pKa, Ka, and Acid Strength
TLDRThis video script delves into the relationship between acid strength, pKa, and Ka values. It explains that a lower pKa value corresponds to a stronger acid, as seen in the comparison between acetic acid and formic acid. Conversely, a higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, as demonstrated by the comparison between HF and H2S. The video also introduces the equations relating pKa and Ka, offering a clear guide for determining acid strength.
Takeaways
- 📌 Acid strength is inversely related to pKa values; a lower pKa indicates a stronger acid.
- 📌 Formic acid (pKa 3.75) is a stronger acid compared to acetic acid (pKa 4.76).
- 📌 Methanol (pKa 15.5) is more acidic than ethanol (pKa 15.9) due to its lower pKa value.
- 📌 The relationship between Ka and acid strength is direct; a higher Ka value corresponds to a stronger acid.
- 📌 Hydrofluoric acid (HF, Ka = 6.3 x 10^-4) is stronger than hydrosulfuric acid (H2S, Ka = 1 x 10^-7) as HF has a higher Ka value.
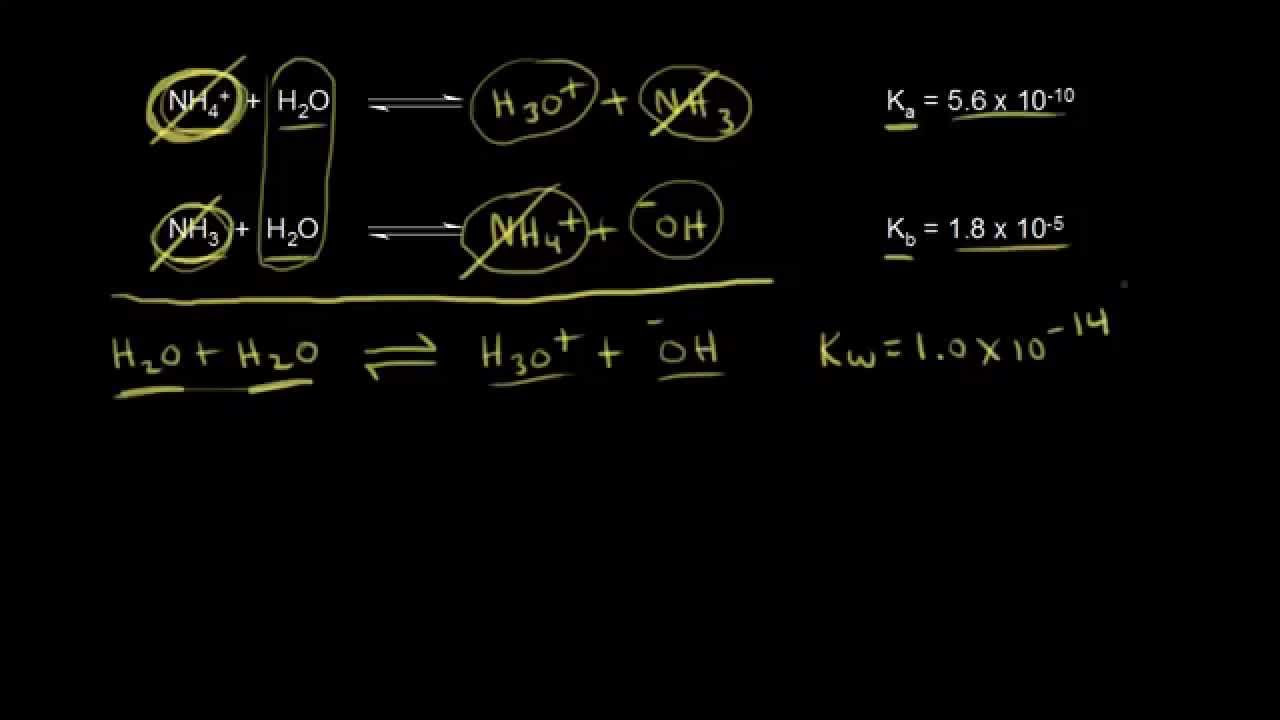
- 📌 Ammonium (NH4+, Ka = 4 x 10^-10) is a stronger acid than methyl ammonium ion (CH3NH3+, Ka = 2 x 10^-11) based on Ka values.
- 📌 The formula to relate pKa and Ka is pKa = -log(Ka), which helps in understanding their inverse relationship.
- 📌 To find Ka from pKa, use the formula Ka = 10^(-pKa), which is essential for comparing acid strengths.
- 📌 The strength of an acid can be quickly determined by comparing its pKa or Ka values with other acids.
- 📌 Understanding the relationship between pKa and Ka is crucial for predicting the behavior of acids in chemical reactions.
- 📌 This knowledge of acid strengths is applicable in various fields such as chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology.
Q & A
What is the relationship between acid strength and pKa values?
-Acid strength is inversely related to pKa values. As the pKa value decreases, the acid strength increases. This means that an acid with a lower pKa value is stronger than one with a higher pKa value.
Which acid is stronger between acetic acid and formic acid, based on their pKa values?
-Formic acid is the stronger acid. It has a lower pKa value of 3.75 compared to acetic acid, which has a pKa value of 4.76.
How can you determine which is the stronger acid between ethanol and methanol using their pKa values?
-Methanol is slightly more acidic than ethanol. Methanol has a pKa value of 15.5, which is lower than ethanol's pKa value of 15.9. The lower pKa value indicates stronger acidity.
What is the relationship between Ka and acid strength?
-There is a direct relationship between Ka and acid strength. As the Ka value increases, the acid strength also increases. The acid with the higher Ka value is the stronger one.
Which acid is stronger between hydrofluoric acid (HF) and hydrosulfuric acid (H2S) based on their Ka values?
-Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is the stronger acid. It has a Ka value of 6.3 x 10^-4, which is higher than the Ka value of 1 x 10^-7 for hydrosulfuric acid (H2S).
What is the Ka value for the ammonium ion (NH4+)?
-The Ka value for the ammonium ion (NH4+) is 4 x 10^-10.
Which is the stronger acid between ammonium (NH4+) and methyl ammonium (CH3NH3+) based on their Ka values?
-Ammonium (NH4+) is the stronger acid as it has a higher Ka value of 4 x 10^-10 compared to the methyl ammonium ion, which has a Ka value of 2 x 10^-11.
How can you convert a pKa value to a Ka value?
-To convert a pKa value to a Ka value, you use the formula Ka = 10^(-pKa). This is because pKa is equal to the negative logarithm of the Ka value.
What does it mean for an acid to be 'stronger'?
-A 'stronger' acid is one that dissociates more completely in solution, releasing more hydrogen ions (H+). This is reflected in a lower pKa value or a higher Ka value.
How can you use the relationship between pKa and Ka to compare the strengths of different acids?
-By comparing the pKa or Ka values of different acids, you can determine which one is stronger. A lower pKa value or a higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, as it dissociates more in solution and releases more hydrogen ions.
What is the significance of understanding the relationship between pKa, Ka, and acid strength?
-Understanding the relationship between pKa, Ka, and acid strength is crucial in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and medicine. It helps in predicting the behavior of acids in reactions, their corrosiveness, and their potential effects on biological systems.
What is the formula to convert Ka to pKa?
-The formula to convert Ka to pKa is pKa = -log(Ka). This allows you to find the pKa value from the known Ka value of an acid.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Acid Strength and its Relation to pKa and Ka
This paragraph introduces the concept of acid strength and its relation to pKa and Ka. It explains that the strength of an acid is inversely related to its pKa value; as the pKa decreases, the acid strength increases. The example of acetic acid and formic acid is used to illustrate this, with formic acid being stronger due to its lower pKa value. The paragraph also touches on the direct relationship between Ka and acid strength, using the comparison between hydrofluoric acid (HF) and hydrosulfuric acid (H2S) to demonstrate that HF is a stronger acid because it has a higher Ka value. The paragraph concludes with another example comparing the strength of NH4+ (ammonium) and CH3NH3+ (methyl ammonium ion), reaffirming that a higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid.
📝 Key Equations for Acid Strength and pKa/Ka Relationship
This paragraph provides two essential equations that relate pKa and Ka, offering a mathematical framework to understand and compare acid strengths. The first equation states that pKa is equal to the negative logarithm of the Ka value. The second equation explains how to find the Ka value from the pKa, which is calculated by 10 raised to the power of negative pKa. These equations are crucial for anyone needing to analyze or compare the strength of different acids and their dissociation constants.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acid Strength
💡pKa
💡Ka
💡Dissociation
💡Conjugate Base
💡pH
💡Logarithm
💡Equilibrium Constant
💡Alcohols
💡Ammonium
💡Inverse Relationship
💡Direct Relationship
Highlights
The relationship between acid strength and pKa is inversely related, with a lower pKa indicating a stronger acid.
Acetic acid has a pKa of 4.76, making it a weaker acid compared to formic acid with a pKa of 3.75.
Formic acid is stronger than acetic acid due to its lower pKa value.
Ethanol is less acidic than methanol as indicated by their pKa values, 15.9 for ethanol and 15.5 for methanol.
Methanol is slightly more acidic than ethanol, having a lower pKa value.
The relationship between Ka and acid strength is directly related, with a higher Ka value indicating a stronger acid.
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a stronger acid than hydrosulfuric acid (H2S), with a Ka of 6.3 x 10^-4 compared to 1 x 10^-7.
Ammonium (NH4+) is a stronger acid than the methyl ammonium ion (CH3NH3+) based on their Ka values.
The Ka value increases as the pKa decreases, indicating a stronger acid.
The pKa is calculated as the negative log of the Ka value.
To find Ka from pKa, the formula is 10 raised to the negative power of the pKa.
This video provides a method to quickly determine the strength of an acid based on pKa and Ka values.
Understanding the relationship between pKa, Ka, and acid strength is essential for various chemical applications.
The video explains the concept of acid dissociation constants and their role in determining acid strength.
The comparison of different acids using pKa and Ka values can help predict their behavior in chemical reactions.
The video is an educational resource for those interested in acid-base chemistry and its practical implications.
The equations provided in the video are essential tools for understanding and calculating acid strengths.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: