How to Use Chemistry Reference Tables : The Marvels of Chemistry
TLDRIn this educational video, Robin Higgins teaches viewers how to effectively utilize chemistry reference tables, specifically focusing on the PKA chart. She emphasizes the importance of understanding the chart's purpose and the meaning of its data before applying it to solve chemistry problems. Higgins demonstrates how to compare the acidity of different compounds like amines and carboxylic acids by examining their PKA values, highlighting that a lower PKA indicates a stronger acid. The video aims to equip viewers with the skills to extract information from reference tables and make informed conclusions.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Understand the purpose of the chart: Before using any chemistry reference table, ensure you understand what information it provides.
- 📚 Know the basics: Familiarize yourself with basic chemistry concepts such as PKA, alkanes, and functional groups to effectively use reference tables.
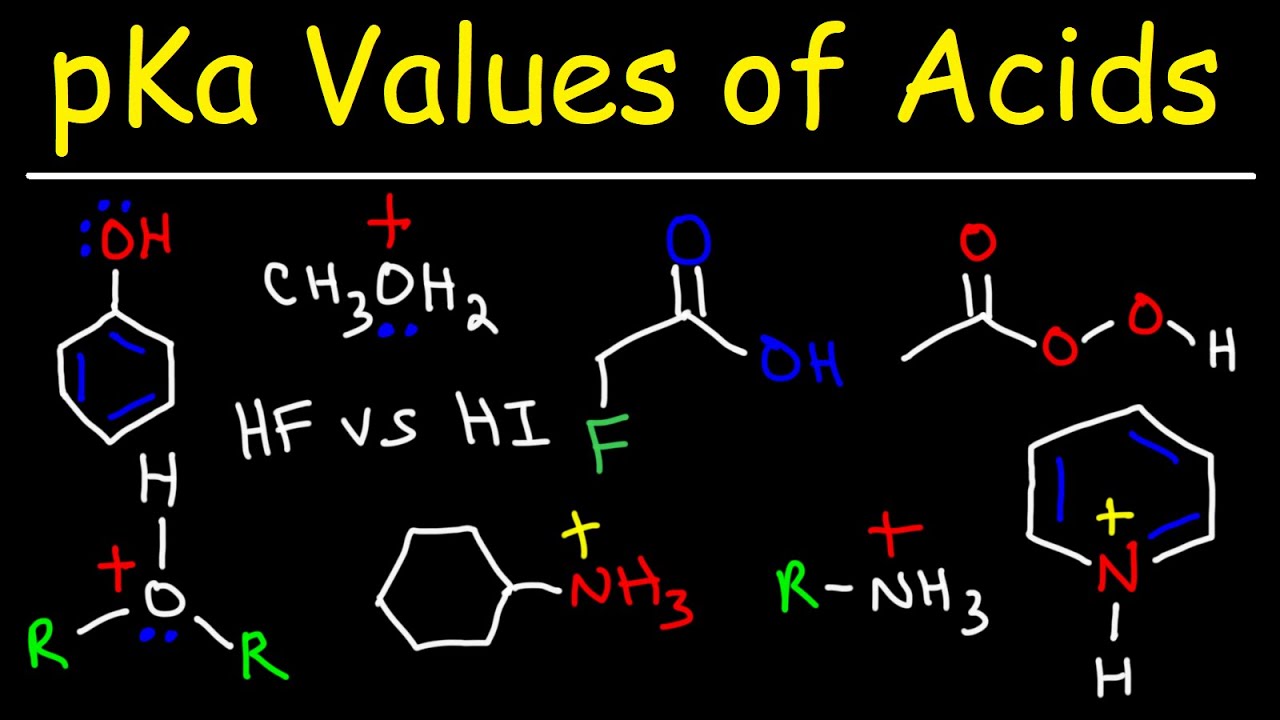
- 📊 PKA as a measure: PKA is a measure of the tendency of a hydrogen atom to dissociate from a molecule, which is crucial for understanding acid-base chemistry.
- 🧬 Functional group impact: The PKA value can vary depending on the functional group present in a molecule, affecting its acidity or basicity.
- 🔑 Appropriate chart selection: Select the right chart for the problem you are solving to ensure accurate results.
- ⚗️ PKA chart usage: Use the PKA chart to compare the acidity of different compounds by looking at their PKA values.
- 📉 Lower PKA value: A lower PKA value indicates a stronger acid, as the hydrogen atom is more likely to dissociate.
- 📈 Higher PKA value: A higher PKA value indicates a weaker acid, with less tendency for the hydrogen atom to dissociate.
- 🆚 Comparing acidity: To determine which compound is more acidic, compare their PKA values and identify the one with the lower number.
- 🤔 Contextual understanding: Knowing the range of PKA values helps in better understanding and interpreting the results of your comparisons.
- 👋 Introduction to the presenter: Robin Higgins introduces the video, providing a guide on how to use chemistry reference tables.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of chemistry reference tables?
-The main purpose of chemistry reference tables is to provide essential data and information that can be used to solve basic chemistry problems.
What is an example of a chemistry reference table mentioned in the script?
-An example of a chemistry reference table mentioned in the script is the PKA table.
What does PKA stand for in the context of the script?
-In the context of the script, PKA stands for the measure of how willing a hydrogen atom is to become disassociated from a given molecule.
What is the significance of PKA values in determining the acidity of a substance?
-The significance of PKA values is that a lower PKA value indicates a higher tendency of a proton to come off, making the substance more acidic.
What are the two key steps mentioned in the script for using a chemistry reference table effectively?
-The two key steps mentioned are understanding what the chart means and knowing how to extract information and make conclusions from it.
What is an alkane according to the script?
-An alkane, as mentioned in the script, is a functional group consisting of single bonds of carbon and hydrogen.
How does the script suggest comparing the acidity of different substances using a PKA table?
-The script suggests comparing the PKA values of the substances in question. The substance with the lower PKA value is more acidic.
What is the script's example of using a PKA table to determine the relative acidity of an amine and a carboxylic acid?
-The script uses the PKA values of 35 for an amine and 5 for a carboxylic acid, concluding that the carboxylic acid is more acidic due to its lower PKA value.
Why is it important to know the range of PKA values before making conclusions about acidity?
-It is important to know the range of PKA values to understand what constitutes a low or high PKA value, which helps in accurately determining the relative acidity of substances.
Who is the presenter of the script and what is the main topic of the video?
-The presenter of the script is Robin Higgins, and the main topic of the video is how to use chemistry reference tables to solve problems related to acidity.
Outlines
🔍 Understanding Chemistry Reference Tables
Robin Higgins introduces the concept of using chemistry reference tables to solve basic chemistry problems. She emphasizes the importance of knowing what each chart or table represents, using a PKA table as an example. PKA measures the tendency of a hydrogen atom to dissociate from a molecule, varying with different functional groups. Higgins explains that understanding the chart's meaning is crucial before extracting information to solve problems.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemistry Reference Tables
💡PKA Table
💡Alkane
💡Functional Group
💡Acid Dissociation Constant (KA)
💡Hydrogen Atom
💡Water
💡Hydrochloric Acid
💡Amine
💡Carboxylic Acid
💡Acidity
Highlights
Introduction to using chemistry reference tables for solving basic chemistry problems.
Explanation of the necessity to understand the chart's meaning before using it.
The importance of selecting the appropriate chart for the specific chemistry problem.
Introduction to the concept of PKA as a measure of a hydrogen atom's dissociation tendency.
Description of PKA's relevance to functional groups in molecules.
Example of using a PKA chart to compare the acidity of alkanes, water, and hydrochloric acid.
Guidance on how to extract information from a PKA chart to make conclusions.
A practical example of using the PKA chart to determine the acidity of an amine versus a carboxylic acid.
The method of identifying the two groups in question for comparison using the PKA chart.
Explanation of PKA values, where lower numbers indicate higher acidity.
Demonstration of how to compare PKA values to determine which substance is more acidic.
The significance of knowing the range of PKA values to accurately answer questions about acidity.
Robin Higgins' closing remarks summarizing the process of using chemistry reference tables.
Emphasis on the importance of understanding the information provided by a chart before solving problems.
Highlighting the need to know how to extract and use information from a chart to solve chemistry problems.
Final note on the practical application of PKA charts in determining the relative acidity of different substances.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: