Dark Energy, Cosmology part 2: Crash Course Astronomy #43
TLDRThis script from Crash Course Astronomy explores the mind-bending concepts surrounding the origins and expansion of our universe. It delves into the Big Bang theory, dark matter, dark energy, and the accelerating rate of cosmic expansion. The video explains how observations of distant supernovae led to the shocking realization that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, defying expectations. It discusses the composition of the universe, with 95% consisting of invisible dark matter and dark energy. Additionally, it touches upon the concept of the observable universe and its cosmic horizon, which is shrinking due to the accelerating expansion driven by dark energy, potentially leaving us in an isolated cosmic void in the distant future.
Takeaways
- ๐ The current model for the origin of the Universe is the Big Bang, where all matter and energy was compressed into a single, infinitely dense point before violently expanding and cooling.
- ๐ซ Distant galaxies appear to be moving away faster due to the expansion of space, but objects like the Andromeda Galaxy are moving towards us due to mutual gravitational attraction.
- ๐ฎ Astronomers expected to see the expansion of the Universe slowing down due to the gravitational pull of matter, but they surprisingly found that the expansion is accelerating.
- ๐ซ This accelerating expansion is attributed to an unknown force called 'dark energy' that pervades space and has a repulsive effect on the expansion.
- ๐ The Universe's composition is approximately 95% dark matter and dark energy, with only 5% being normal matter.
- ๐ฆ Dark energy's influence means that the Universe's expansion will likely continue forever, rather than eventually slowing down and contracting.
- ๐ The geometry of the Universe, which describes its overall curvature and shape, is no longer the sole determinant of its ultimate fate due to dark energy's effects.
- ๐ There is a 'cosmic horizon' beyond which galaxies are moving away from us faster than the speed of light due to the expansion of space.
- ๐ฑ The observable Universe is getting smaller over time, as the accelerating expansion causes distant galaxies to eventually become unobservable.
- ๐ค We may only have a few trillion more years left to study and understand the Universe before it becomes largely unobservable from our vantage point.
Q & A
What is the current working model for how the Universe started?
-According to the video, the current working model for how the Universe started is with a Big Bang, where all of space, time, matter, and energy was compressed into a single, infinitely dense point (known as the singularity) 13.82 billion years ago, which then suddenly expanded violently, cooling and forming the Universe we see today.
What was the shocking discovery made by astronomers in the 1990s regarding the expansion of the Universe?
-When astronomers used supernovae as standard candles to measure the expansion rate of the Universe on large scales, they found that the Universe's expansion was not slowing down as expected due to gravity, but instead was accelerating, which was completely unexpected and defied our understanding of gravity.
What is dark energy, and how does it affect the Universe's expansion?
-Dark energy is a mysterious energy that seems to be a property of space itself, pushing on the expansion of the Universe. It is thought to be responsible for the accelerated expansion of the Universe, overcoming the gravitational pull of matter.
What is the overall composition of the Universe based on our current understanding?
-According to the video, 95% of the Universe is made up of stuff we can't directly see - 68% is dark energy, and 27% is dark matter. Only 5% of the Universe is made up of normal matter.
What is the geometry of the Universe, and how does it relate to the fate of the Universe?
-The geometry of the Universe refers to the overall curvature or shape of space on the largest scales. It was once thought that the geometry, determined by the amount of matter in the Universe, would dictate whether the Universe would expand forever or eventually collapse. However, with the discovery of dark energy, the geometry alone does not determine the eventual fate of the cosmos.
Can we see galaxies that are moving away from us faster than the speed of light?
-Yes, we can see galaxies that are currently moving away from us faster than the speed of light. This is possible because when the light was emitted from those galaxies in the early Universe, they were much closer to us, and the space between us was not expanding as rapidly. The light from those galaxies is not itself traveling faster than light.
What is the observable Universe, and how is it affected by the accelerating expansion of space?
-The observable Universe is the region of the Universe that we can currently see, with a radius of about 45 billion light-years. Due to the accelerating expansion of space, the observable Universe is actually getting smaller over time, as the light from distant galaxies will eventually be unable to reach us due to the ever-increasing expansion rate.
What is the ultimate fate of the observable Universe according to the video?
-According to the video, due to the accelerating expansion of space driven by dark energy, the observable Universe will continue to shrink until eventually only our own galaxy will be visible in the sky, with the edge of the observable Universe just a few hundred thousand light-years away instead of tens of billions.
How does the expansion of space affect the redshift of light from distant galaxies?
-As light travels from distant galaxies to us, it loses energy due to the expansion of space, causing its wavelength to become longer - this is known as cosmological redshift. The more distant the galaxy, the faster it recedes from us, and the more energy the light loses, resulting in a greater redshift.
Why is it important to study the Universe while we can, according to the video?
-The video emphasizes that it is important to study the Universe while we can because our view of it is shrinking due to the accelerating expansion of space. Eventually, we may only have a few trillion more years left to figure out and understand the mysteries of the Universe before our observable view becomes extremely limited.
Outlines
🌌 The Big Bang and Cosmic Expansion
This paragraph provides an overview of the Big Bang theory, explaining how the Universe began as an infinitely dense singularity that expanded rapidly about 13.82 billion years ago. It discusses the concept of the expanding Universe, where galaxies are moving away from each other due to the expansion of space. The paragraph also touches on the local motion of galaxies, such as the Andromeda galaxy, which is moving towards us due to gravitational attraction, overcoming the expansion on smaller scales.
🔭 Dark Energy and the Accelerating Universe
This paragraph explores the surprising discovery that the expansion of the Universe is not slowing down due to gravity, but rather accelerating. It discusses the efforts of astronomers in the 1990s to measure the expansion rate using Type Ia supernovae, which led to the realization that the supernovae were farther away than expected, indicating an accelerated expansion. The paragraph introduces the concept of dark energy, an unknown energy permeating space, which is believed to be responsible for this acceleration. It also provides an inventory of the Universe, revealing that dark energy and dark matter make up 95% of its composition.
🔜 The Fate of the Expanding Universe
This paragraph delves into the implications of dark energy on the fate of the Universe. It discusses the concept of the geometry of the Universe and how it relates to the amount of matter present, which was once thought to determine the eventual fate of the cosmos. However, with the discovery of dark energy, the expansion is expected to continue forever, driven by this mysterious force. The paragraph also explores the concept of the cosmic horizon and the observable Universe, explaining how distant galaxies will eventually disappear from our view as the expansion accelerates. It concludes with a poignant remark about the irony of the expanding yet shrinking observable Universe, emphasizing the importance of studying it while we still can.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Big Bang
💡Expansion
💡Redshift
💡Dark Matter
💡Dark Energy
💡Supernovae
💡Cosmic Horizon
💡Geometry of the Universe
💡Standard Candles
💡Singularity
Highlights
The Universe is expanding, with galaxies moving away from each other as space expands between them.
The Big Bang theory describes the origin of the Universe, where all matter and energy was compressed into a single, infinitely dense point called the singularity 13.82 billion years ago.
On small scales, gravity can overcome the expansion of space, as seen with the Andromeda galaxy moving toward the Milky Way.
Astronomers expected to find evidence of the expansion of the Universe slowing down due to the gravitational attraction of matter, but instead discovered that the expansion is accelerating.
The accelerating expansion of the Universe is attributed to a mysterious entity called dark energy, which pervades space and pushes the expansion.
The Universe's composition is approximately 95% dark matter and dark energy, with only 5% being normal matter.
The geometry of the Universe, describing its curvature and fate, was once thought to be determined by the amount of matter, but dark energy has changed this understanding.
Current understanding suggests that dark energy will ensure the Universe expands forever, despite its geometry.
Light from distant galaxies loses energy due to the expansion of space, resulting in cosmological redshift.
There is a cosmic horizon, or the radius of the observable Universe, beyond which galaxies are moving away from us faster than the speed of light.
The observable Universe is getting smaller over time due to the accelerating expansion of space, making it harder for light from distant galaxies to reach us.
Eventually, the cosmic horizon will be so close that all galaxies except our own will be beyond it, leaving a black sky.
The Universe's expansion is accelerating, but our view of it is shrinking, emphasizing the need to study it while we can.
Dark energy is a mysterious entity that pervades space and accelerates the expansion of the Universe.
The fate of the Universe is believed to be eternal expansion due to the dominance of dark energy over matter and geometry.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Dark Matter and Dark Energy: The Frontier of Astronomy
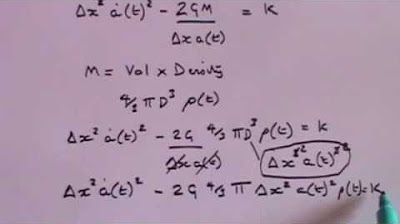
Dark Energy

Why is our universe fine-tuned for life? | Brian Greene

Cosmic Queries – Cosmological Curiosities with Neil deGrasse Tyson

Why is the Universe accelerating? Nobel Laureate Brian Schmidt explains

Lecture 9 | Quantum Entanglements, Part 3 (Stanford)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: