The Science of Light and Color for Kids: Rainbows and the Electromagnetic Spectrum - FreeSchool
TLDRThe video from Freeschool explains light as a form of energy that travels in waves, made when matter heats up or gains energy. It covers the electromagnetic spectrum, including visible light and other types like radio waves and gamma rays. Visible light, which includes all colors we can see, is broken down through prisms and rainbows. The video explains how objects' colors are determined by the wavelengths of light they reflect. It highlights the importance of light for color and visibility, making science engaging and accessible.
Takeaways
- 🔆 Light is a type of energy that travels in waves and is made when matter is heated or gains energy.
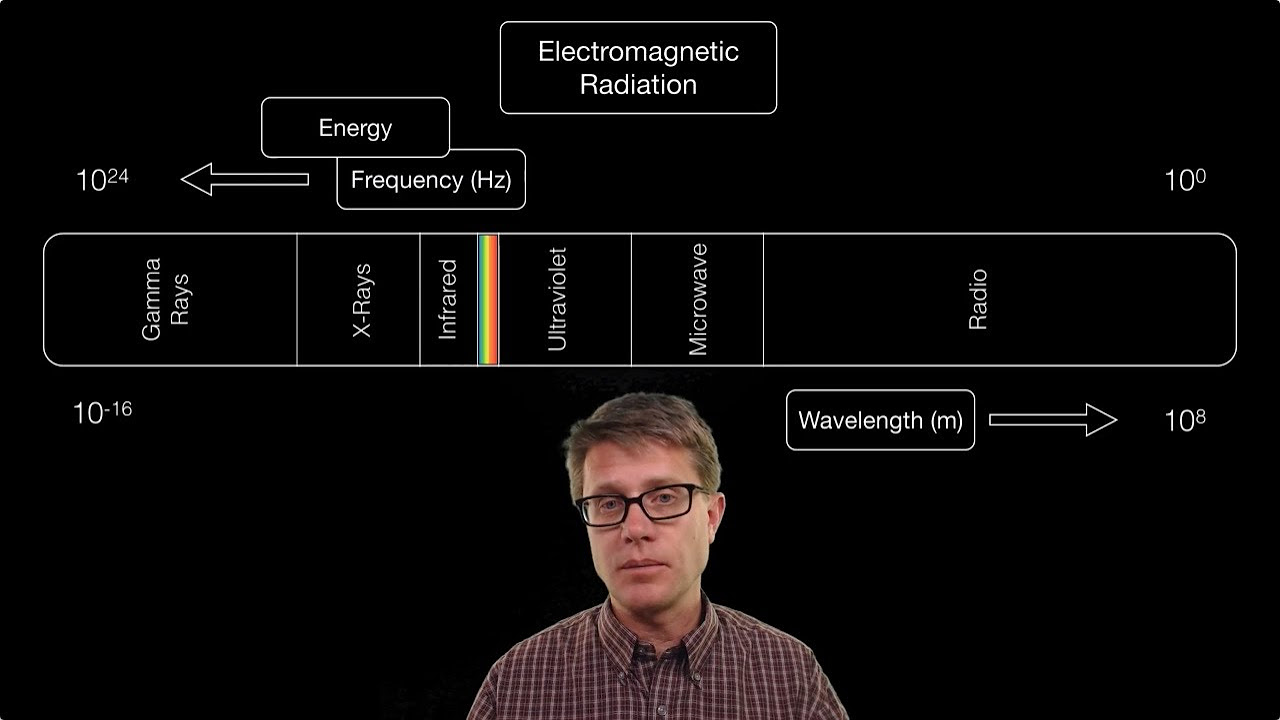
- 🌈 Visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes other types like radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and gamma rays.
- 🔭 Scientists use special tools to detect and measure invisible types of electromagnetic radiation.
- 📏 Different types of electromagnetic radiation have different wavelengths, with longer wavelengths having less energy and shorter wavelengths having more energy.
- ☀️ The most important source of light on Earth is the Sun, and ordinary sunlight, or white light, includes all colors of visible light.
- 🌈 A prism can reveal the colors of visible light by slowing down and bending the light, spreading it into the spectrum.
- 🌈 Rainbows are formed when water droplets in the air bend sunlight, acting like a prism, and always display colors in the same order due to their wavelengths.
- 🔴 Red light has the longest wavelength in the visible spectrum, while violet light has the shortest wavelength.
- 👁️ We see objects because of the light that bounces off them; an object looks green because it reflects green light and absorbs other colors.
- ⚪ White objects reflect almost all visible light, while black objects absorb almost all visible light, showing no color.
Q & A
What is light and how is it related to energy?
-Light is a form of energy that travels in waves. It is created when matter is heated up or gains energy, and the excess energy is released as electromagnetic radiation, which includes light.
What are the different types of electromagnetic radiation mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions visible light, radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and gamma rays as different types of electromagnetic radiation.
How can scientists detect and measure invisible electromagnetic radiation?
-Scientists use special tools to detect and measure invisible electromagnetic radiation.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum and what does it include?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light and invisible types like radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and gamma rays.
How is the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation related to its energy?
-The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is inversely related to its energy. Light with a longer wavelength, such as radio waves, has less energy, while light with a shorter wavelength, like gamma rays, has more energy.
What is the primary source of light on Earth?
-The Sun is the most important source of light on Earth, providing us with white light that includes all the colors of visible light.
How does a prism reveal the colors of visible light?
-A prism reveals the colors of visible light by bending the light as it passes through, causing different parts of the light to slow at different rates and spread out into the colors of the spectrum.
What causes a rainbow and how does it display the colors of the visible light spectrum?
-A rainbow is caused by water droplets in the air bending sunlight much like a prism. This bending separates the sunlight into its component colors, displaying the visible light spectrum.
What are the seven colors of a rainbow and how are they ordered?
-The seven colors of a rainbow are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. They are ordered according to their wavelengths, with red having the longest and violet the shortest.
What is the difference between visible light and infrared or ultraviolet light?
-Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that human eyes can detect. Infrared light has a longer wavelength than the red light we can see, while ultraviolet light has a shorter wavelength than the violet light we can see.
How do we perceive the color of an object?
-We perceive the color of an object based on the light it reflects. For example, a green leaf appears green because it absorbs all colors except green, which it reflects, and our eyes detect this reflected green light.
Why do white and black objects appear as they do?
-White objects appear white because they reflect almost all of the visible light shining on them, while black objects appear black because they absorb almost all of the visible light.
Outlines
🌞 Understanding Light and its Properties
This paragraph introduces light as a form of energy that travels in waves, originating from heated matter or energy gain. It explains light as electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light and other invisible types like radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and gamma rays. The visible light spectrum is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, with colors revealed through a prism or rainbow, each color having a unique wavelength. The most important source of light mentioned is the Sun, which emits white light containing all visible colors.
🌈 The Spectrum of Visible Light and Color Perception
This section delves deeper into the concept of the visible light spectrum, explaining how a prism or similar object can separate white light into its constituent colors. It describes the formation of rainbows as a natural example of this dispersion, where sunlight is bent by water droplets. The paragraph lists the colors of the rainbow in the order of their wavelengths, with red having the longest and violet the shortest. It also touches on the concept of color perception, explaining how objects appear colored based on the wavelengths of light they reflect.
🔍 Invisible Electromagnetic Radiation Beyond the Visible Spectrum
This paragraph discusses the existence of electromagnetic radiation beyond the visible spectrum, specifically infrared and ultraviolet light, which are outside the range of human vision. It explains how we perceive objects based on the light they reflect, with green leaves appearing green because they reflect green light and absorb all other colors. The paragraph also explains that white objects reflect most light, while black objects absorb it, emphasizing that all visible colors are simply different wavelengths of reflected light.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Light
💡Electromagnetic Radiation
💡Wavelength
💡Visible Light
💡Prism
💡Spectrum
💡Sun
💡Color
💡Infrared Light
💡Ultraviolet Light
💡Reflection
Highlights
Light is a form of energy that travels in waves and is produced when matter is heated or gains energy.
Electromagnetic radiation is the term for energy released as light, which includes both visible and invisible types.
Visible light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which also contains radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and gamma rays.
Scientists use special tools to detect and measure invisible electromagnetic radiation.
The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is directly related to its energy, with longer wavelengths having less energy and shorter wavelengths having more.
Sunlight, which we perceive as white light, actually contains all colors of the visible light spectrum.
A prism can reveal the colors within white light by bending and spreading the light into a spectrum.
Rainbows are formed when sunlight is bent and dispersed by water droplets in the air, displaying the colors of the visible light spectrum.
The sequence of colors in a rainbow follows the order of their wavelengths, with red having the longest and violet the shortest.
Infrared light has a wavelength longer than the red light visible to our eyes, while ultraviolet light has a shorter wavelength than violet.
The color of an object is determined by the light it reflects, with a green leaf reflecting green light and absorbing all other colors.
White objects reflect almost all visible light, while black objects absorb almost all visible light.
All visible objects are seen due to the wavelengths of reflected light, emphasizing the importance of light in our perception of color.
Without light, colors as we perceive them would not exist, highlighting light's fundamental role in our visual experience.
The video encourages viewers to observe the world with a new understanding of how different wavelengths of light create the colors we see.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: