Physics - What Is The Difference Between Mass and Weight?
TLDRThis video elucidates the distinction between mass and weight, emphasizing that mass is a measure of matter and inertia, while weight is the force due to gravity. It explains how weight varies by location—differentiating Earth's gravity from that of the Moon and Mars—while mass remains constant. The video also demonstrates how to calculate gravitational acceleration and the force of gravity on an object, using formulas and practical examples to clarify the concepts.
Takeaways
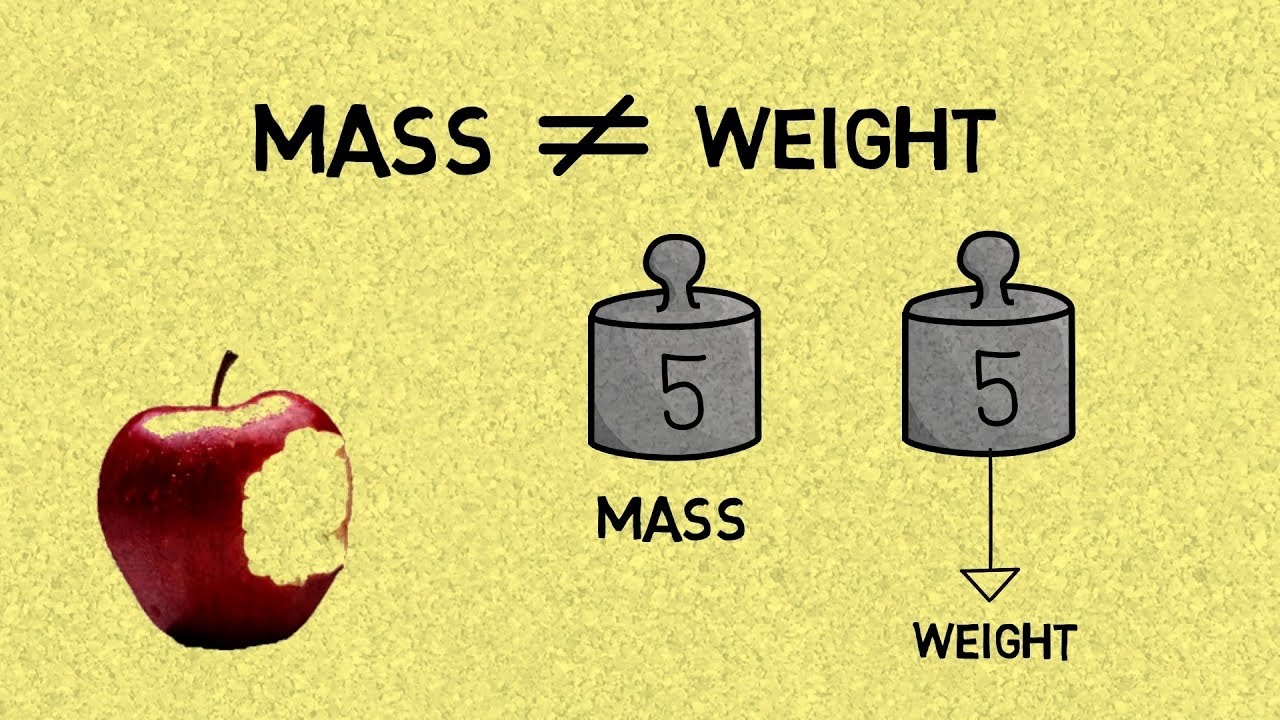
- 📏 Mass and weight are distinct concepts: mass is a measure of the quantity of matter and inertia, while weight is the force exerted by gravity.
- 🌍 The mass of an object (in kg) remains constant regardless of its location, but its weight (in newtons) changes based on the gravitational acceleration of the environment.
- 🌕 On Earth, weight is calculated as the product of mass (kg) and the gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s²).
- 🌖 On the Moon, the gravitational acceleration is approximately 1.7 m/s², resulting in a weight that is about 1/6th of what it would be on Earth.
- 🚀 Weightlessness or reduced weight is experienced when an object's acceleration is zero, such as in free fall or when in space.
- 📐 The weight force equation is W = mg, where W is the weight, m is the mass, and g is the gravitational acceleration.
- 🌟 On other planets, the gravitational acceleration varies, affecting the weight an object experiences. For example, Mars has a gravitational acceleration about 3.7 m/s², less than Earth's.
- 🔢 To find the gravitational acceleration of an unknown planet, use the weight force equation rearranged to solve for g (gravitational acceleration): g = W/m.
- ⚖️ When an object is at rest on a horizontal surface, the force of gravity acting on it (its weight) is balanced by the normal force exerted by the surface.
- 📈 Converting weight from pounds to newtons requires the use of a conversion factor: 1 pound is approximately equal to 4.45 newtons.
- 👤 To calculate a person's mass in kilograms given their weight in pounds, first convert the weight to newtons using the conversion factor, then apply the weight force equation W = mg with Earth's gravitational acceleration.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between mass and weight?
-Mass represents the quantity of matter and is a measure of an object's inertia, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravitational acceleration.
How is mass measured?
-Mass is measured in kilograms.
What is the formula to calculate weight based on mass?
-Weight is calculated as mass times gravitational acceleration (W = mg).
How does the weight of an object change when it is taken from Earth to the Moon?
-The weight of an object changes because the gravitational acceleration on the Moon is different from Earth's, but the mass remains the same.
What is the gravitational acceleration on the Moon?
-The gravitational acceleration on the Moon is about 1.7 meters per second squared.
How does the weight of an object change based on the planet it is on?
-The weight of an object changes based on the gravitational acceleration of the planet it is on. For example, on Mars, the weight would feel lighter than on Earth due to lower gravitational acceleration.
What is the gravitational acceleration of Earth?
-The gravitational acceleration of Earth is 9.8 meters per second squared.
How can you find the gravitational acceleration of another planet if you know the weight force and mass of an object on that planet?
-You can find the gravitational acceleration by dividing the weight force by the mass (g = W/m).
What is the force of gravity acting on a 24 kilogram object resting on a table?
-The force of gravity acting on the object is 235.2 newtons (24 kg * 9.8 m/s^2).
How do you convert a weight in pounds to newtons?
-You can convert a weight in pounds to newtons by multiplying the weight in pounds by 4.45 (1 pound is equal to 4.45 newtons).
What is the mass of a person weighing 225 pounds in kilograms?
-The mass of a person weighing 225 pounds is approximately 102.2 kilograms (225 * 4.45).
Outlines
📚 Understanding the Concepts of Mass and Weight
This paragraph introduces the fundamental difference between mass and weight. Mass is defined as the measure of the quantity of matter in an object and its inertia, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. The example of a 5-kilogram block is used to illustrate that mass remains constant regardless of location (measured in kilograms), but weight varies based on gravitational acceleration (measured in newtons). The difference in weight on Earth and the Moon is explained, highlighting how the same object can feel lighter on the Moon due to its lower gravitational acceleration.
🚀 Calculating Gravitational Acceleration and Comparing Weights
The second paragraph focuses on practical calculations related to gravitational acceleration and how it affects the weight of objects. It begins with a problem-solving example where the gravitational acceleration of an unknown planet (Planet X) is calculated based on the weight force of a 12-kilogram object. The concept of 'g's' is introduced to compare the gravitational acceleration of different celestial bodies. The paragraph continues with examples of calculating the force of gravity on a stationary object and determining the mass of a person based on their weight in pounds. The importance of understanding the relationship between mass, weight, and gravitational acceleration is emphasized, and viewers are directed to further resources for learning about physics.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mass
💡Weight
💡Gravitational Acceleration
💡Inertia
💡Newton
💡Planet X
💡Normal Force
💡Conversion Factor
💡Weight Equation
💡Force
💡Equilibrium
Highlights
The difference between mass and weight is discussed, emphasizing that mass represents the quantity of matter and inertia, while weight is a force.
Mass is measured in kilograms and is a constant property of an object, independent of location.
Weight is calculated as mass times gravitational acceleration (weight = mg), and it varies based on the gravitational force of the celestial body.
An example is given where a 5 kg object has a different weight on Earth (49 newtons) compared to the Moon (8.5 newtons), despite having the same mass.
The video explains how the weight of an object changes based on the planet it is on, but its mass remains constant.
A problem is solved to find the gravitational acceleration of an unknown planet (Planet X) based on the weight force of a 12 kg object.
It is determined that Planet X has a gravitational acceleration five times greater than Earth's.
The force of gravity acting on a 24 kg object at rest on a table is calculated to be 235.2 newtons.
The concept of normal force is introduced as the upward force exerted by a surface that balances the weight force when an object is at rest.
A method to convert weight from pounds to newtons is provided, using the conversion factor of 1 pound equal to 4.45 newtons.
The mass of a person weighing 225 pounds is calculated to be 102.2 kilograms using the weight to mass conversion formula (w = mg).
The video emphasizes the importance of understanding the distinction between mass and weight for practical applications in different gravitational environments.
The concept of inertia is linked to mass, explaining why objects with more mass have greater resistance to changes in motion.
The video provides a clear explanation of how gravitational acceleration affects the weight of an object, with Earth's acceleration set at 9.8 m/s^2.
The example of astronauts on the Moon demonstrates the effect of low gravitational acceleration on movement and jumping.
The hypothetical scenario of surviving on the Sun is discussed, illustrating the immense gravitational force and its effects.
Comparing Mars' gravitational acceleration to Earth's, the video explains how one would feel lighter on Mars due to its lower gravity.
The video concludes with an invitation for viewers to explore more physics content through a dedicated playlist.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: