The Other Reason Why Food Prices Are Rising
TLDRThe video script highlights the rising grocery prices due to inflation and the significant increase in fertilizer costs, which have surged by up to 300% since 2020. This impacts farmers' budgets and global food prices. Fertilizer is crucial for crop yields but poses environmental challenges. The U.S. and other countries are seeking ways to increase fertilizer supplies and develop sustainable practices. The Russia-Ukraine conflict exacerbates the issue, with sanctions disrupting fertilizer exports. Innovations and government support aim to mitigate these challenges, emphasizing the importance of efficient fertilizer use and sustainable agriculture.
Takeaways
- 📈 Grocery prices are rising due to inflation, with food prices in the United States experiencing a significant increase.
- 🌐 The United Nations predicts a potential global food price increase of 8.5% by 2027, partly due to higher fertilizer costs.
- 💰 Fertilizer prices have surged, with some increasing by 300% since 2020, impacting the cost of farming and ultimately food prices.
- 🌱 Farmers are facing increased costs for energy and fertilizers, which they are forced to pass on to consumers, affecting the affordability of food.
- 🌳 Fertilizers are essential for feeding the global population, but their production and use have significant environmental impacts.
- 📈 The demand for synthetic fertilizers has led to a surge in stocks in the fertilizer industry, reflecting the economic impact of the fertilizer crisis.
- 🌽 Farmers are adjusting their planting strategies, with a shift towards crops like soybeans that require less fertilizer, in response to rising costs.
- 🌿 The three main nutrients provided by fertilizers—nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus—are crucial for crop growth, but some crops like legumes can utilize atmospheric nitrogen more efficiently.
- 🌾 The production of nitrogen fertilizers relies heavily on the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive and primarily uses natural gas, linking fertilizer costs to energy prices.
- 🌎 The world is heavily dependent on fertilizers from Russia and Ukraine, and disruptions in these regions due to conflict have led to supply shortages and price increases.
- 🌱 There is a push towards more sustainable farming practices and the development of alternatives to synthetic fertilizers to reduce environmental impacts and dependence on volatile markets.
Q & A
What is the current situation with grocery prices in the United States?
-Grocery prices are on the rise due to the grip of inflation, with the U.S. experiencing very high inflation on food.
What is the United Nations' worst-case scenario for global food prices by 2027?
-The United Nations predicts that food prices globally could rise by an additional 8.5% by 2027.
How have fertilizer prices changed since 2020, and what is the current cost per ton?
-Fertilizer prices have increased by 300% since 2020, with the cost per ton rising from around $270 to over $1400.
Why are farmers being forced to pass costs along to customers?
-Farmers are being forced to pass costs along to customers because of the rise in energy and fertilizer prices, which impacts the cost of food production.
What is the importance of fertilizer in global food production?
-Fertilizer is essential for global food production as it helps increase crop yields. Without it, we would only be able to feed about half of the global population.
What are the three main nutrients that plants need from fertilizer?
-The three main nutrients that plants need from fertilizer are nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
Which crops require less fertilizer and why?
-Certain crops like legumes, soybeans, chickpeas, and peas require less fertilizer because they can fix nitrogen from the air, unlike other crops that need synthetic nitrogen.
How have fertilizer costs affected grocery prices?
-Fertilizer costs have contributed to higher grocery prices, as the increased input costs for food production are passed on to consumers.
What is the connection between the Haber-Bosch process and nitrogen fertilizer production?
-The Haber-Bosch process is used to manufacture nitrogen fertilizers by combining nitrogen with hydrogen in a chemical process that requires a lot of heat and energy, primarily from natural gas.
Why are fertilizer firms and their stocks important in the current situation?
-Fertilizer firms and their stocks are important because as world demand for synthetic fertilizers has surged, these stocks have soared, indicating the significant role of the fertilizer industry in the economy and food production.
What are some of the environmental concerns associated with the use of fertilizers?
-Overusing fertilizers can contribute to nutrient pollution, causing issues like algae blooms in waterways, contamination of drinking water, and creating dead zones in oceans. It also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the U.S. government doing to support farmers against rising fertilizer costs?
-The U.S. government has announced a new global fertilizer challenge to raise money for developing alternatives to fertilizers and has provided $250 million through a new USDA grant program to support domestic sustainable fertilizer production.
What is the potential impact of the Russia-Ukraine war on the global fertilizer market?
-The Russia-Ukraine war has disrupted shipments of fertilizers, particularly potash, which Russia and Belarus are major exporters of, leading to a shortage and skyrocketing prices until the conflict ends.
How can farmers mitigate the need for synthetic fertilizers in the long term?
-Farmers can mitigate the need for synthetic fertilizers by adopting sustainable practices such as growing cover crops, intercropping, no-till farming, and enriching the soil with organic matter to improve nutrient availability.
Outlines
🌾 Fertilizer Prices Surge Amid Inflation
The first paragraph discusses the impact of inflation on grocery prices, particularly the cost of food in the United States. It highlights the United Nations' projection that global food prices could increase by 8.5% by 2027. The rise in fertilizer costs, which have seen a 300% increase since 2020, is a significant factor in this trend. Farmers are being forced to pass these increased costs onto consumers, leading to higher food prices. The paragraph also touches on the environmental impact of fertilizer production and the potential for alternative, more sustainable practices.
🌍 Global Fertilizer Dependency and Environmental Concerns
This paragraph delves into the global reliance on fertilizers, especially from Russia and Belarus, which together account for a significant portion of the world's potash exports. The paragraph discusses the disruptions caused by sanctions on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine, leading to skyrocketing fertilizer prices. It also addresses the environmental consequences of overusing fertilizers, such as nutrient pollution and its effects on waterways and soil. The potential for sustainable practices and the need for better soil management are highlighted, along with the economic challenges farmers face in transitioning to these methods.
🌱 Efforts to Increase Fertilizer Efficiency and Develop Alternatives
The final paragraph focuses on the efforts to increase fertilizer efficiency and develop alternatives. It mentions the U.S.'s announcement of a global fertilizer challenge aimed at raising funds for these initiatives, as well as a new grant program to support domestic sustainable fertilizer production. The paragraph also discusses the upcoming farm bill and the opportunities it presents for encouraging sustainable agricultural practices. The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war is noted as a factor that will likely keep fertilizer prices high until its resolution.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Inflation
💡Fertilizers
💡Food Prices
💡Farmers
💡Synthetic Fertilizers
💡Nutrients
💡Haber-Bosch Process
💡Sustainability
💡Fertilizer Stocks
💡Food Shortages
💡Environmental Impact
Highlights
Grocery prices are rising due to inflation, with the U.S. experiencing high food inflation.
The United Nations predicts a global increase in food prices by 8.5% by 2027.
Fertilizer prices have increased by 300% since 2020, impacting farming costs.
Energy price increases are driving up fertilizer costs, affecting food prices.
Farmers are forced to pass increased costs to customers, leading to higher grocery bills.
Fertilizers are essential for feeding the global population, but their production has environmental costs.
Synthetic fertilizers are becoming more expensive, with farmers spending nearly 18% of their budget on them.
Farmers are planting less corn and more soybeans due to fertilizer cost considerations.
Fertilizer costs are a significant input cost for food, leading to higher prices at the store.
The food price index increased by 10.9% year over year as of July 2022.
Manufacturing nitrogen fertilizers uses the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive.
The U.S. produces a significant amount of nitrogen and phosphorus, but consolidation in the fertilizer industry has reduced competition.
Russia and Belarus are major suppliers of potash, but geopolitical tensions are affecting supply and prices.
Sanctions on Russia have disrupted fertilizer shipments, causing prices to skyrocket.
Natural gas costs have surged, impacting fertilizer prices directly.
Overusing fertilizers contributes to nutrient pollution, a major environmental problem.
Better soil management could reduce the need for fertilizer, enriching the soil with organic matter.
Sri Lanka's ban on fertilizers led to economic turmoil and a reversal of the policy.
The U.S. has announced support for sustainable fertilizer production and a global fertilizer challenge.
Innovative approaches like carbon capture and renewable energy are being explored to make fertilizer production more sustainable.
The U.S. is working on developing alternatives to traditional fertilizers and improving fertilizer efficiency.
The next farm bill in 2023 presents an opportunity to encourage sustainable farming practices.
Ukraine has resumed exporting agricultural products, but fertilizer prices are likely to remain high until the Russia-Ukraine war ends.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

A global hunger crisis: how did we get here?

The chemical reaction that feeds the world - Daniel D. Dulek
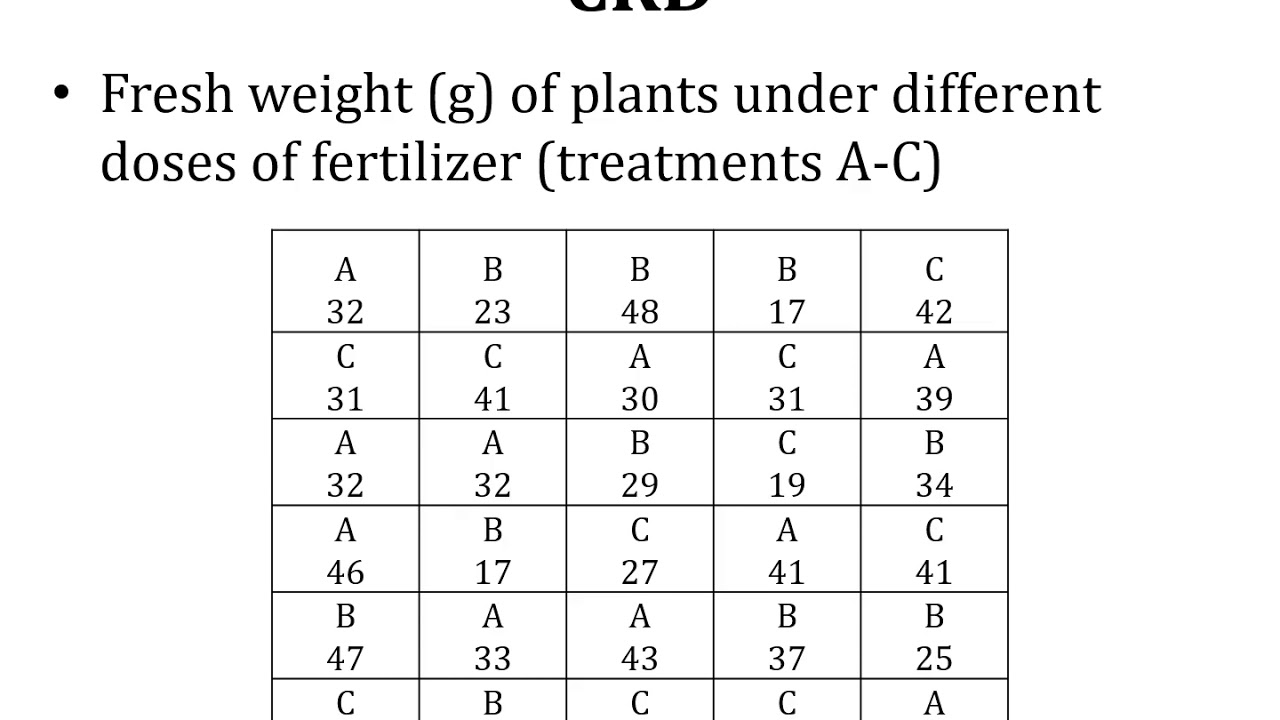
Experimental Designs; CRD; Completely Randomized Design; One-Way ANOVA
Lecture 18 Experimental Designs; Completely Randomized Design CRD; One Way ANOVA

Food security - A growing dilemma | DW Documentary

What is Inflation?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: