Weight and Mass are Not the Same
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the nuanced differences between weight and mass, clarifying common misconceptions. It explains that mass, measured in kilograms, is a scalar quantity and an intrinsic property of an object, while weight, measured in Newtons, is a vector quantity dependent on the force of gravity. The script uses examples from NASA, Michio Kaku's book, and YouTube videos to illustrate how weight is often incorrectly used to mean mass. It emphasizes that while mass remains constant across different planets, weight varies with the gravitational force exerted on the object.
Takeaways
- 📏 Weight and mass are not the same; they are often confused but represent different physical concepts.
- 📐 The base SI unit for mass is kilograms, while for weight (force), it is Newtons.
- 🌍 Weight is the force of gravity acting between the Earth and an object, making it dependent on location.
- 🔽 Weight is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction (downward), whereas mass is a scalar, with only magnitude.
- 🚀 Mass is an intrinsic property of an object and does not change regardless of location, while weight can vary with gravity.
- 🌕 On Earth, the acceleration due to gravity (g) is approximately 9.81 meters per second squared.
- 🌕🌑 On the moon, the weight of an object is 1/6th of its weight on Earth due to the lower gravity.
- 📚 The media sometimes incorrectly uses weight and mass interchangeably, even using kilograms to describe weight.
- 🧠 Understanding the distinction between weight and mass is important for accurate scientific communication and comprehension.
- 🛰️ Future space travel and living may make the difference between weight and mass more apparent to the general public.
Q & A
What is the base SI unit for mass?
-The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram.
Is weight the same as mass?
-No, weight and mass are not the same. Weight is the force of gravity acting on an object, while mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object.
What is the SI unit for force?
-The SI unit for force is the Newton.
How is a Newton defined in base SI dimensions?
-A Newton is defined as a kilogram meter per second squared (1 kg·m/s²).
Why do people sometimes confuse weight and mass?
-People often confuse weight and mass because they are used interchangeably in everyday language, even though they have different physical meanings.
Is weight a scalar or a vector quantity?
-Weight is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction (downward due to gravity).
Does an object's mass change when it is on a different planet?
-No, an object's mass does not change when it is on a different planet. Mass is an intrinsic property of an object and is constant regardless of location.
How does the acceleration due to gravity affect weight?
-Weight is calculated as the product of an object's mass and the acceleration due to gravity (W = m·g). Therefore, changes in the acceleration due to gravity will result in changes in weight.
What is the standard acceleration due to gravity on Earth?
-The standard acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.81 meters per second squared (9.81 m/s²).
How would the weight of a 70 kg person change on the moon?
-On the moon, a person with a mass of 70 kg would weigh about 110 Newtons or approximately 26 pounds, which is less than their weight on Earth due to the moon's lower acceleration due to gravity.
What is the range of variation for the acceleration due to gravity on Earth's surface?
-The acceleration due to gravity varies only slightly on Earth's surface, ranging from 9.78 to 9.83 meters per second squared (9.78 to 9.83 m/s²).
How might the common understanding of weight and mass change in the future?
-With the potential for space travel and living in different gravitational environments becoming more common, people may become more aware of the distinction between weight and mass as they experience changes in weight due to different gravitational forces.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Weight vs Mass
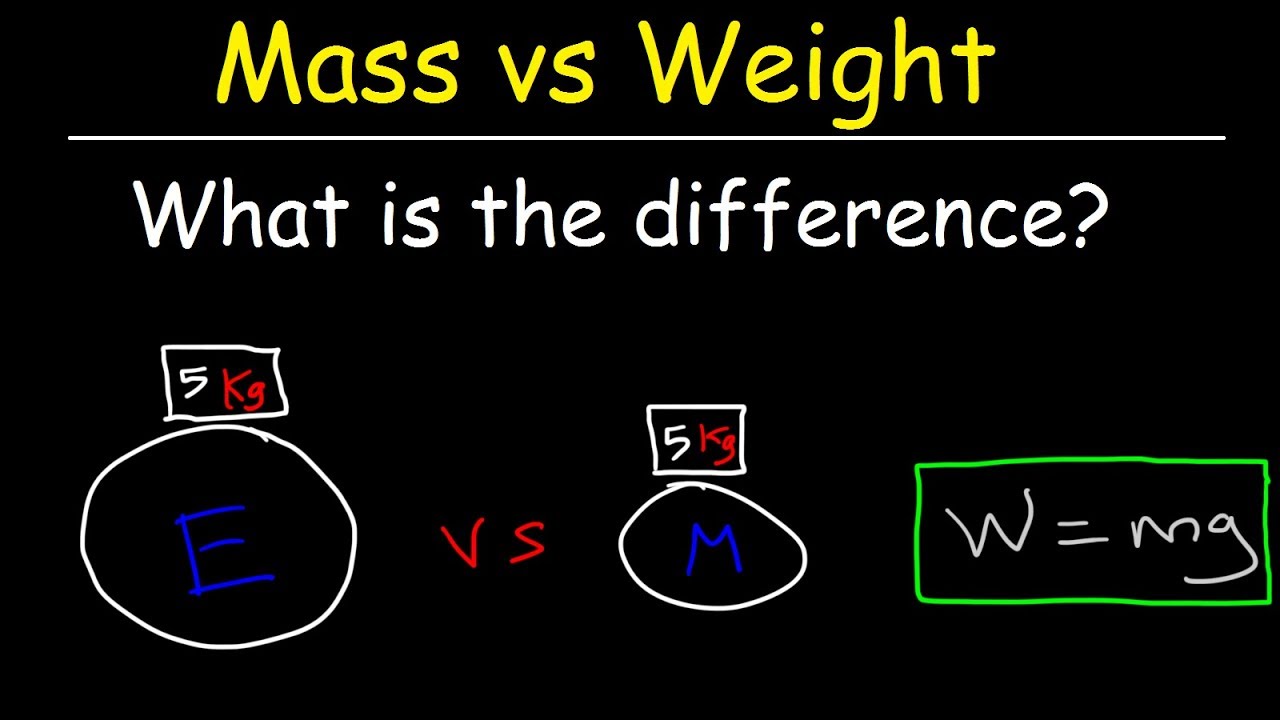
This paragraph discusses the fundamental differences between weight and mass. It clarifies that while weight and mass are often used interchangeably, they are distinct concepts. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is measured in kilograms, the base SI unit for mass. Weight, on the other hand, is the force of gravity acting on an object and is measured in Newtons, which are equivalent to a kilogram meter per second squared. The paragraph also highlights that weight is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, while mass is a scalar, having only magnitude. Additionally, it points out that weight can change when one moves to a different planet due to varying gravitational forces, whereas mass remains constant as it is an intrinsic property of the object. The discussion includes references to common misconceptions in the media and scientific literature, emphasizing the importance of using the correct terminology.
🚀 The Future of Weight and Mass Perception
The second paragraph envisions a future where the common confusion between weight and mass might be reduced. It suggests that with advancements such as space elevators, people will experience changes in gravity and, consequently, in weight more frequently. This could lead to a better understanding and distinction between the concepts of weight and mass. The paragraph ends on a hopeful note, looking forward to a time when the variations in gravitational force will be a regular part of human experience, potentially enhancing the public's comprehension of these physical properties.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Weight
💡Mass
💡Gravity
💡Newton
💡SI Units
💡Vector
💡Scalar
💡Intrinsic Property
💡Extrinsic Property
💡Acceleration Due to Gravity
💡Space Elevators
Highlights
Weight and mass are not the same but often used interchangeably.
The base SI unit for mass is kilograms.
Weight is also known as the force of gravity, representing the attraction between Earth and an object.
Weight is a force and has the dimensions of force.
The SI unit for force is the Newton.
One Newton equals one kilogram meter per second squared.
Mass is measured in kilograms, while weight is measured in Newtons.
Weight given in kilograms in the media is technically incorrect.
Examples of incorrect weight usage in media include NASA's description of the Saturn V rocket and Michio Kaku's reference to Earth's weight.
Weight is a vector with both magnitude and direction, whereas mass is a scalar with only magnitude.
Mass is an intrinsic property, while weight is an extrinsic property.
The weight of an object depends on its mass and the acceleration due to gravity.
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.81 meters per second squared.
An object's mass remains constant while its weight changes when on different celestial bodies.
On the moon, an object that weighs 70 kilograms on Earth would weigh about 26 pounds.
The almost constant value of Earth's gravity leads to the frequent interchangeability of weight and mass in everyday language.
The variation in Earth's gravity is minimal, ranging from 9.78 to 9.83 meters per second squared.
The dream of space elevators and the experience of changing gravity could lead to better understanding of weight and mass differences.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Difference between MASS and WEIGHT

GCSE Physics Revision "Gravity and Weight"

Weight, Force, Mass & Gravity | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool

What is Mass Vs. Weight in Physics? - [1-5-11]

Are Mass and Weight the same thing? | Physics | Don't Memorise
Physics - What Is The Difference Between Mass and Weight?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: