GCSE Physics - Energy Stores, Transferring Energy & Work Done #1
TLDRThis video script introduces the fundamental concept that energy is never created or destroyed, but only transferred between different forms and objects. It explores various forms of energy like thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, and nuclear energy. The script explains how energy can be transferred mechanically, electrically, by heating, or radiation and distinguishes between open and closed systems. It also discusses the concept of work done, differentiating between mechanical and electrical work, using relatable examples like a kettle boiling water and a train applying brakes to illustrate the transfer of energy.
Takeaways
- 🔋 The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred between different forms and objects.
- 🌡️ Energy stores include thermal (internal) energy, kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical energy, magnetic energy, electrostatic energy, and nuclear energy.
- 🔄 Energy can be transferred through various means such as mechanics, electricity, heat, or radiation.
- 🎯 A system in physics refers to a specific collection of matter that can exchange energy with its surroundings (the outside world).
- 🚫 An open system can gain or lose energy through interaction with the outside world, whereas a closed system does not exchange matter or energy with the outside world.
- ⚖️ In a closed system, the total amount of energy remains constant despite internal transfers.
- 💡 Examples of energy transfer include electrical energy heating a kettle's element and then transferring to water, and mechanical work done when kicking a ball.
- 🔧 Work done is another way of describing energy transfer, with mechanical work involving force and motion, and electrical work involving current flow.
- 🚂 Practical application: Friction does work by slowing a train down, converting kinetic energy into thermal energy through heat.
- 📚 The concepts discussed are fundamental to understanding physics and the various forms and transformations of energy.
Q & A
What is the fundamental principle regarding energy discussed in the video?
-The fundamental principle discussed is the conservation of energy, which states that energy is never created or destroyed, only transferred between different forms and objects.
What are the different forms of energy mentioned in the video?
-The forms of energy mentioned include thermal (internal), kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, and nuclear energy.
How is thermal energy related to an object's temperature?
-Thermal or internal energy is the heat energy trapped within an object and is directly related to the object's temperature.
What is kinetic energy associated with?
-Kinetic energy is associated with the movement or motion of an object.
How can energy be transferred between objects or their energy stores?
-Energy can be transferred mechanically, electrically, by heating, or by radiation such as light or sound waves.
What is a system in the context of physics?
-A system is a collection of matter that can be considered as a whole for the purpose of studying energy transfer, either between objects within the system or between the system and its surroundings.
What is an open system in terms of energy transfer?
-An open system is one where matter and energy can be exchanged with the outside world, meaning it can lose or gain energy through interaction with its surroundings.
How is a closed system different from an open system?
-A closed system is separate from the outside world, meaning neither matter nor energy can enter or leave it, and while energy can be transferred within the system, the overall change is always zero.
What are the two main types of work done mentioned in the video?
-The two main types of work done are mechanical and electrical. Mechanical work involves using a force to move an object, while electrical work is done when current flows, overcoming resistance in a circuit.
How does the video illustrate the concept of work done through energy transfer?
-The video illustrates this by showing how electrical energy from a plug socket is transferred to the thermal energy store of a kettle's heating element, and then to the water, and also by the example of friction doing work to slow down a train, transferring kinetic energy to thermal energy.
What happens when energy is transferred to an object's thermal energy store?
-When energy is transferred to an object's thermal energy store, it increases the object's internal energy, which is usually manifested as an increase in temperature.
What is the role of chemical energy in the context provided?
-Chemical energy is the energy stored in chemical bonds, which can be released, for example, when kicking a ball, where it is transferred from the chemical energy store of the leg to the kinetic energy store of the ball.
Outlines
🌟 Energy Conservation and Transformation
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concept of energy conservation, stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed but only transferred between different forms and objects. It outlines various forms of energy such as thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, and nuclear energy. The paragraph also explains the concept of energy stores and how energy can be transferred between them through mechanical, electrical, heating, or radiation means. The idea of a system in physics is introduced, differentiating between open and closed systems and their interaction with energy transfer. The practical application of energy transfer is illustrated with the example of a kettle boiling water, demonstrating the conversion of electrical energy to thermal energy.
🚀 Work Done: Mechanical and Electrical Aspects
This paragraph delves into the concept of work done, which is another way of describing energy transfer. It distinguishes between mechanical and electrical work. Mechanical work involves using force to move an object, exemplified by kicking a ball, which transfers chemical energy from the leg to the ball's kinetic energy. Electrical work is associated with the flow of current and is illustrated by the energy required to overcome resistance in a circuit, such as stopping a train by applying brakes that create friction, converting kinetic energy into thermal energy in the surroundings. The paragraph concludes with an invitation for viewers to share their thoughts in the comments and signals the end of the session.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Energy Conservation
💡Thermal Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Elastic Potential Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Magnetic Energy
💡Electrostatic Energy
💡Nuclear Energy
💡Work Done
💡Open System
💡Closed System
Highlights
Energy is never created or destroyed, only transferred between different forms and objects.
The principle of energy transfer is fundamental to physics courses.
Energy can take various forms such as thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, and nuclear energy.
Energy stored in an object is referred to as being in that object's energy store.
Energy transfer can occur through mechanisms like stretching an elastic band, plugging in an electrical device, heating, or radiation.
A system in physics refers to a collection of matter where energy can be transferred between objects or different forms.
An open system can exchange energy with the outside world, leading to a potential gain or loss of energy.
A closed system is isolated from the outside world, with no exchange of matter or energy across its boundaries.
The concept of work done is related to energy transfer, with two main types being mechanical and electrical.
Mechanical work involves using force to move an object, transferring energy from one form to another.
Electrical work is done when current flows, overcoming resistance in a circuit.
An example of mechanical work is kicking a ball, transferring chemical energy from the leg to the ball's kinetic energy.
Friction does work by slowing down a train, converting kinetic energy into thermal energy through heat.
The video provides practical examples to illustrate the theoretical concepts of energy transfer and work done.
The kettle example demonstrates the conversion of electrical energy to thermal energy and then to the kinetic energy of boiling water.
The video concludes with an invitation for viewers to share their thoughts in the comments section.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

What is Kinetic and Potential Energy? [Stored Energy & Energy of Movement]

GCSE Physics - Conservation of Energy #4

Energy Stores and Transfers

First Law of Thermodynamics, Basic Introduction - Internal Energy, Heat and Work - Chemistry
6.1 Energy and the First Law of Thermodynamics | High School Chemistry
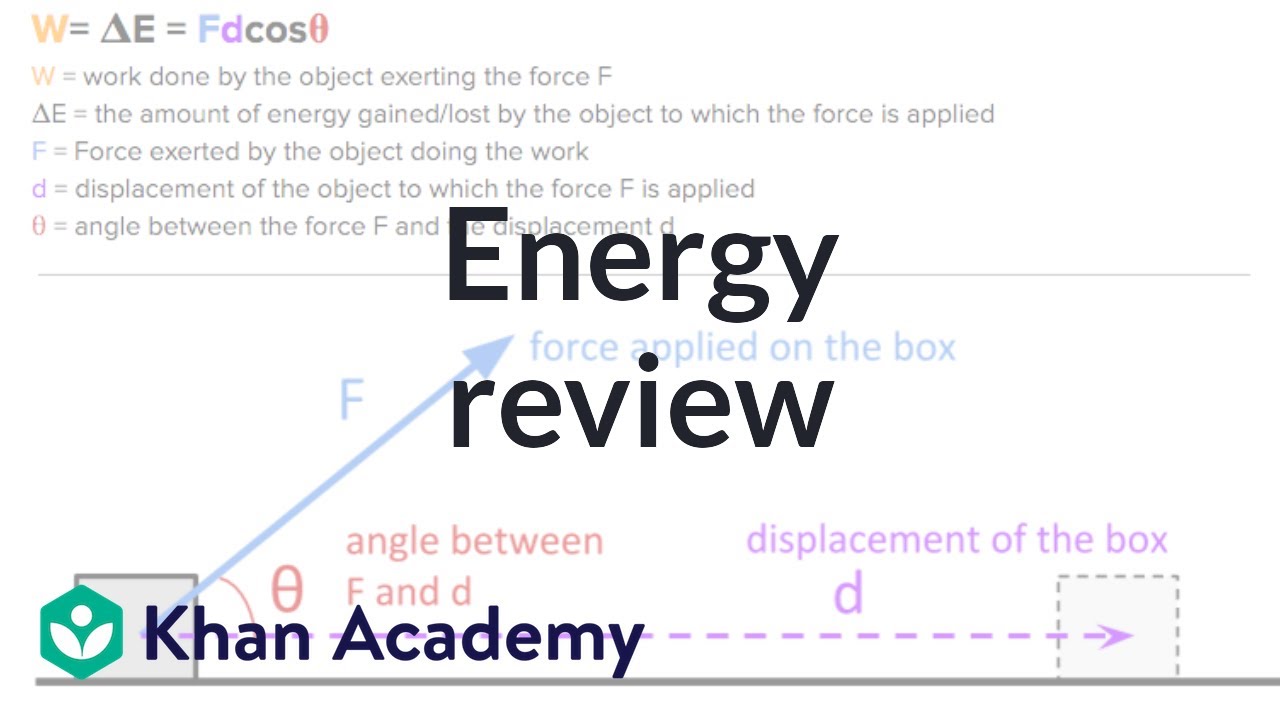
AP Physics 1 review of Energy and Work | Physics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: