2017 #1 Free Response Question - AP Physics 1 - Exam Solution
TLDRIn this instructional video, the hosts tackle a free response question from the 2017 AP Physics 1 exam. They analyze three different circuits with identical batteries and light bulbs, explaining the ranking of potential differences across the bulbs. The video then delves into the concept of electric power, current, and resistance to determine which circuit's battery will deplete first and last. The hosts emphasize the importance of a clear, coherent argument in the response, even if the conclusions are incorrect, to meet the exam's requirements.
Takeaways
- 📝 The task involves solving a free response question from the 2017 AP Physics 1 exam, focusing on comparing circuits with identical batteries and light bulbs.
- 🔋 Circuit one has a single light bulb (resistor) connected to a battery, while circuits two and three have two light bulbs connected differently.
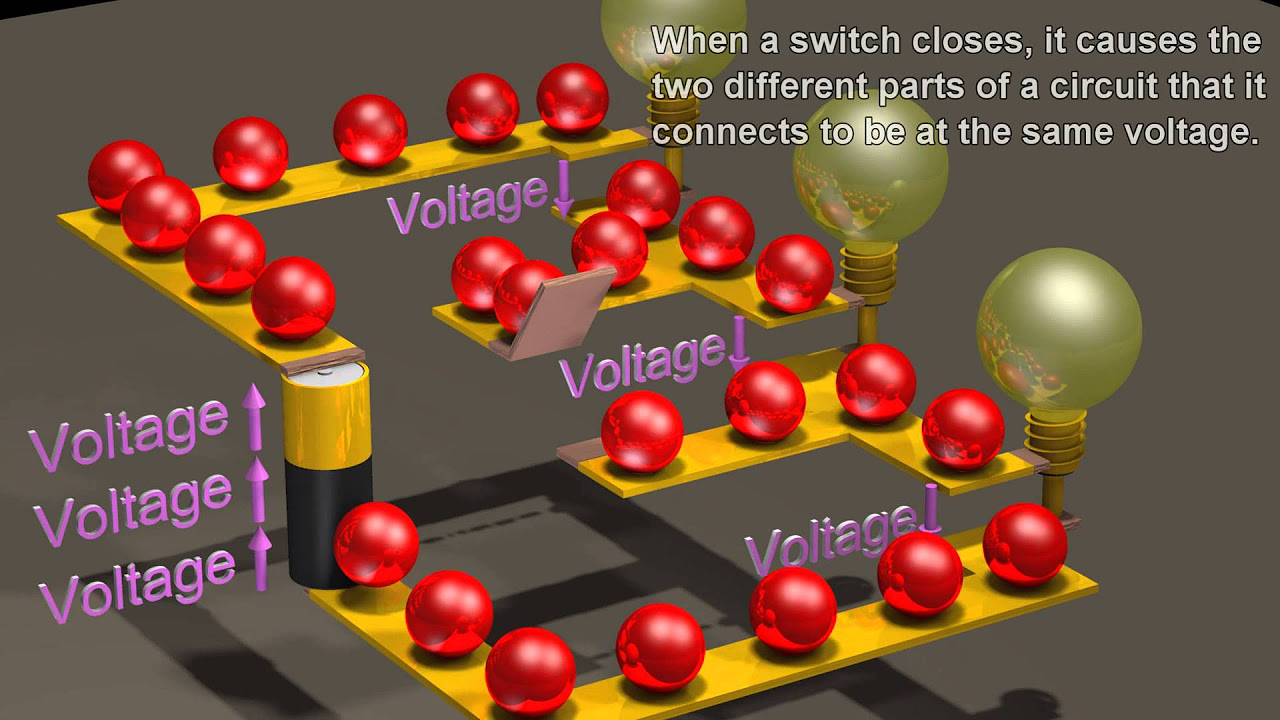
- 💡 In part A, the ranking of potential differences across the light bulbs is crucial, with bulbs A, D, and E having the same potential difference as the battery, and bulbs B and C having less.
- 🔄 Part B addresses which circuit's battery will run out of usable energy first and last, considering the circuit's resistance and the power consumption.
- ⚡️ Electric power (P) is directly proportional to current (I) and potential difference (V), and inversely proportional to resistance (R), as described by the formula P = IV.
- 🔌 Circuit three, with light bulbs in parallel, has the smallest equivalent resistance and will deplete the battery's energy first.
- 🔌 Circuit two, with light bulbs in series, has the largest equivalent resistance and will deplete the battery's energy last.
- 📈 The analysis involves understanding series and parallel circuits, as well as the impact of adding resistors in these configurations on the overall resistance.
- 🎯 For part B, a logical, relevant, and internally consistent argument is essential, even if the conclusion is incorrect, as it can still earn points according to the AP Physics exam guidelines.
- 📝 The importance of a clear, coherent paragraph-length response is emphasized, which should include qualitative and quantitative analysis, translation, and argumentation.
- 👨🏫 The video script serves as a learning tool, providing insights into how to approach and solve problems on the AP Physics 1 exam.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the free response question from the 2017 AP Physics 1 exam?
-The main topic is the analysis of three different circuits with identical batteries and light bulbs, focusing on ranking the potential differences across the light bulbs and determining which circuit's battery will run out of usable energy first and last.
How many light bulbs are connected in circuit one of the exam problem?
-In circuit one, there is a single light bulb connected to the battery.
What is the configuration of the light bulbs in circuit two?
-In circuit two, two light bulbs are connected in series to the battery.
How are the light bulbs connected in circuit three?
-In circuit three, the two light bulbs are connected in parallel to the battery.
According to the ranking in part A of the exam problem, which light bulbs have the same potential difference as the battery?
-Light bulbs A, D, and E each have the same potential difference as the battery.
What is the ranking of the potential differences across the light bulbs from largest to smallest?
-The ranking is A = D = E > B = C.
Which circuit will run out of usable energy first according to part B of the exam problem?
-Circuit 3 will run out of usable energy first because it has the smallest equivalent resistance due to the parallel connection of the light bulbs.
Which circuit will run out of usable energy last?
-Circuit 2 will run out of usable energy last because it has the largest equivalent resistance due to the series connection of the light bulbs.
What is the relationship between electric power, current, and resistance?
-Electric power is equal to the current times the electric potential difference. Since electric potential difference equals current times resistance, power is directly proportional to current and inversely proportional to resistance.
How does adding a resistor in parallel affect the equivalent resistance in a circuit?
-Adding a resistor in parallel decreases the equivalent resistance, resulting in a higher current delivered by the battery.
How does adding a resistor in series affect the equivalent resistance in a circuit?
-Adding a resistor in series increases the equivalent resistance, resulting in a lower current delivered by the battery.
What is the importance of a clear, coherent paragraph length response in the AP Physics exam?
-A clear, coherent paragraph length response is important for demonstrating a logical, relevant, and internally consistent argument that addresses the required question or argument. It can also contribute to earning points even if the conclusions are incorrect.
Outlines
🔌 Solving AP Physics 1 Free Response Question
The paragraph discusses the process of solving a free response question from the 2017 AP Physics 1 exam. It involves analyzing three circuits with identical batteries and light bulbs to rank the potential differences across the bulbs and determining which circuit's battery will run out of energy first and last. The explanation includes the concepts of series and parallel circuits, Ohm's Law, and the relationship between electric power, current, and resistance. The importance of providing a clear, coherent argument in the response is emphasized, even if the conclusions are incorrect.
📚 AP Physics Exam Strategy and Scoring
This paragraph focuses on the exam strategy for the AP Physics 1 exam, specifically for paragraph argument short answer questions. It highlights the scoring guidelines, emphasizing the importance of a logical, relevant, and internally consistent argument that addresses the required question. The paragraph also mentions that a point can be gained for an argument that follows the guidelines, even if the conclusions are incorrect. The speaker encourages the viewers to employ the strategies discussed in the video for effective exam responses.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Free Response Question
💡Circuit
💡Light Bulb
💡Potential Difference
💡Series Connection
💡Parallel Connection
💡Electric Power
💡Resistance
💡Equivalent Resistance
💡Usable Energy
💡Paragraph Argument
Highlights
The problem-solving session focuses on a free response question from the 2017 AP Physics 1 exam.
The circuits discussed involve identical batteries and light bulbs.
Circuit one has a single light bulb connected to the battery.
Circuit two and three have two light bulbs connected differently to the battery, with Circuit two in series and Circuit three in parallel.
Light bulbs are considered as resistors that emit light.
The ranking of potential differences across the light bulbs is based on their connection to the battery and each other.
Light bulbs A, D, and E each have the same electric potential difference as the battery.
Light bulbs B and C, being in series, have the same but less potential difference than those connected directly to the battery.
The ranking from largest to smallest potential difference is A=D=E > B=C.
Part B of the question examines which circuit's battery will run out of usable energy first and last.
The rate at which a battery uses its electric potential energy is determined by electric power, which is current times electric potential difference.
Circuit three, with resistors in parallel, has the smallest equivalent resistance and thus the highest current, running out of energy first.
Circuit two, with resistors in series, has the largest equivalent resistance and thus the lowest current, running out of energy last.
The explanation for Part B involves concepts of electric power, current, and resistance.
Even with incorrect conclusions, a logical, relevant, and internally consistent argument can earn a point according to the AP Physics exam scoring guidelines.
The importance of a clear, coherent paragraph-length response is emphasized for Part B.
The use of qualitative, quantitative translation, and paragraph argument is recommended for a comprehensive answer.
The session concludes with an encouragement for the value of learning and the enjoyment of the educational process.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

2017 AP Physics 1 Free Response #1

AP Physics 1 2017 Free Response Solutions

2015 AP Physics 1 Free Response #2

Circuits, Voltage, Resistance, Current - Physics 101 / AP Physics Review with Dianna Cowern
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws.

DC Resistors & Batteries: Crash Course Physics #29
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: