Qualitative and Quantitative Variables Explained | Discrete and Continuous
TLDRThis script delves into the categorization of variables in statistics, distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative types. Qualitative variables are identifiers or characteristics, often words or names, while quantitative variables represent counts, measurements, or quantities. Examples provided include birthday month (qualitative), number of French fries (quantitative), GPA (quantitative), and student ID (qualitative). The script further divides quantitative variables into discrete, which are countable like the number of French fries, and continuous, which can take any value along a number line, such as time, temperature, and weight. The explanation aims to clarify these concepts for a better understanding of statistical analysis.
Takeaways
- 📊 In statistics, variables can be classified as either qualitative or quantitative.
- 🔢 Quantitative variables are numerical and represent quantities such as counts, measurements, or rankings.
- 🏷 Qualitative variables are categorical and represent characteristics or identifiers, often in the form of words or names.
- 📅 'Birthday month' is an example of a qualitative variable because it identifies a characteristic (the month of birth).
- 🍟 'Number of French fries' is a quantitative variable as it represents a countable quantity.
- 💯 GPA (Grade Point Average) is a quantitative variable because it measures academic performance.
- 🆔 Student ID numbers are qualitative variables as they serve as unique identifiers rather than representing quantities.
- ⏱ 'Screen time' is a quantitative variable because it measures the amount of time spent on screens.
- 👩🦰 'Hair color' is qualitative as it categorizes a characteristic (color of hair).
- 🐶 'Type of pet' is qualitative, identifying different kinds of pets.
- 🤔 'Weight' is a quantitative variable, representing a measurable amount in pounds or kilograms.
- 🔄 Quantitative variables can be further classified into discrete or continuous. Discrete variables are countable, while continuous variables can take on any value within a range.
- 🍟 'Number of French fries' is a discrete variable because it is counted in whole numbers.
- 📊 GPA is a continuous variable because it can take on any value on the number line, representing a range of academic performance.
- ⏳ 'Screen time' and 'Weight' are continuous variables as they can vary smoothly over time or with small changes.
- 📈 Understanding the difference between qualitative, quantitative, discrete, and continuous variables is crucial for proper data analysis and interpretation.
Q & A
What are the two main types of variables in statistics?
-The two main types of variables in statistics are qualitative and quantitative variables.
What characterizes a quantitative variable?
-A quantitative variable is characterized by numbers that represent counts, measurements, rankings, or quantities.
What is a qualitative variable and what does it represent?
-A qualitative variable represents characteristics or identifiers, usually in the form of words or names, and sometimes numbers used only as identifiers.
Can you provide an example of a qualitative variable from the script?
-An example of a qualitative variable from the script is 'birthday month', which identifies the month of birth.
How is the number of French fries considered in terms of variable type?
-The number of French fries is considered a quantitative variable because it represents a count or quantity.
What makes GPA a quantitative variable?
-GPA is a quantitative variable because it is a numerical measurement that represents the grades a student is receiving.
Why is a student ID number classified as a qualitative variable?
-A student ID number is classified as a qualitative variable because it is used as an identifier to distinguish one student from another, rather than representing a quantity.
How does screen time differ from other quantitative variables mentioned in the script?
-Screen time is a quantitative variable that represents an amount of time, similar to other quantitative variables like weight or age, but it is continuous rather than discrete.
What is the difference between discrete and continuous quantitative variables?
-Discrete quantitative variables are counted in whole numbers and cannot take on any value along the number line, while continuous quantitative variables can take on any value within a range, like time or weight.
How would you classify the type of pet as a variable?
-The type of pet would be classified as a qualitative variable because it identifies different kinds of pets using names or words.
What are some examples of continuous variables mentioned in the script?
-Examples of continuous variables mentioned in the script include time, age, temperature, weight, and height.
Outlines
📊 Understanding Qualitative and Quantitative Variables
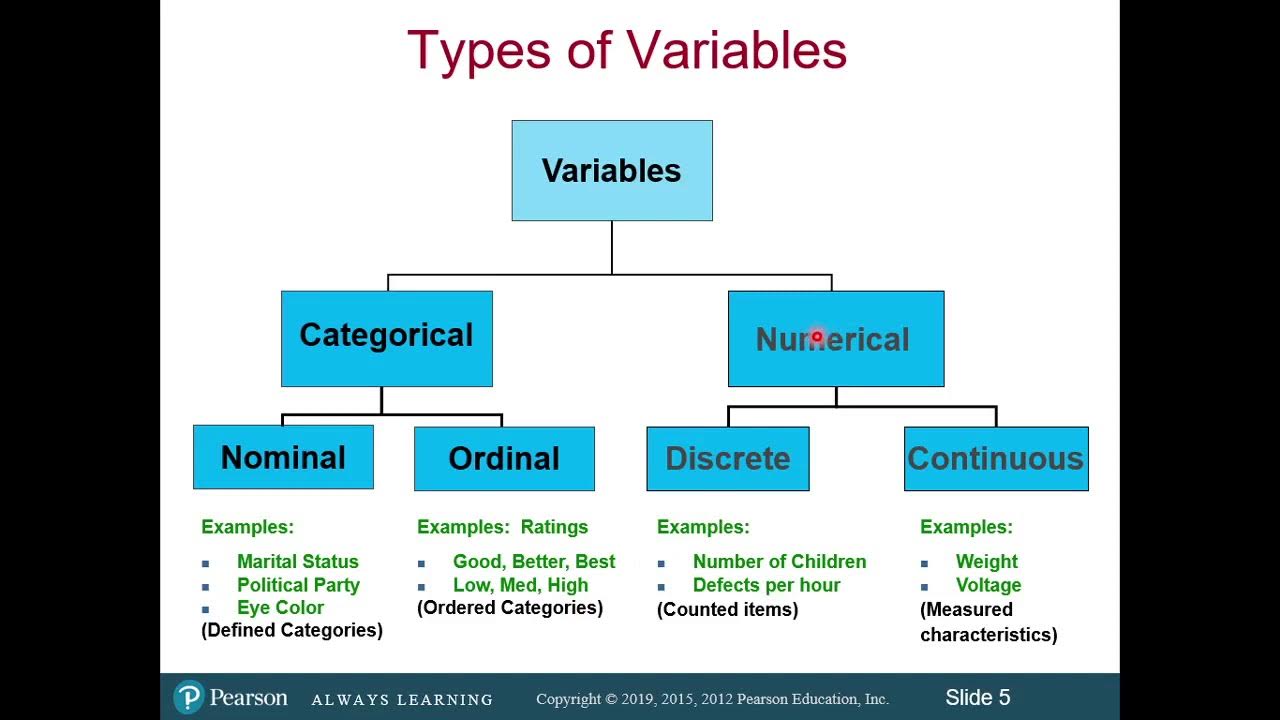
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of qualitative and quantitative variables in statistics. Qualitative variables are characteristics or identifiers, often represented by words or names, and can include numbers used solely for identification. Quantitative variables, on the other hand, represent counts, measurements, rankings, or quantities and are typically represented by numbers. Examples provided include 'birthday month' as a qualitative variable and 'number of french fries' as a quantitative variable. The paragraph also distinguishes between quantitative variables that are further classified into discrete (countable, such as the number of french fries) and continuous (can take any value, like weight or time) types.
📈 Further Classification of Quantitative Variables
Building upon the previous explanation, this paragraph delves deeper into the classification of quantitative variables. It emphasizes the difference between discrete and continuous variables. Discrete variables are countable and cannot take on all possible values within a range, exemplified by the count of french fries. Continuous variables, however, can take any value within a range and are illustrated with examples such as GPA, screen time, and weight. The paragraph clarifies that variables like GPA and screen time are continuous because they can have infinite decimal places and do not require counting individual units.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Qualitative Variables
💡Quantitative Variables
💡Discrete Variables
💡Continuous Variables
💡Identifier
💡Measurement
💡Count
💡Characteristic
💡Ranking
💡Quantity
💡Statistical Analysis
Highlights
Statistics variables can be classified as either qualitative or quantitative.
Quantitative variables represent numbers with meaning, such as counts, measurements, rankings, or quantities.
Qualitative variables are characteristics or identifiers, often words or names, and can also be numbers used as identifiers.
Birthday month is a qualitative variable as it identifies the month of birth.
Number of french fries is a quantitative variable as it represents a count.
GPA is a quantitative variable, representing a measurement of academic performance.
Student ID number is a qualitative variable, used to identify students.
Screen time is a quantitative variable, measuring the amount of time spent on screens.
Hair color is a qualitative variable, identifying different colors.
Type of pet is a qualitative variable, categorizing pets by their species or type.
Weight is a quantitative variable, indicating the amount of pounds or kilograms.
Quantitative variables can be further classified as discrete or continuous.
Continuous variables can take any value along a number line, like time, age, temperature, weight, and height.
Discrete variables are counted and do not cover the entire number line, such as the number of french fries.
GPA is a continuous variable because it can take on any value on the number line.
Screen time and weight are continuous variables as they can change in a smooth, continuous manner.
The video provides further classification and examples of discrete and continuous variables.
The video concludes with an invitation to watch more statistics and variables videos.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Classification of Variables and Types of Measurement Scales

Qualitative and Quantitative Data

Basic Terms of Statistics/ Population/Sample/Parameter/Variable/ urdu and hindi

Qualitative and Quantitative

Empirical Research - Qualitative vs. Quantitative

Research Design: Choosing a Type of Research Design | Scribbr 🎓
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: