Difference between MASS and WEIGHT
TLDRThe video script from moomoomath and science clarifies the distinction between mass and weight. It explains that mass, measured in kilograms, is the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location, while weight, measured in Newtons, is the force of gravity on an object and varies with location. The script uses examples to illustrate how an object's weight changes on different celestial bodies but its mass remains the same, emphasizing the fundamental difference between these two physical properties.
Takeaways
- 📈 Mass and weight are distinct concepts; mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force of gravitational attraction.
- 📊 Mass is measured using a balance and comparing it to a known mass, whereas weight is measured using a scale.
- 🌍 The mass of an object remains constant regardless of its location, but its weight varies depending on the gravitational pull of different celestial bodies.
- 📐 The SI unit for mass is the kilogram, which was originally defined in 1795 as the mass of one liter of water.
- 🇺🇸 In the imperial system, the unit for mass is the slug, which is equivalent to 32 pounds.
- ⚖️ Weight is technically measured in Newtons, with one Newton equal to the force exerted on a 1-kilogram mass accelerating at 1 meter per second squared.
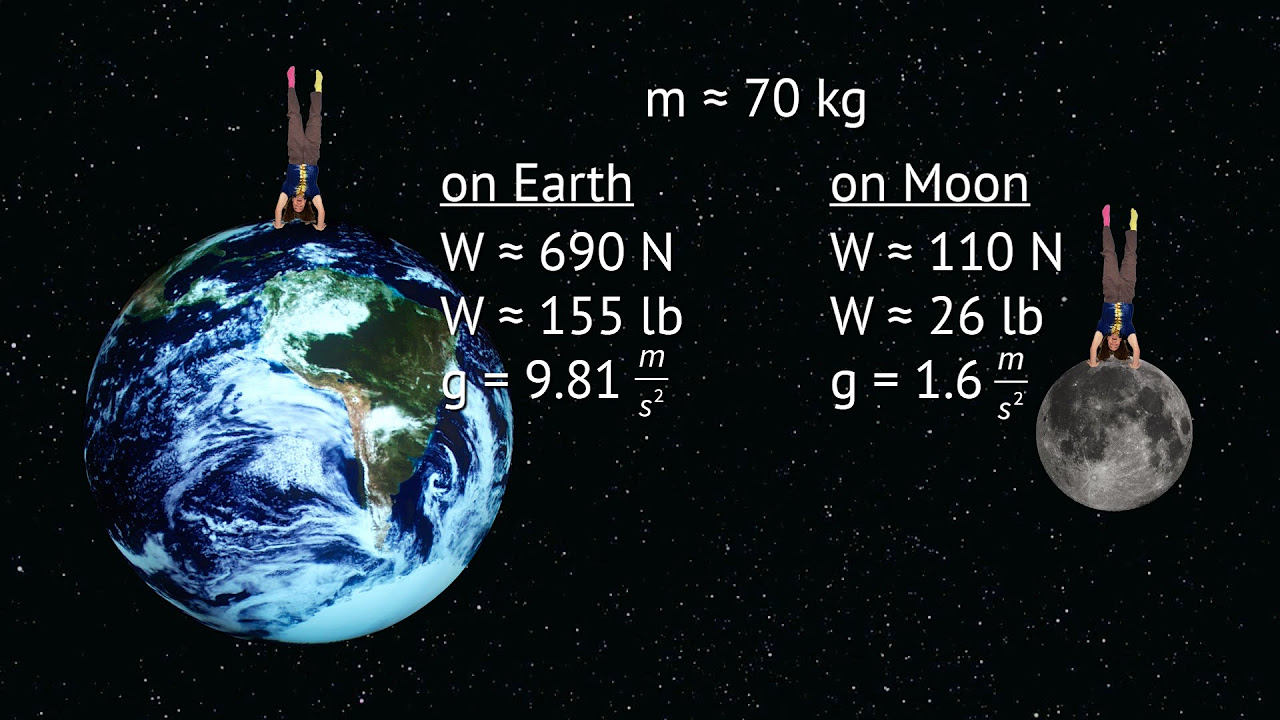
- 🌕 An object with a mass of 1 kilogram has a weight of approximately 9.8 Newtons on Earth.
- 🌙 On the moon, an object's weight is about one-sixth of what it is on Earth, due to the moon's lower gravitational pull.
- 🚀 Weight can change on different planets due to varying gravitational forces, but the mass remains constant.
- 📈 An example: a cube with a mass of 90.91 kilograms and a weight of 200 pounds on Earth would weigh 32 pounds on the moon and 76 pounds on Mars, but its mass remains 90.91 kilograms.
- 🎓 Understanding the difference between mass and weight is crucial for accurate scientific calculations and comprehension.
Q & A
What is the difference between mass and weight?
-Mass is the amount of matter an object contains, while weight is the force of gravitational attraction the object feels towards another object, like the Earth's center.
How is mass measured?
-Mass is measured using a balance by comparing a known amount of matter to an unknown amount of matter.
What is the SI unit for mass?
-The SI unit for mass is the kilogram.
How was the kilogram originally defined in 1795?
-It was defined as the amount of mass of one liter of water.
What is the unit for mass in the imperial system?
-In the imperial system, the unit for mass is the slug, which has a mass of 32 pounds.
How is weight measured?
-Weight is measured on a scale.
What should weight technically be measured in?
-Technically, weight should be measured in Newtons.
What is the weight of an object with a mass of 1 kilogram on the surface of the Earth?
-It has a weight of about 9.8 Newtons.
How does weight change with location?
-Weight changes with location based on the gravitational pull. For example, it varies on the moon and other planets, but mass remains the same.
If a cube has a mass of 90.91 kilograms and weighs 200 pounds on Earth, how much would it weigh on the moon?
-It would weigh 32 pounds on the moon.
What would be the weight of the same cube on Mars?
-The cube would weigh 76 pounds on Mars.
How much would the cube weigh on Jupiter?
-The cube would weigh 468 pounds on Jupiter.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Mass and Weight
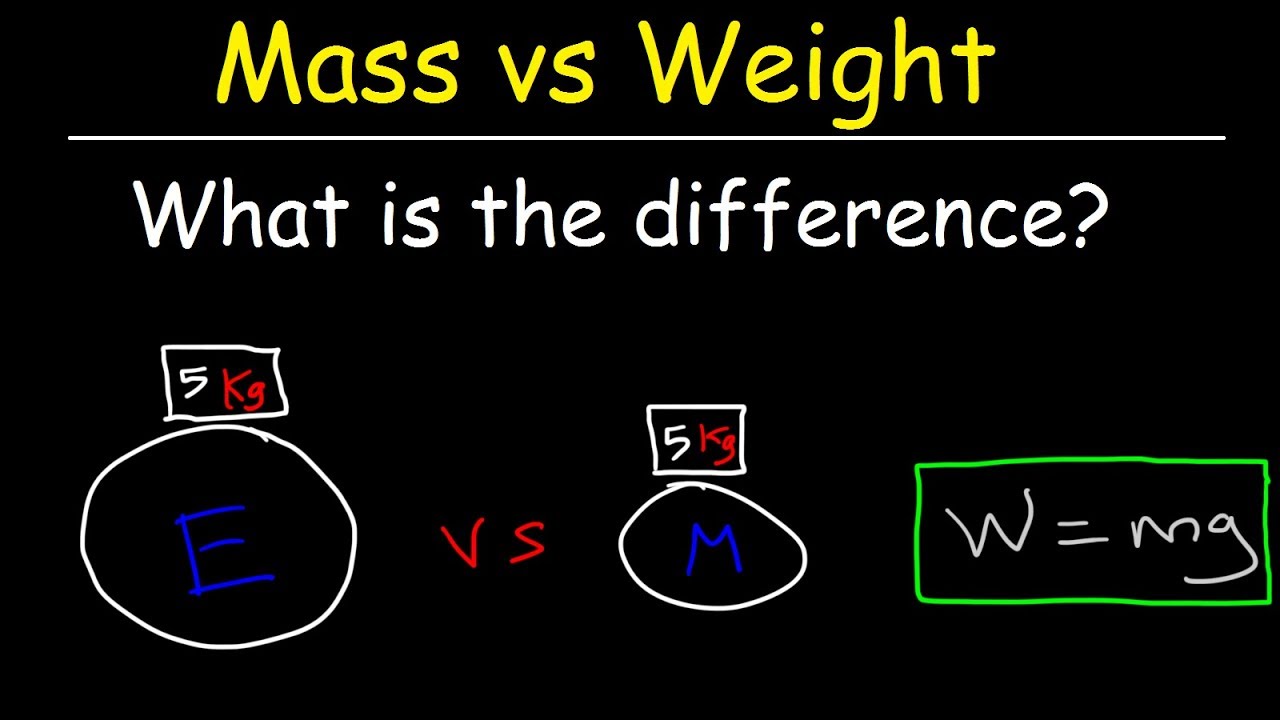
This paragraph explains the difference between mass and weight. It emphasizes that mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force of gravitational attraction. The mass of an object is constant regardless of location, measured in kilograms using a balance. Weight, however, varies with location and is measured in Newtons, with the additional context that 1 kilogram has a weight of about 9.8 Newtons on Earth's surface.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mass
💡Weight
💡Gravitational Attraction
💡Balance
💡Kilogram
💡Newton
💡Slug
💡Matter
💡Gravity
💡Measurement
💡Celestial Bodies
Highlights
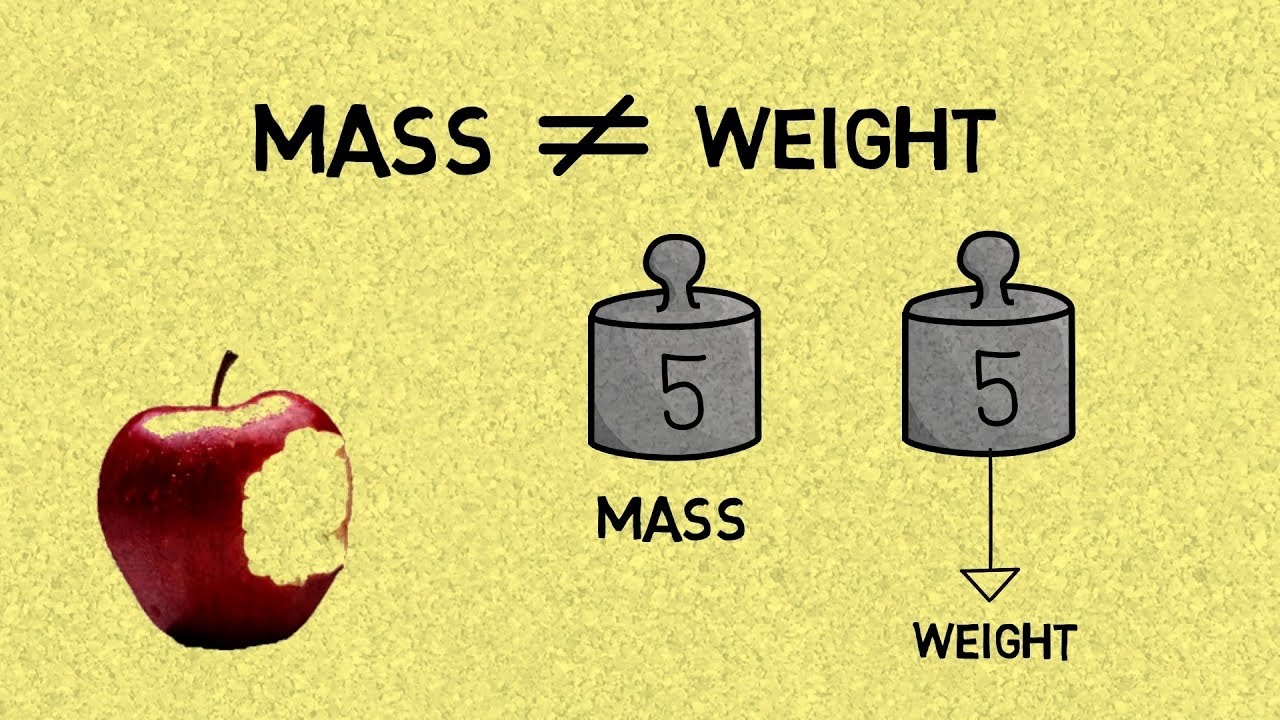
Mass and weight are not the same thing.
Mass is the amount of matter an object contains.
Weight is the force of gravitational attraction an object feels towards another object, like Earth's center.
Mass is measured using a balance by comparing a known amount of matter to an unknown amount of matter.
Weight is measured on a scale.
The mass of an object doesn't change when its location changes.
Weight changes with location due to varying gravitational pull.
The SI unit for mass is the kilogram.
The kilogram was originally defined in 1795 as the amount of mass of one liter of water.
In the imperial system, the unit for mass is the slug, which has a mass of 32 pounds.
Weight should technically be measured in Newtons, with a Newton equal to the acceleration of 1 kilogram at 1 meter per second squared.
An object with a mass of 1 kilogram has a weight of about 9.8 Newtons on the surface of the Earth.
Weight can be described in units that sound like a measure of mass, like pounds in the imperial system.
Your weight varies on different celestial bodies like the Moon and other planets, but your mass remains the same.
A cube with a mass of 90.91 kilograms will weigh 200 pounds on Earth, 32 pounds on the Moon, 76 pounds on Mars, and 468 pounds on Jupiter, but its mass remains constant at 90.91 kilograms.
In conclusion, mass is a measure of how much matter something contains, while weight is a measure of how strongly gravity pulls on something.
Moomoomath uploads new math and science videos every day.
The video encourages viewers to subscribe and share for more educational content.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Weight, Force, Mass & Gravity | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool

Are Mass and Weight the same thing? | Physics | Don't Memorise

What is Mass Vs. Weight in Physics? - [1-5-11]
Weight and Mass are Not the Same
The Difference Between Mass & Weight
Physics - What Is The Difference Between Mass and Weight?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: