Qualitative and Quantitative Data
TLDRThis animation, sponsored by Smart Image Base, introduces the distinction between qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data comprises subjective descriptions without numeric values, such as taste impressions, while quantitative data includes numerical values derived from counting or measuring. The video further explains discrete data, which has specific exact values, and continuous data, which can take almost any value. The script aims to clarify these concepts for educational purposes.
Takeaways
- 🎨 The video is sponsored by Smart Image Base, a subscription website offering medical images and videos for educational and professional use.
- 🔍 The script discusses the fundamental difference between qualitative and quantitative data types.
- 📝 Qualitative data includes non-numeric descriptions and is often subjective, such as impressions of taste.
- 🔢 Quantitative data involves numerical values obtained through counting or measuring.
- 📏 The term 'qualitative' implies a focus on quality, while 'quantitative' emphasizes the quantity of data.
- 👦👧 An example of quantitative data is counting the number of boys versus girls in a class.
- 📏 Quantitative data can be further categorized into discrete and continuous data types.
- 🎲 Discrete data can only have specific, exact values and cannot be subdivided, like the outcome of rolling dice.
- 📐 Continuous data can have a wide range of values, such as height measurements in meters.
- 🌐 The script provides a clear distinction between the two types of data, emphasizing their characteristics and examples.
- 🔑 The takeaway is that qualitative data is descriptive and non-numeric, while quantitative data is numeric and can be either discrete or continuous.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the Smart Image Base subscription website?
-The Smart Image Base is a subscription website where users can download thousands of medical images and videos for use in lectures, courses, presentations, professional training, and more.
What are the two main types of data that scientists observe and collect?
-The two main types of data are qualitative data and quantitative data.
What is qualitative data and how is it characterized?
-Qualitative data includes descriptions that do not contain numeric values and tends to be subjective, such as impressions and observations that can be described and recorded in non-numerical ways.
Can you provide an example of qualitative data?
-An example of qualitative data could be subjective impressions such as how tasty one school lunch is compared to another.
What is quantitative data and how does it differ from qualitative data?
-Quantitative data contains numbers obtained by counting or measuring, making it different from qualitative data which is non-numeric and subjective.
How can quantitative data be categorized further?
-Quantitative data can be broken down into discrete data and continuous data.
What is discrete data and provide an example?
-Discrete data can only have certain exact values that can't be subdivided. An example is rolling a typical pair of dice, where you can only roll whole numbers between two and twelve.
What is continuous data and how does it differ from discrete data?
-Continuous data can have almost any value within a range, differing from discrete data which is limited to specific, indivisible values. An example of continuous data is height, which can be measured in fractions of a unit, such as meters.
Why are both qualitative and quantitative data important in scientific research?
-Both qualitative and quantitative data are important as they provide different perspectives and insights into the subject of study. Qualitative data offers depth and context, while quantitative data provides measurable and statistical insights.
How can the terms 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' be understood in the context of data types?
-In the context of data types, 'qualitative' refers to data that is descriptive and non-numeric, emphasizing quality and subjective aspects. 'Quantitative' refers to data that is numeric and measurable, emphasizing quantity and objective aspects.
What is an example of quantitative data involving measurements?
-Examples of quantitative data involving measurements include length, width, height, volume, mass, or temperature.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Data Types
This paragraph introduces the educational purpose of the video, which is to differentiate between qualitative and quantitative data. It explains that the video is sponsored by Smart Image Base, a subscription platform offering a vast collection of medical images and videos for various professional uses. The script then delves into the definition of data and the two main types: qualitative, which includes non-numeric descriptions and is subjective, and quantitative, which involves numerical values obtained through counting or measuring.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Qualitative Data
💡Quantitative Data
💡Discrete Data
💡Continuous Data
💡Data Collection
💡Observation
💡Subjective
💡Objective
💡Measurement
💡Counting
💡Protons
Highlights
The animation is sponsored by Smart Image Base, a subscription website offering medical images and videos for various professional uses.
Introduction to the distinction between qualitative and quantitative data in scientific observation and collection.
Qualitative data includes non-numeric descriptions and is often subjective, such as impressions of taste.
Quantitative data is numerical, obtained by counting or measuring, and is more objective.
The term 'qualitative' implies a focus on quality and description, while 'quantitative' emphasizes quantity and measurement.
Examples of qualitative data include subjective assessments like comparing the tastiness of school lunches.
Quantitative data examples include counting the number of boys versus girls in a class or measuring physical dimensions.
Quantitative data can be further categorized into discrete and continuous data types.
Discrete data has exact values that cannot be subdivided, such as rolling a pair of dice or counting protons in an atom.
Continuous data can take on almost any value within a range, like height measurements in meters.
The importance of understanding both qualitative and quantitative data for comprehensive scientific analysis.
The practical applications of qualitative data in describing observable phenomena beyond numerical representation.
The role of quantitative data in providing measurable and countable information for scientific research.
The distinction between discrete data, which includes whole numbers only, and continuous data with a broader range of values.
The educational value of the animation in clarifying the concepts of different data types for students and professionals.
The potential of Smart Image Base in enhancing lectures, courses, presentations, and professional training with medical imagery.
The animation's contribution to simplifying complex scientific concepts for better understanding and retention.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Qualitative and Quantitative

Types and Sources of Data in Statistics | Primary & Secondary data | Qualitative & Quantitative data
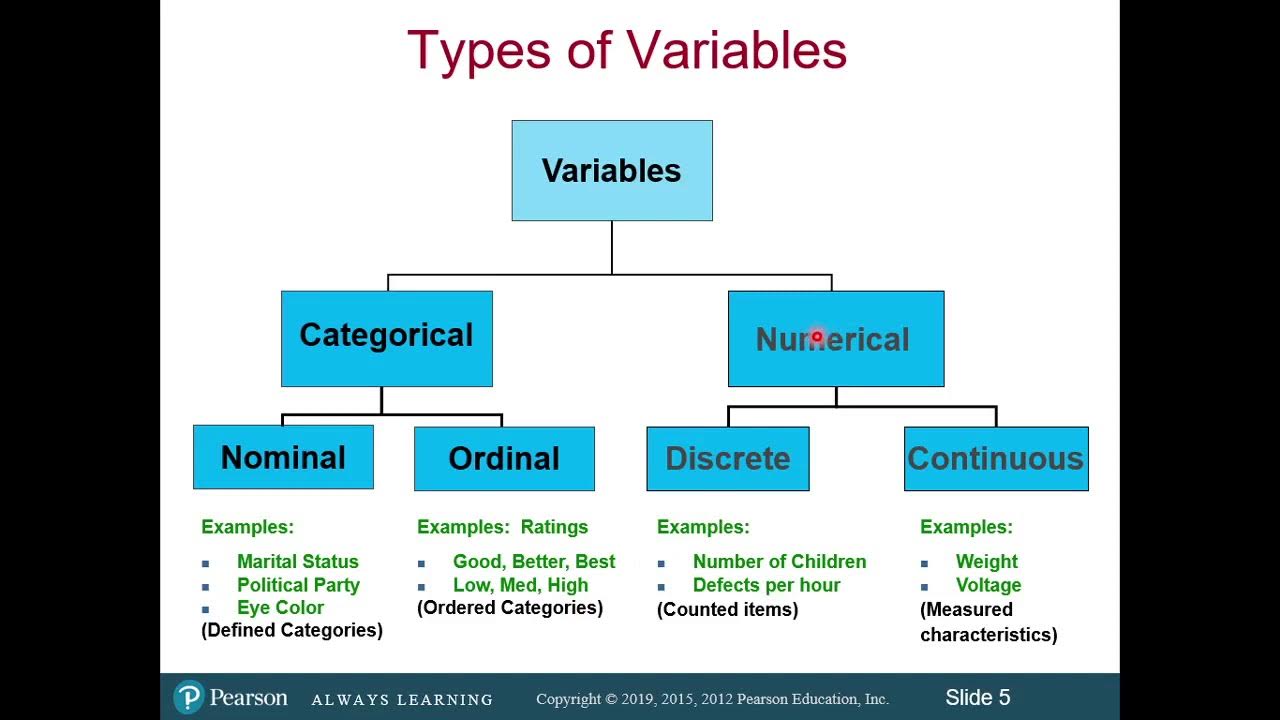
Classification of Variables and Types of Measurement Scales

Quantitative or Qualitative (Categorical)? Discrete or Continuous?

Qualitative and Quantitative Variables Explained | Discrete and Continuous
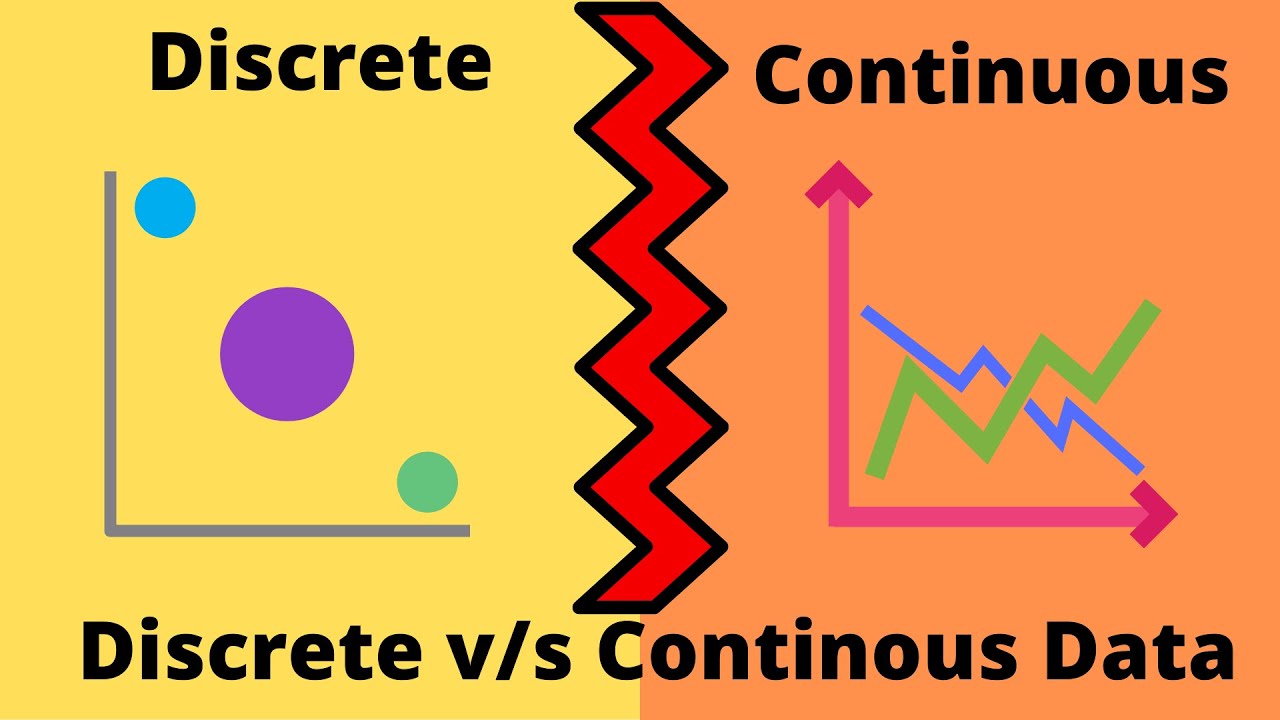
Discrete v/s Continuous Data - What ? How ? || Discrete Data || Continuous Data || Basic Statistics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: