Understanding Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive Value and Negative Predictive Value
TLDRThis video script from 'spi ultrasound physics bridges review' offers a comprehensive overview of medical ultrasound quality assurance, focusing on Doppler phantoms. It explains key concepts like positive predictive value, true and false positives, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy in a Q&A format. The speaker also provides guidance on how to calculate these values and their implications in medical diagnostics. Viewers are encouraged to reach out for further assistance or study materials, with details provided for contacting the instructor and accessing additional resources.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is a review of ultrasound physics for a 'spi ultrasound physics bridges review' course.
- ⏸️ Viewers are encouraged to pause the video to answer questions before the instructor provides the answers.
- 📊 The script discusses a chart representing the quality assurance of a Doppler phantom and explains the concept of positive predictive value (PPV).
- 🧐 The positive predictive value is calculated as true positives divided by the sum of true positives and false positives, with the correct answer being option B in the script.
- 🙅♂️ A true negative indicates the correct identification of the absence of disease by a test.
- 🤒 A false positive means the test incorrectly indicates the presence of disease when there is none, making the exam incorrect.
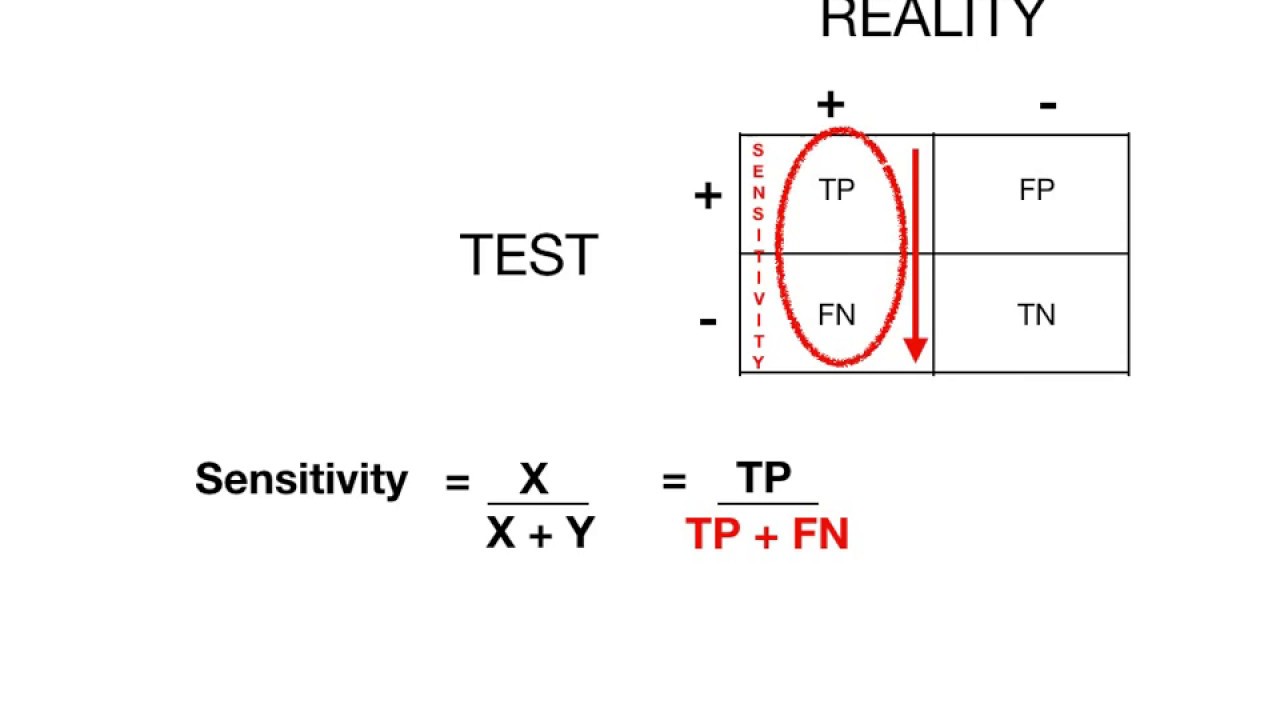
- 🔍 Sensitivity is calculated by dividing true positives by the sum of true positives and false negatives, with the script indicating an 83% sensitivity.
- 📉 Specificity is explained as true negatives divided by the sum of true negatives and false positives, resulting in a 63% specificity in one of the examples.
- 🤖 An objective result means that the test outcome is not influenced by personal feelings or opinions but is based on facts.
- 📉 Another method to calculate specificity is presented, resulting in a 75% specificity, which is option B in the script.
- 📉 Sensitivity is also recalculated in another example, resulting in a different percentage, indicating the importance of accurate data for these calculations.
- ❌ A false positive result indicates an incorrect diagnosis, which affects the test's accuracy negatively.
- 🛑 The terms specificity, sensitivity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value are explained in the context of testing for disease presence or absence.
- 📧 The instructor provides contact information for questions about upcoming exams and offers additional study materials and tutoring services.
Q & A
What is the positive predictive value (PPV) and what is the correct formula to calculate it according to the script?
-The positive predictive value (PPV) is the proportion of true positive cases among the total number of positive cases identified by a test. The correct formula to calculate it, as mentioned in the script, is the number of true positives divided by the sum of true positives plus false positives, which is represented as 32 divided by the sum of 32 plus 4.
What does a true negative result in a medical test indicate?
-A true negative result indicates that the patient does not have the disease and the test correctly shows that there is no disease present.
What is a false positive in the context of medical testing?
-A false positive occurs when a test incorrectly indicates that a patient has a disease when they actually do not.
What is the correct answer for the question about a patient testing positive and what it best describes?
-The correct answer is 'D true positive', which means the test result indicates that the patient has the disease and the result is accurate.
How is sensitivity calculated in the context of the Doppler phantom quality assurance chart?
-Sensitivity is calculated by dividing the number of true positives by the sum of true positives plus false negatives. In the script, it is given as 83, which is calculated by dividing the true positives by the sum of true positives and false negatives.
What does a positive test result for a patient signify in terms of objectivity?
-A positive test result signifies an objective finding, meaning it is based on the test results without bias.
How is specificity calculated, and what is the correct answer from the script?
-Specificity is calculated by dividing the number of true negatives by the sum of true negatives plus false positives. According to the script, the correct calculation is 49 divided by the sum of 49 plus 45, which equals 63%.
What does a negative test result for disease mean in terms of specificity?
-A negative test result for disease means that the test has correctly identified the absence of the disease, which is an indication of specificity.
What is the correct answer for the question about a patient testing negative and truly being negative?
-The correct answer is 'D negative predictive value', which refers to the proportion of true negative results among all negative test results.
What does a positive disease test result indicate in terms of sensitivity?
-A positive disease test result indicates that the test has correctly identified the presence of the disease, which is a measure of sensitivity.
What does a false positive result imply about the accuracy of the test?
-A false positive result implies that the test was incorrect, as it diagnosed a patient with a disease when they do not have it.
Outlines
📚 Doppler Phantom QA and Ultrasound Physics Review
This paragraph introduces a review session on ultrasound physics, specifically focusing on the quality assurance of a Doppler phantom. The presenter explains the concept of positive predictive value (PPV) using a multiple-choice question format, guiding viewers to understand the correct calculation method. The paragraph also covers the definitions of true and false positives and negatives, and their implications in medical testing. Sensitivity and specificity are discussed with examples, including how to calculate them. The presenter concludes with the meaning of a positive test result in the context of medical diagnostics, emphasizing the objectivity of the test outcome.
📘 Understanding Test Results and Additional Resources for Ultrasound Board Review
The second paragraph delves into the interpretation of test results, explaining the meaning of specificity and negative predictive value when a patient tests negative or positive for a disease. It also revisits the concept of false positives and their impact on test accuracy. The presenter offers contact information for those with questions about their upcoming board exams and directs viewers to additional study materials and mock exams available on the 'ultrasoundboardview.com' website. The paragraph concludes with instructions on how to subscribe to the website for access to these resources and mentions the option for one-on-one tutoring in SPI physics.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Ultrasound Physics
💡Doppler Phantom
💡Quality Assurance
💡Positive Predictive Value (PPV)
💡True Positive
💡False Positive
💡Sensitivity
💡Specificity
💡True Negative
💡Accuracy
💡Negative Predictive Value
Highlights
Introduction to the SPI Ultrasound Physics Bridge review session.
Invitation to pause the video to answer questions before the presenter provides the answer.
Explanation of the chart representing the quality assurance of a Doppler phantom.
Introduction of the positive predictive value (PPV) and its calculation method.
Correct answer to the PPV calculation is provided as 32 divided by the sum of 32 plus 4.
Definition and explanation of a true negative in the context of medical testing.
Explanation of a false positive, its implications, and its answer as 'B' for incorrect.
Clarification of terms: true positive, false positive, negative, and their meanings in medical testing.
Identification of 'D' as the correct answer for a true positive test result.
Calculation of sensitivity as 83% using true positives and false negatives.
Explanation of what it means when a patient tests positive, emphasizing objectivity.
Calculation of specificity as 63% using true negatives and false positives.
Correct answer provided for specificity calculation as 49 divided by the sum of 49 plus 45.
Explanation of sensitivity calculation and its correct answer as 39 divided by the sum of 39 plus 32.
Discussion on the meaning of a false positive in terms of test accuracy, with the answer being incorrect.
Explanation of specificity in the context of a patient being negative for disease.
Definition of negative predictive value in relation to a patient testing negative and truly being negative.
Clarification of sensitivity as the measure of a test's ability to detect disease when present.
Contact information provided for questions about upcoming SBI boards and study material.
Instructions on how to access extra study material and mock exams on the presenter's website.
Details on subscribing to the presenter's website for access to mock exams and tutoring.
Closing remarks with an invitation to the next session and acknowledgment of the viewers.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: