Different Types of Waves : Longitudinal & Transverse Waves | Mechanical Wave | Physics
TLDRThis video script introduces the concept of waves, focusing on two primary types: transverse and longitudinal. Transverse waves are characterized by medium particles moving perpendicular to the wave's direction of propagation, with examples including water waves and light waves. Longitudinal waves involve particles moving parallel to the wave's direction, as seen in sound waves. The script uses relatable examples, such as people in a queue and a slinky, to illustrate wave behavior and propagation, promising a detailed exploration of sound waves in future content.
Takeaways
- 🌊 A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another without transporting any matter.
- 📏 Mechanical waves require a medium like solid, liquid, or gas to travel, as exemplified by water waves formed when a stone is thrown into a lake or pond.
- 🔄 The particles in the medium of a mechanical wave undergo to and fro motion about their mean position, while the disturbance itself moves forward.
- 🌀 Transverse waves are characterized by the particles of the medium moving perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, such as in water waves, light waves, and radio waves.
- 🐍 A slinky can be used to visually demonstrate the properties of a transverse wave, showing how it moves in a wavy pattern while its particles oscillate about their mean position.
- 🤝 In the example of a group of people, a disturbance can also be propagated through a push and pull motion, which is different from the up and down motion observed when they are holding each other's shoulders.
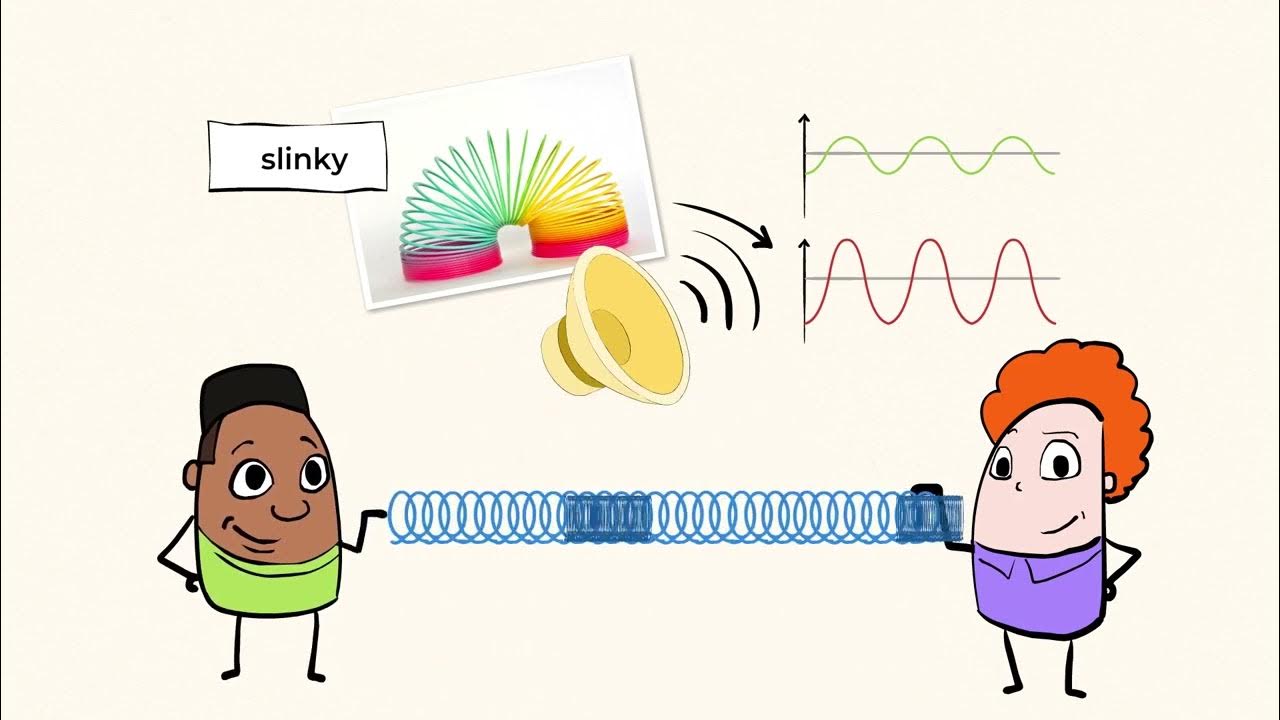
- 🔄 Longitudinal waves are the second type of wave, where the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave propagation, as seen in sound waves and waves in a slinky.
- 📊 Compressions and rarefactions are features of longitudinal waves, where the medium's particles come together (compressions) and move apart (rarefactions) along the direction of wave travel.
- 💬 Sound waves are a common example of longitudinal waves, created when speaking or producing any form of audible noise.
- 📚 The distinction between transverse and longitudinal waves lies in the direction of particle motion relative to the wave's propagation direction.
- 🔜 Future modules will delve into the specifics of sound waves, building on the foundational understanding of wave types established in this script.
Q & A
What is the definition of a wave?
-A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another without transporting any matter.
What is a mechanical wave?
-A mechanical wave is a type of wave that travels through a medium such as a solid, liquid, or gas, causing the particles of the medium to move and transmit energy.
How do particles move in a mechanical wave?
-In a mechanical wave, particles of the medium undergo to and fro motion about their mean position, but they do not travel with the wave itself.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
-In a transverse wave, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, while in a longitudinal wave, the particles move parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
Can you provide an example of a transverse wave?
-An example of a transverse wave is the ripples formed when a stone is dropped into a lake or pond, as well as light waves and radio waves.
How does a slinky demonstrate a transverse wave?
-When a slinky is whipped, it moves in a wavy pattern, representing a transverse wave where the particles (rings of the slinky) move up and down about their mean position while the wave itself moves horizontally.
What are compressions and rarefactions in a longitudinal wave?
-Compressions are regions in a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are closer together, and rarefactions are regions where the particles are farther apart. Both compressions and rarefactions move forward through the medium.
What is an example of a longitudinal wave?
-Sound waves are an example of longitudinal waves. When speaking, the sound waves that emanate from the mouth cause the air particles to compress and rarefy as they propagate through the air.
How does the movement of particles in a wave relate to the type of wave?
-The movement of particles in a wave determines whether it is a transverse or longitudinal wave. If particles move perpendicular to the wave propagation, it is a transverse wave; if parallel, it is a longitudinal wave.
What will be discussed in the next module of the script?
-The next module will discuss sound waves in detail, exploring their properties and behavior in more depth.
How does the script use the example of people standing in a queue to illustrate wave motion?
-The script uses the example of people standing in a queue to demonstrate how a disturbance (one person sitting and standing) can propagate through a medium (the group of people) in the form of a wave, with each person moving up and down or side to side, depending on the arrangement.
Outlines
🌊 Introduction to Wave Types
This paragraph introduces the concept of waves, describing them as disturbances that travel through a medium without transporting matter. It differentiates between mechanical and transverse waves, using examples such as water waves and the motion of people in a queue to illustrate the concept. The paragraph explains that in mechanical waves, particles of the medium move in a to-and-fro motion about their mean position, and the wave's direction of propagation is perpendicular to this motion. It also introduces the idea of transverse waves, providing examples like water waves, light waves, and radio waves, and uses the demonstration of a slinky to visually explain the wave's movement.
🚀 Understanding Longitudinal Waves
The second paragraph delves into longitudinal waves, contrasting them with transverse waves. It describes how in longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave propagation. The paragraph uses the example of a slinky being pushed to demonstrate how compressions and rarefactions occur and travel along the slinky, representing the wave's movement. Sound waves are highlighted as a common example of longitudinal waves, with the speaker's voice being a relatable instance. The paragraph concludes by summarizing the two types of waves discussed: transverse and longitudinal, providing clear examples for each and setting the stage for a more detailed discussion on sound waves in the subsequent module.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Waves
💡Mechanical Waves
💡Transverse Waves
💡Longitudinal Waves
💡Disturbance
💡Medium
💡Propagation
💡Oscillation
💡Compression and Rarefaction
💡Energy Transfer
Highlights
Introduction to the topic of types of waves.
Definition of a wave as a disturbance that travels through a medium without transporting matter.
Description of a mechanical wave and its relation to disturbances in solid, liquid, or gas mediums.
Example of water waves as a mechanical wave when a stone is thrown into a lake or pond.
Explanation of how particles in a medium move in a to-and-fro motion about their mean position in a mechanical wave.
Introduction to transverse waves and their definition.
Examples of transverse waves including water waves, light waves, and radio waves.
Demonstration of a transverse wave using a slinky to show the to-and-fro motion and wave propagation.
Introduction to longitudinal waves and their definition.
Description of particle motion in longitudinal waves as parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
Examples of longitudinal waves such as sound waves and waves in a slinky.
Explanation of compressions and rarefactions in longitudinal waves, with regions of crowded and far-apart rings.
Summary of the two types of waves discussed: transverse and longitudinal waves, with their respective particle motions.
预告下个模块将详细讨论声波。
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: