System Boundaries
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen discusses the concept of system boundaries, using examples from a game of pool and a fruit exchange to illustrate how defining a system can simplify the analysis of physical problems. He emphasizes the conservation of momentum within a system and encourages viewers to consider which elements are necessary to include within the system's boundaries for easier problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 🎱 The concept of system boundaries is introduced using a pool game as an analogy for a system where linear momentum is conserved.
- 🚀 The system boundary is drawn to include only objects that are interacting or relevant to the problem at hand, simplifying the analysis.
- 🔄 When solving physics problems, non-interacting objects outside the defined system boundary can be ignored for ease of problem-solving.
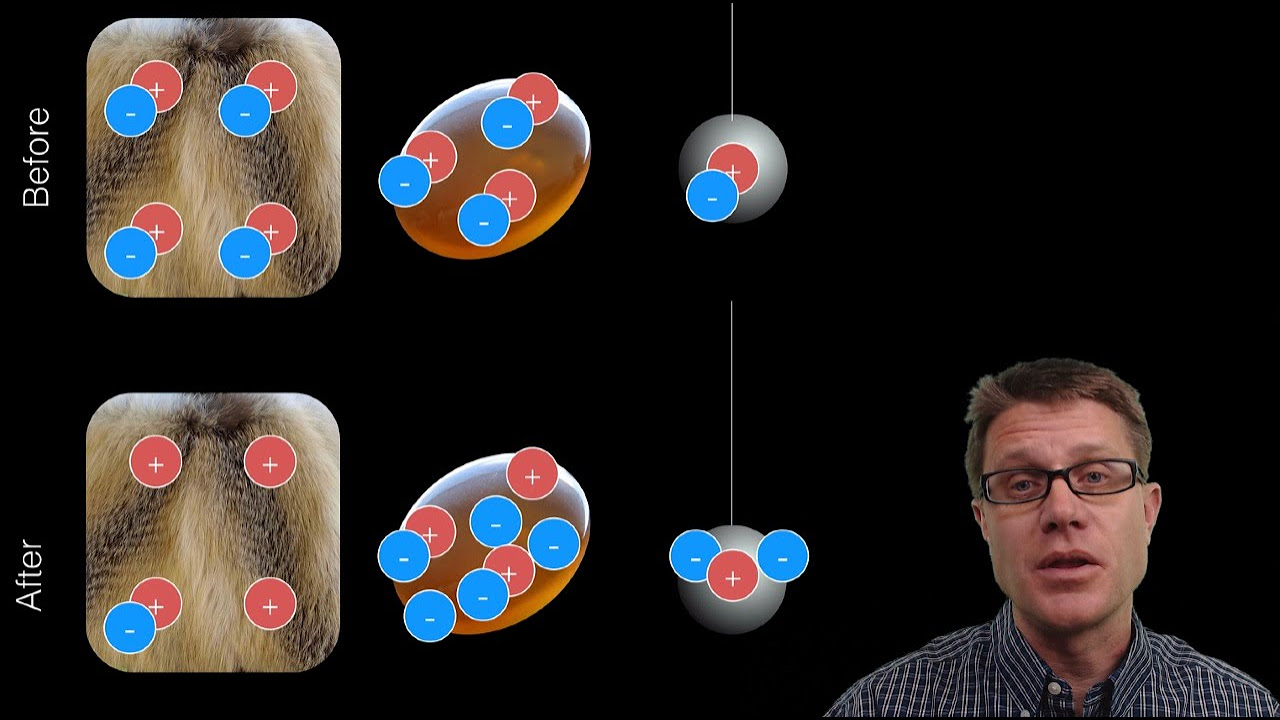
- 💰 An analogy with a fruit exchange illustrates the conservation of quantity, where the amount of money and fruit remains constant.
- 🍏 In the fruit exchange scenario, by defining a system that includes only the man, woman, and apple, the problem becomes easier to analyze.
- 🔄 The system in the pool game includes the cue ball and the other balls directly involved in the collision, excluding the non-interacting object.
- 🍎 In the apple collision example, the system should include both apples, the table (due to friction), and potentially the air (for air resistance).
- 📏 The choice of system boundary is subjective and depends on the problem solver's aim to simplify the analysis of the physics problem.
- 🎓 Understanding the concept of system boundaries is crucial for solving problems in physics, especially those involving conservation laws.
- 📚 The video aims to help viewers grasp the idea that defining a system is a tool to make physics problems more manageable and less complex.
- 📈 The script emphasizes the importance of identifying and including all relevant components within the system boundary for accurate problem-solving.
Q & A
What is the main concept discussed in the video?
-The main concept discussed in the video is the idea of system boundaries in physics, specifically how they can be defined to simplify the analysis of a problem.
How does the video introduce the concept of system boundaries?
-The video introduces the concept by using the analogy of a person playing pool, where the entire setup of the pool table can be considered a system, and the conservation of momentum within this system is highlighted.
What is the significance of drawing a line around the system?
-Drawing a line around the system helps to define the scope of the analysis by including only the relevant objects and interactions, thus simplifying the problem to be solved.
Why is it useful to eliminate certain objects when defining a system?
-Eliminating certain objects from the system can make the problem easier to solve by focusing only on the interactions and elements that are directly relevant to the analysis.
What is the analogy used in the video to explain system boundaries?
-The analogy used is a scenario involving three people trading money and fruit, where the conservation of money and fruit is maintained, but certain individuals and items can be eliminated from the problem for simplification.
How does the video demonstrate the conservation of momentum within a system?
-The video demonstrates the conservation of momentum by showing how the linear momentum remains constant when balls in a game of pool interact, assuming no external forces are acting on the system.
What is the example given in the video to illustrate defining a system for a physics problem?
-The example given is of an apple sliding across a counter and colliding with another apple, where the system includes both apples, the table, and potentially the air, but excludes everything else outside of this interaction.
What factors should be considered when deciding what to include in a system?
-When deciding what to include in a system, one should consider which objects and interactions are directly relevant to the problem at hand, as well as any external forces or factors that may affect the outcome.
Who chooses the boundary between the system and the environment?
-The boundary between the system and the environment is chosen by the person solving the problem as a way to simplify the analysis of that problem.
How does the concept of system boundaries apply to the example of trading fruit and money?
-In the example, the system could be defined to include only the two individuals trading and the apple, excluding the woman in the upper right and the banana, as they are not part of the transaction being analyzed.
What is the purpose of defining a system in physics problems?
-Defining a system in physics problems allows for a more focused and manageable analysis by clearly delineating the relevant objects and interactions, which can make solving the problem more straightforward.
Outlines
🎱 Introduction to System Boundaries in Physics
This paragraph introduces the concept of system boundaries in the context of physics, specifically within the scenario of a game of pool. It explains how the conservation of linear momentum applies to the system, which in this case includes the player, the cue ball, and the other balls on the table. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of defining the system's boundaries to simplify the analysis of physical problems, such as the interaction and momentum transfer between the balls. An analogy involving a transaction between three people is used to illustrate the idea of conservation within a system, where all elements remain constant despite the exchange. The paragraph concludes with a question to engage the viewer in considering how to define the system when solving a physics problem.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡System Boundaries
💡Conservation of Momentum
💡Interaction
💡Linear Momentum
💡Frictional Forces
💡Air Resistance
💡Physics Problem
💡Analogy
💡Simplify Analysis
💡Environment
💡Transfer of Momentum
Highlights
The concept of system boundaries in physics is introduced, relating to the conservation of linear momentum.
A pool game scenario is used as an analogy to explain how a system can be defined for ease of analysis.
The importance of considering only the interacting objects within a system for momentum conservation is emphasized.
An analogy involving a transaction between three people illustrates the concept of conservation in a simplified system.
The conservation of money and fruit in the transaction analogy is highlighted to demonstrate the principle of conservation.
The process of eliminating non-essential elements from a problem to simplify the analysis is discussed.
A physics problem involving apples colliding on a counter is presented to demonstrate the application of system boundaries.
The inclusion of both apples in the system due to their involvement in the collision is mentioned.
The necessity of including the table in the system due to frictional forces is discussed.
The potential inclusion of air in the system to account for air resistance is considered.
The choice of system boundary is based on the problem solver's need to simplify the analysis.
The video aims to teach the viewer about the strategic selection of system boundaries in problem-solving.
The importance of understanding the role of system boundaries in physics problems is stressed for effective problem analysis.
The video provides practical examples to help grasp the abstract concept of system boundaries in physics.
The concept of conservation is central to the understanding of system boundaries, as shown through the examples.
The video concludes with a hopeful message that the viewer has learned about the strategic selection of system boundaries.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: