GCSE Physics Revision "Gravity and Weight"
TLDRThis educational video explains the concepts of mass and weight, emphasizing that mass is a scalar quantity, constant regardless of location, and measured in kilograms. Weight, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that depends on gravity's force and is measured in Newtons. The weight of an object on Earth's surface is calculated by multiplying its mass in kilograms by the gravitational field strength, 9.8 Newtons per kilogram. The video also introduces the concept of the center of mass, highlighting that weight acts at this single point.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Gravity is a universal force of attraction between all objects and is a non-contact force.
- 📈 Mass is a scalar quantity that measures the amount of matter in an object, with the unit being the kilogram.
- 📍 An object's mass is constant regardless of its location (e.g., Earth, Moon, or deep space).
- 🔢 Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity and is measured in Newtons.
- 📉 The weight of an object depends on its location, as different places have different gravitational field strengths.
- 🔄 The gravitational field strength at the Earth's surface is approximately 9.8 Newtons per kilogram.
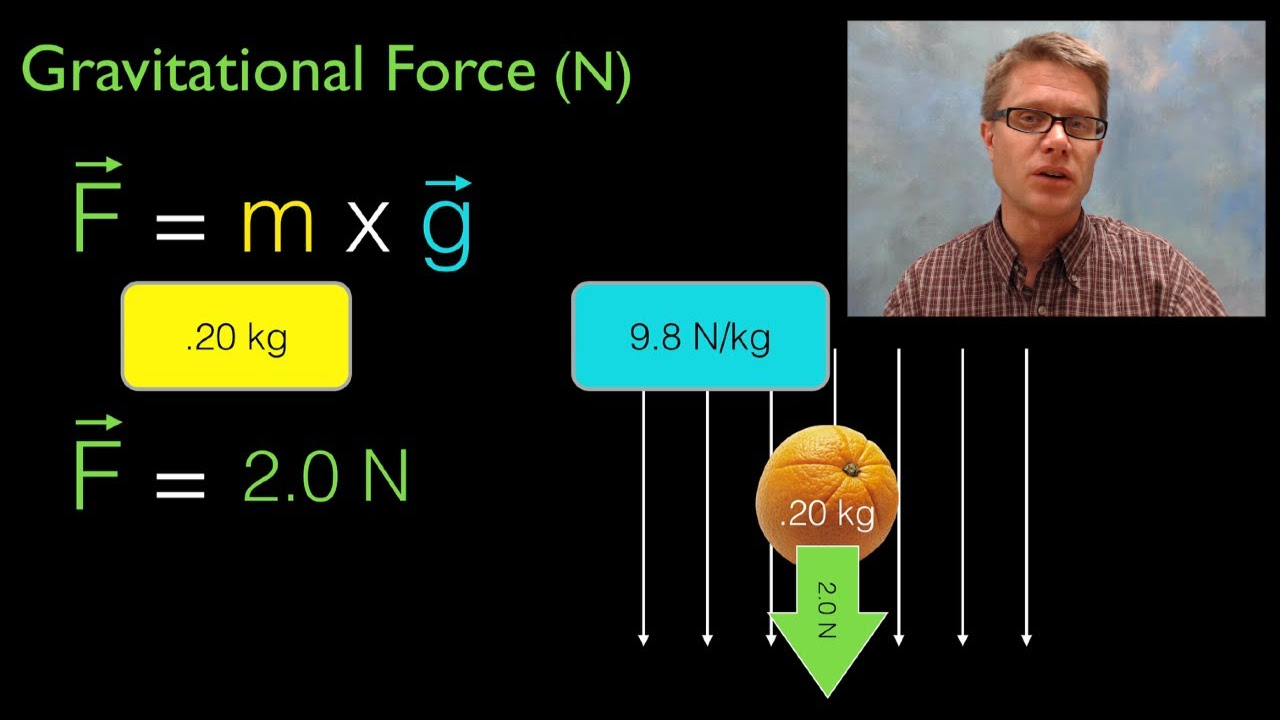
- 🧮 The weight of an object can be calculated using the formula: Weight (in Newtons) = Mass (in kilograms) × Gravitational Field Strength (in Newtons per kilogram).
- 🔍 The weight of an object is directly proportional to its mass; doubling the mass doubles the weight.
- 📊 A calibrated spring balance, or Newton meter, can be used to determine an object's weight.
- 🌕🌖 The gravitational field strength varies by location; for example, it's 1.6 Newtons per kilogram on the Moon.
- 🌀 The center of mass is the point where the force of gravity can be considered to act on an object.
Q & A
What is the definition of weight in the context of this video?
-Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity.
How is weight different from mass?
-Weight is a force measured in Newtons and depends on the gravitational field strength, while mass is a scalar quantity measured in kilograms and represents the amount of matter in an object, independent of location.
What is the unit of mass?
-The unit of mass is the kilogram.
Why doesn't the mass of an object change when it is in different locations?
-The mass of an object doesn't change because it is a measure of the amount of matter, which is intrinsic to the object and does not depend on its location.
What is the gravitational field strength at the surface of the Earth?
-The gravitational field strength at the surface of the Earth is 9.8 Newtons per kilogram.
How can you calculate the weight of an object?
-You can calculate the weight of an object using the equation: weight (in Newtons) = mass (in kilograms) × gravitational field strength (in Newtons per kilogram).
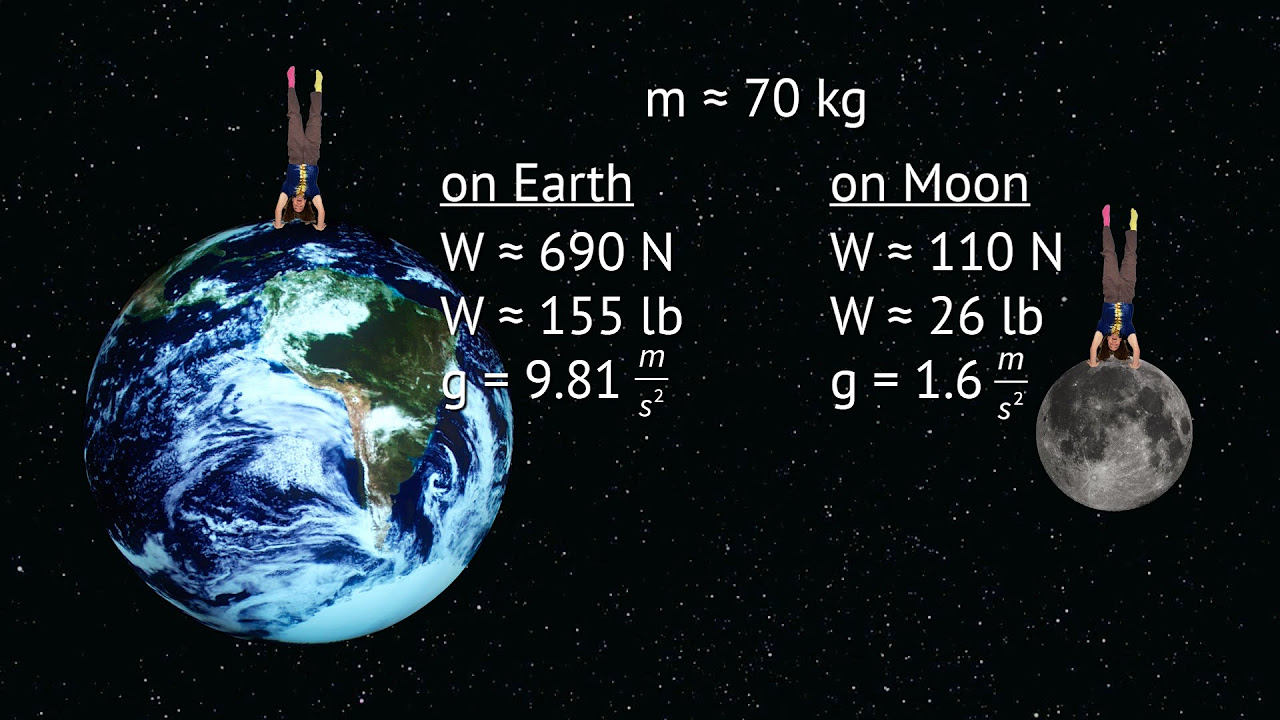
How does the weight of an object change if you change its location, such as from Earth to the Moon?
-The weight of an object changes because it is dependent on the gravitational field strength of the location. For example, on the Moon, which has a gravitational field strength of 1.6 Newtons per kilogram, the weight would be less than on Earth.
What is a calibrated spring balance used for?
-A calibrated spring balance is used to determine an object's weight by measuring the force of gravity acting on it.
What is the center of mass?
-The center of mass is the point at which the force due to gravity can be considered to act on an object.
Why is it important to understand the concept of the center of mass?
-Understanding the concept of the center of mass is important because it helps in analyzing the stability and balance of objects under the influence of gravity.
How does the gravitational field strength vary with location?
-The gravitational field strength varies with location because it is dependent on the mass of the celestial body and the distance from its center. For instance, the Moon's gravitational field strength is 1.6 Newtons per kilogram, different from Earth's 9.8 Newtons per kilogram.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Weight and Mass
This paragraph introduces the concepts of weight and mass, explaining that weight is the force of gravity acting on an object and is measured in Newtons, while mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms. It emphasizes that mass is a scalar quantity and does not change regardless of location, unlike weight, which is a vector quantity and can vary depending on the gravitational field strength of the location. The paragraph also introduces the gravitational field strength (G) and its role in calculating weight using the equation: Weight (Newtons) = Mass (kg) * Gravitational Field Strength (N/kg).
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Gravity
💡Mass
💡Weight
💡Vector Quantity
💡Gravitational Field Strength
💡Center of Mass
💡Spring Balance
💡Direct Proportionality
💡Newton
💡Scalar Quantity
💡Kilogram
Highlights
Gravity is a force of attraction between all objects and is a non-contact force.
Gravity is a vector quantity because it has magnitude and direction.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is measured in kilograms.
Mass is a scalar quantity and does not depend on the location of the object.
The weight of an object is the force acting on it due to gravity and is measured in Newtons.
The weight of an object depends on its location, unlike its mass.
On Earth's surface, the gravitational force is 9.8 Newtons per kilogram, known as gravitational field strength.
Weight can be calculated using the equation: Weight (in Newtons) = Mass (in kilograms) × Gravitational Field Strength (in Newtons per kilogram).
Weight is directly proportional to the mass of an object; doubling the mass doubles the weight.
A calibrated spring balance, or Newton meter, can be used to determine an object's weight.
The gravitational field strength varies depending on the location, affecting the weight of objects.
On the Moon, the gravitational field strength is 1.6 Newtons per kilogram, significantly less than Earth's.
The center of mass is the point where the force of gravity can be considered to act on an object.
Understanding the concepts of mass, weight, and gravitational field strength is crucial for exams and practical applications.
The video provides a comprehensive lesson on describing weight and calculating the weight of an object.
The concept of mass being constant regardless of location is a key fact to remember.
The video emphasizes the importance of learning and understanding the equation for calculating weight.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Weight and Mass are Not the Same
Gravitational Force

Weight, Force, Mass & Gravity | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool

Are Mass and Weight the same thing? | Physics | Don't Memorise

Difference between MASS and WEIGHT

Understanding the Relationship Between Mass and Weight | Modeling Instruction Lab | Arbor Scientific
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: