Basic Terms of Statistics/ Population/Sample/Parameter/Variable/ urdu and hindi
TLDRThe script discusses various concepts related to data collection and statistical analysis in the context of a classroom setting. It delves into the definitions and distinctions between population, sample, descriptive statistics, and parameters. The importance of understanding these basic terms is emphasized for effective data analysis. The script also explores different types of variables, including qualitative and quantitative variables, and their subtypes such as discrete and continuous variables. The discussion aims to clarify these concepts to facilitate better data interpretation and statistical implementation.
Takeaways
- 📚 The class discusses basic technology and the importance of understanding data before implementing statistics on father data.
- 🔍 Data knowledge is crucial, including basic terms like sample, population constant, parameter variable, and inference.
- 🌐 Population refers to the entire group under study, and the collection should be based on the research.
- 🔢 A complete collection is essential for proper research, and it should be targeted towards the specific region of interest.
- 💡 Understanding the collection and sample size is vital for ease in relaxation on the data.
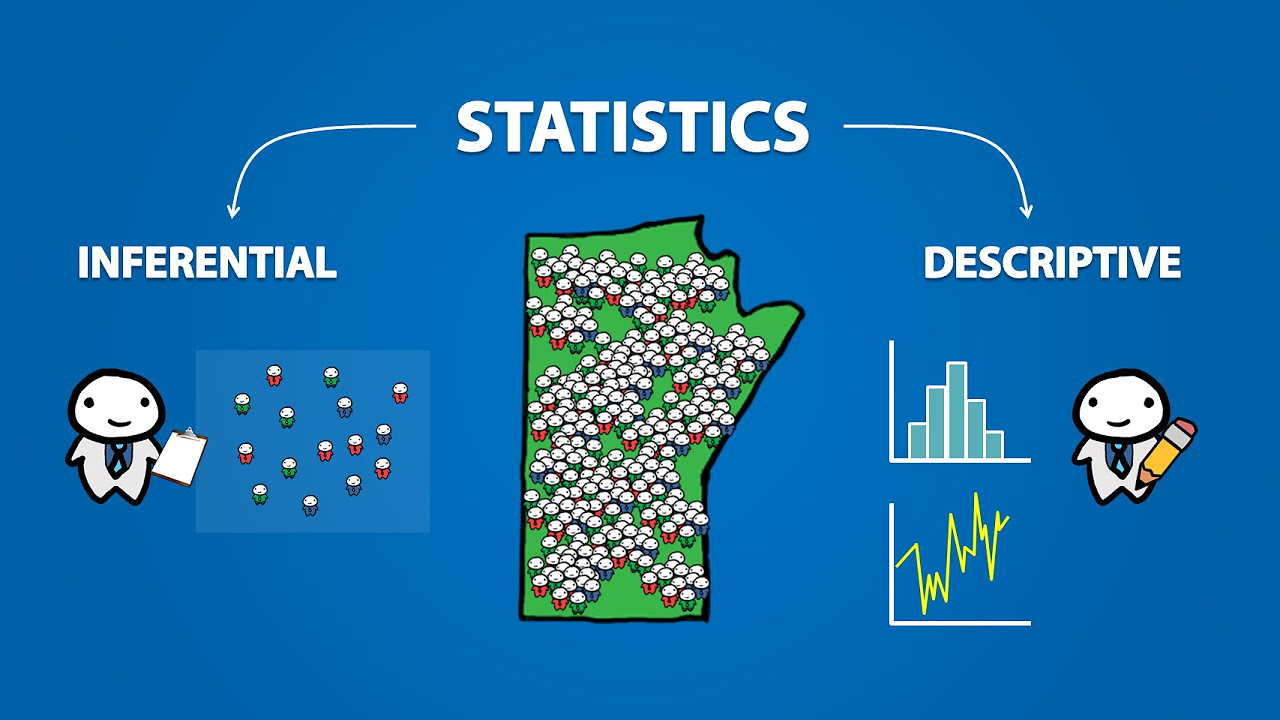
- 📈 Descriptive and statistical analysis are different; descriptive statistics do not involve data collection presentation or analysis.
- 📊 Parameters are calculated from the population and describe characteristics of the population quantity.
- 🔎 A sample is a subset of individuals selected from the college, and the data collected is specific to the research target.
- 🔍 Variables are different types of data that can be qualitative or quantitative, and they can be further classified as discrete or continuous.
- 📐 The type of variable (qualitative or quantitative) determines how the data is collected and represented.
- 🔑 Understanding the difference between population and sample is crucial for accurate data analysis and research conclusions.
- 🚀 The class aims to enhance the students' understanding of these concepts to improve their data analysis skills.
Q & A
What is the main focus of today's class?
-The main focus of today's class is to discuss basic technology and how to implement statistics on father data before understanding the data's knowledge, including basic terms like sample, population constant, parameter variable, and in.
Why is it important to have knowledge of the data before implementing statistics?
-It is important to have knowledge of the data before implementing statistics because understanding the data, such as its structure and the relationships between variables, allows for more accurate and meaningful statistical analysis.
What is a population in the context of the class?
-In the context of the class, a population refers to the complete collection of individuals or objects that are the subject of a particular study. For example, it could be all the students in a college.
What is a sample in research?
-A sample is a smaller subset of the larger population that is used to represent the whole population in a study. It allows researchers to make inferences about the entire population based on the data collected from the sample.
What is the difference between a finite and infinite population in research?
-A finite population refers to a population that has a known and limited number of individuals or objects, whereas an infinite population is one that is too large or unlimited in size, making it impractical or impossible to count or study every individual.
What is a parameter in statistics?
-A parameter is a numerical value calculated from the population that describes a characteristic of the population. For example, the mean or average grade point of all students in a college would be a parameter.
What is a variable in a statistical context?
-A variable is a factor or attribute that can change or vary within a dataset. In statistics, variables can be either qualitative (categorical) or quantitative (numerical) and can be further classified as discrete or continuous.
What is a discrete variable?
-A discrete variable is a variable that can take on only specific, separate values. For example, the number of students in a college can only be a whole number and cannot be a fraction or a decimal.
What is a continuous variable?
-A continuous variable is a variable that can take on any value within a certain range or interval. For example, a student's height can be expressed in inches or centimeters with decimal points, representing a continuous range of possible values.
What is the role of descriptive statistics in data analysis?
-Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in data analysis by summarizing and presenting data in an organized manner. It helps in describing the basic features of the data, such as the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation, without making any inferences about the population.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative variables?
-Qualitative variables are categorical in nature and describe attributes or characteristics that cannot be measured numerically, such as gender or race. Quantitative variables, on the other hand, are numerical and can be measured or counted, such as age, income, or test scores.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Basic Technology and Data Collection
The paragraph introduces the basic concepts of technology and data collection in a classroom setting. It emphasizes the importance of understanding foundational terms such as sample, population, constant parameter, and random variable. The discussion revolves around the need to grasp these concepts to effectively analyze data and implement statistical methods. The paragraph also touches on the definition of population in the context of research and the collection of data from students across different departments within a college, highlighting the process of narrowing down the focus to specific groups for more targeted research.
🔍 Understanding Population and Sample in Research
This paragraph delves deeper into the concepts of population and sample within the context of research. It explains the difference between finite and infinite populations and how these are determined based on the scope of the research. The paragraph also discusses the idea of a sample being a subset of the population and how it is used to make inferences about the entire population. Additionally, it touches on the concept of a sample error and how it can be addressed through proper sampling techniques.
📈 Types of Variables and Their Characteristics
The paragraph discusses the different types of variables that can be encountered in research, specifically qualitative and quantitative variables. It explains the characteristics of each type and provides examples to illustrate the differences. The paragraph also introduces the concept of discrete and continuous variables, explaining how they can be represented and used in data analysis. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of understanding these variable types to accurately interpret and apply statistical methods in research.
📊 Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
This paragraph focuses on the techniques used for data collection and analysis. It discusses the process of selecting a sample from a population and the various methods that can be employed to do so. The paragraph also covers the steps involved in transforming raw data into a usable form for analysis, including data cleaning and preparation. Additionally, it touches on the use of statistical tools and techniques to draw meaningful conclusions from the data, emphasizing the importance of proper data handling and interpretation in research.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Population
💡Sample
💡Variable
💡Parameter
💡Descriptive Statistics
💡Inferential Statistics
💡Qualitative Variable
💡Quantitative Variable
💡Discrete Variable
💡Continuous Variable
Highlights
The class discusses basic technology concepts, emphasizing the importance of understanding data before implementing statistics on father data.
It is crucial to have knowledge of basic terms like sample, population constant, parameter variable, and interval to understand the nature of data.
The term 'population' is defined as a complete collection of individuals, objects, and major elements under consideration for a particular study.
A 'sample' is a subset of the population, selected for study, and understanding the difference between population and sample is essential for data analysis.
The concept of 'finite and infinite population' is introduced, with examples provided to illustrate the differences in data collection and analysis.
The transcript explains the term 'sample' in the context of a college, where data from a small group of students is collected to infer conclusions.
The importance of understanding the target population in research is emphasized, as it determines the collection and relevance of the data.
The concept of 'parameter' is introduced, which is a numerical value calculated from the population and defines a characteristic of the population.
The transcript discusses the process of calculating parameters from a sample to make inferences about the population.
The difference between 'descriptive' and 'inferential' statistics is highlighted, with the former focusing on data presentation and the latter on drawing conclusions from data.
The role of 'variables' in data analysis is explained, distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative variables and their types.
The transcript delves into the classification of quantitative variables into discrete and continuous, providing examples for better understanding.
The concept of 'discrete variable' is defined, with examples of data that can only take on specific, separate values.
The 'continuous variable' is introduced, explaining that it can take any value within a range and is often measured on a scale.
The transcript emphasizes the importance of correctly identifying and categorizing variables as either qualitative or quantitative for accurate data analysis.
The class touches on the concept of 'parameter estimation' and how it is used in statistical analysis to make predictions about a population from a sample.
The transcript concludes by reinforcing the significance of understanding the basics of data, population, sample, and variables for effective statistical analysis and research.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Introduction to Statistics (1.1)

Qualitative and Quantitative Variables Explained | Discrete and Continuous

Statistics - The vocabulary of statistics

Tutorial 1- What Is Statistics And What Are Its Types In Hindi?
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PARAMETER AND STATISTIC | STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY | TAGLISH

Quantitative or Qualitative (Categorical)? Discrete or Continuous?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: