ALEKS: Predicting the products of dissolution
TLDRThis educational video offers a step-by-step guide to solving the 'Alex Problem' of predicting the products of dissolution for various compounds. It emphasizes the importance of using a periodic table and a table of polyatomic ions to determine if a compound will remain intact or dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. The video explains that compounds made of non-metals typically stay whole, except for those containing the NH4+ ion, which always dissociate. It also highlights the role of the periodic table in predicting charges of metal ions, using sodium as an example.
Takeaways
- 📚 To solve the 'Alex problem' of predicting products of dissolution, access to a periodic table and a table of polyatomic ions is recommended.
- 🎨 The periodic table should ideally color-code metals and non-metals for easy identification.
- 🧬 The names of the compounds are not important; it's their solubility in water that matters for the problem.
- 🌊 When a substance dissolves in water, the first thing to note is the presence of water itself.
- 🧩 If a molecule is composed entirely of non-metals, it will generally remain intact upon dissolving in water.
- ⚠️ There is an exception to the rule for molecules made of non-metals: the NH4+ polyatomic cation, which will split into cations and anions.
- 🔍 When a molecule contains a metal, it will split into cations and anions upon dissolving in water.
- 🔑 Having three or more different types of atoms in a molecule often indicates the presence of a polyatomic ion.
- 📝 For molecules with metals, identify the polyatomic ion and its charge, which is crucial for understanding the dissolution process.
- ⚡ The charge of an ion can often be predicted using the periodic table, especially for elements in columns with predictable charges.
- 🚫 The quantity of ions is not required in the final answer; only the types of ions present are needed.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the video?
-The main purpose of the video is to help viewers solve a problem called predicting the products of dissolution, focusing on identifying the major species present when a substance dissolves in water.
Why is a periodic table useful for this problem?
-A periodic table is useful because it color codes metals and non-metals, which helps in determining whether a molecule will stay intact or split apart when it dissolves in water.
What is the significance of the table of polyatomic ions in this context?
-The table of polyatomic ions is important for identifying polyatomic ions in a compound, which can help in determining how the compound will dissociate when dissolved in water.
What is the first thing to consider when a substance dissolves in water?
-The first thing to consider is that water is always present because the substance is being dissolved in it.
How can you determine if a molecule will stay intact or split apart when it dissolves in water?
-You can determine this by consulting the periodic table and checking if the molecule is made up of all non-metals or if it contains a metal, which would cause it to split into cations and anions.
What is the general rule for molecules made up of all non-metals?
-In general, if a molecule is made up of all non-metals, it will stay intact when it dissolves in water.
What is the exception to the rule for molecules made up of all non-metals?
-The exception is the NH4+ polyatomic cation, which will cause the molecule to split into cations and anions even if the molecule is made up of non-metals.
What is a polyatomic ion and why is it important in this context?
-A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that stay together in a molecule and can carry a charge. It is important because it helps in understanding how a compound will dissociate in water.
How can you identify a polyatomic ion in a compound?
-You can identify a polyatomic ion by looking for three or more different types of atoms in the compound and consulting a table of polyatomic ions.
What is the role of the periodic table in predicting the charge of ions?
-The periodic table helps in predicting the charge of ions by showing the typical charges associated with elements in different columns, such as +1 for the first column and +2 for the second column.
Why is it important to note the presence of sodium ions in the solution?
-It is important to note the presence of sodium ions because they are cations that will be present in the solution when a compound containing sodium dissolves in water, and their charge needs to be identified.
Outlines
🔍 Analyzing Solubility and Molecular Breakdown in Water
This paragraph introduces the process of predicting the products of dissolution for compounds in water. The speaker emphasizes the importance of having a periodic table to identify metals and non-metals, and a table of polyatomic ions for reference. The paragraph explains that the names of the three given compounds are irrelevant, but their solubility in water is key. The main task is to determine the major species present after dissolution. The speaker advises that if a molecule is composed entirely of non-metals, it will likely remain intact upon dissolving in water, as demonstrated with the first molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. However, there's an exception to this rule, hinted at with an asterisk, which will be explained later.
🧩 Dealing with Ions and Polyatomic Ions in Dissolution
The second paragraph delves into the dissolution of molecules containing metals, which tend to split into cations and anions. The speaker uses an example with sodium, carbon, and oxygen atoms, identifying the presence of a polyatomic ion, likely CO3, based on the number of different atom types. The speaker explains the process of identifying and separating polyatomic ions using a reference table and emphasizes the importance of recognizing the charge on ions, using the periodic table to predict charges based on the element's column. An exception to the rule about non-metal molecules staying intact is also mentioned, specifically the NH4+ polyatomic cation, which behaves like a metal-containing compound and will split into ions despite being composed of non-metals.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Periodic Table
💡Polyatomic Ions
💡Solubility
💡Non-metals
💡Metals
💡Dissociation
💡Cations
💡Anions
💡Charge
💡NH4+
💡Molecular Formula
Highlights
The video helps solve the Alex problem called predicting the products of dissolution.
Access to a periodic table is recommended, particularly one that color codes metals and non-metals.
A table of polyatomic ions is also necessary, with a recommendation for the one from socratic.org.
The names of the compounds are not important for solving the problem.
All three compounds are soluble in water, which is a key factor in the problem.
The major species present when the substance dissolves in water need to be identified.
Water is always present as the solvent, and should be the first thing to note.
Molecules made up of all non-metals generally stay intact when they dissolve in water.
An exception to the rule of non-metal molecules staying intact is the NH4+ polyatomic cation.
The periodic table helps in determining whether a molecule will split apart or stay intact upon dissolving in water.
If a molecule contains a metal, it will likely split into cations and anions.
Polyatomic ions stay together in a molecule and can be identified using a table of polyatomic ions.
The presence of three or more types of atoms in a molecule indicates a polyatomic ion.
The charge on sodium ions can be predicted using the periodic table, typically a +1 charge.
The quantity of ions is not to be included in the answer, only the type of ions.
Non-metal molecules that do not contain the NH4 group are the ones that stay intact.
Double-check for the NH4 group in non-metal molecules as it indicates ionic splitting.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Naming Ionic Compounds with Transition Metals Introduction

ALEKS: Deducing the ions in a polyatomic ionic compound from its empirical formula

Solubility Rules

Writing Formulas with Polyatomic Ions

ALEKS: Identifying the correct sketch of a compound in aqueous solution
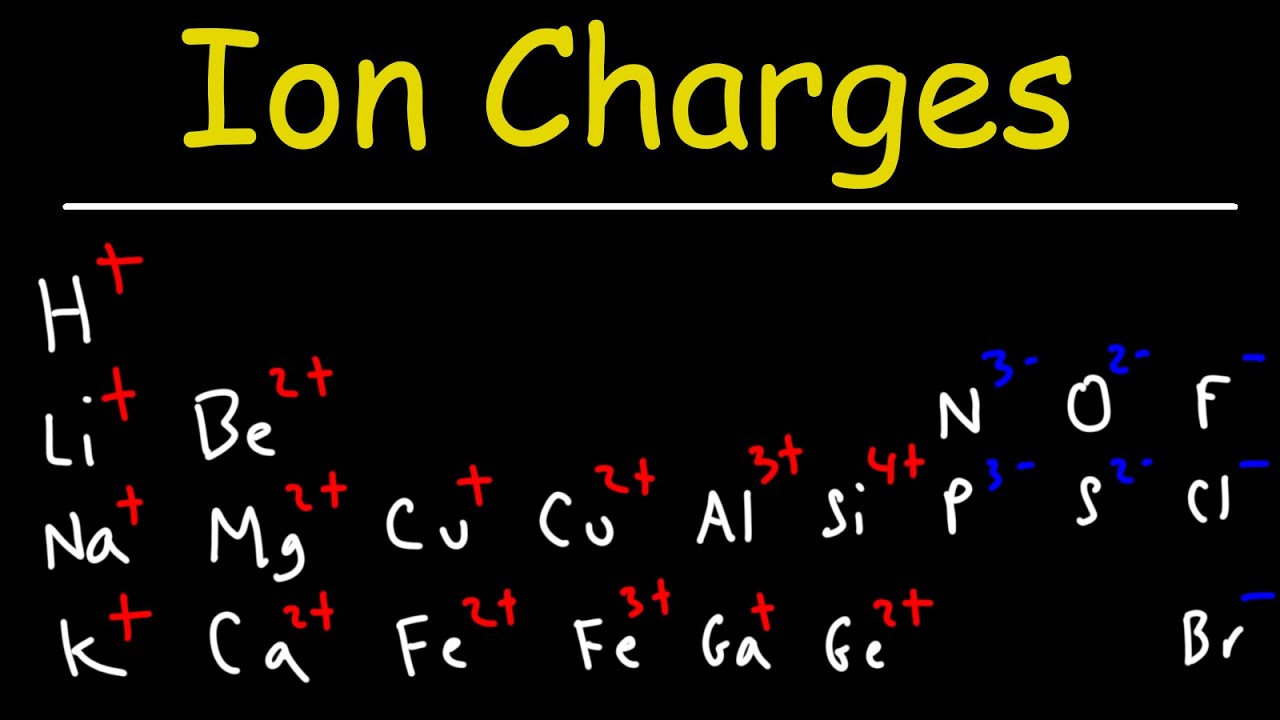
How To Determine The Charge of Elements and Ions - Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: