Amadeo Cristobal. The paragraph explains that systematic sampling involves selecting every nth element from a population after determining the sample size. It provides an example with a target population of 300 and a sample size of 60, illustrating how the nth element is identified and how the sampling proceeds from there.
🎯 Conducting Systematic Sampling
This paragraph delves deeper into the methodology of systematic sampling. It describes the process of listing all elements of the target population, such as 1000 high school students, and then identifying the nth element using a predetermined interval. The example continues with the calculation of the interval and the selection of every fifth element from the list to form the sample. The paragraph emphasizes the precision and efficiency of systematic sampling as a method and concludes with a prompt for the audience to engage in the next video.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Probability Sampling
💡Simple Random Sampling
💡Respondents
💡Population
💡Systematic Sampling
💡Sample Size
💡Interval
💡List
💡Research
💡Generalization
💡Validity
Highlights
Introduction to probability sampling and its importance in research
Discussion on simple random sampling from the previous video
Definition of systematic sampling as per Dr. Amadeo Cristobal's book
Explanation of how to determine the size of the sample for systematic sampling
Process of selecting every nth element from the population list
Comparison of systematic sampling to simple random sampling in terms of precision
Illustrative example of systematic sampling with a population of 300
Formula for calculating the interval for systematic sampling
Selection of respondents from the list using the determined interval
Mention of the target sample size and its role in systematic sampling
Practical application of systematic sampling with high school students
Use of random numbers for the initial selection in systematic sampling
Instructions for the next steps in conducting systematic sampling
Conclusion and transition to the next video with a call to action
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: