1. Radiation History to the Present — Understanding the Discovery of the Neutron
TLDRIn this introductory lecture for the course 22.01, Mike Short, the instructor, delves into the historical discovery of the neutron by James Chadwick. The lecture revisits the scientific methods and principles that led to this groundbreaking finding, emphasizing the importance of conservation of energy and mass in understanding nuclear reactions. Short also outlines the course structure, highlighting the balance of theoretical and practical assignments, and stresses the significance of effective scientific communication. The lecture sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of nuclear science, promising engaging experiments and lively discussions on contemporary nuclear issues.
Takeaways
- 🎓 The lecture is an introduction to the course 22.01, Introduction to Ionizing Radiation, taught by Mike Short at MIT.
- 👩🏫 Amelia Trainer, along with Ka-Yen Yau and Caitlin Fisher, are the TAs for the course, and they all have recent experience with the material.
- 🤔 The course aims to update the students' physics knowledge from the 1800s to the discovery of the neutron in 1932, which is fundamental to nuclear engineering.
- 📜 The lecture focuses on James Chadwick's discovery of the neutron and his methodology, using the principles of conservation of energy and momentum.
- 🧪 Chadwick's experiments involved alpha particles hitting a beryllium foil and the resulting high penetrating radiation indicated the presence of a new particle, the neutron.
- 📊 The lecture discusses the importance of accurately balancing nuclear reactions in terms of both mass and energy, using the q equation and rest mass energy.
- 📈 The discovery of the neutron was significant because it explained the observed phenomena that couldn't be accounted for by existing theories and it deepened the understanding of nuclear interactions.
- 🔬 The course will involve both theoretical problem sets and take-home laboratory assignments, emphasizing hands-on experience and scientific communication skills.
- 📝 Students are expected to submit assignments as PDFs on the Stellar site and to communicate their findings effectively, targeting their writing to an audience of undergraduate engineering students.
- 🏆 The course aims to bring students' knowledge from the 1800s to the present day, covering modern physics and the latest developments in nuclear science.
- 🚀 The course concludes with a debate on societal misconceptions about nuclear energy and other related topics, encouraging students to engage with environmental and scientific issues confidently.
Q & A
What is the significance of the neutron in the field of nuclear engineering?
-The neutron is significant in nuclear engineering because it is the basis behind reactors and differentiates nuclear engineers from high-energy physicists. The discovery of the neutron by James Chadwick was a foundational moment for the field.
What is the role of the TAs in the course?
-The TAs, including Amelia Trainer, Ka-Yen Yau, and Caitlin Fisher, will assist students throughout the term. They can provide alternative explanations to the course material, having recently taken the course themselves and experienced the challenges of understanding the concepts.
What experiment did James Chadwick conduct to discover the neutron?
-Chadwick conducted an experiment where alpha particles from a polonium source were directed at a beryllium foil. The interaction produced a highly penetrating radiation that couldn't be explained by current theories, leading Chadwick to propose the existence of the neutron.
What is the importance of the conservation laws in physics?
-Conservation laws are fundamental in physics, ensuring the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy. They are used to verify that nuclear reactions are balanced and play a critical role in deriving and understanding the behavior of particles and systems in nuclear engineering.
What was the role of the ionization chamber and oscillograph in Chadwick's experiment?
-The ionization chamber and oscillograph were used to measure the amount of ionization caused by the radiation produced in Chadwick's experiment. This measurement helped estimate the energy of the unknown particles, leading to the discovery of the neutron.
Why is it important for students to understand nuclear reactions and how to balance them?
-Understanding nuclear reactions and how to balance them is crucial for nuclear engineers as it allows them to predict and calculate the outcomes of these reactions, which is essential for designing and operating nuclear reactors and other applications of nuclear processes.
What is the difference between an alpha particle and a neutron in terms of their interaction with matter?
-An alpha particle, being a helium nucleus with a +2 charge, interacts strongly with matter due to the Coulomb force with electrons and nuclei. In contrast, a neutron, having no charge, does not interact with the electrons in matter and primarily interacts with the nuclei, giving it a higher penetrating power.
What is the mass defect, and how is it related to the binding energy of a nucleus?
-The mass defect is the difference in mass between the individual nucleons (protons and neutrons) and the combined mass of the nucleus when they are assembled. This mass difference is converted into binding energy, which holds the nucleus together and is released when the nucleus is formed.
Why is it essential for students to learn how to communicate scientific findings effectively?
-Effective communication of scientific findings is essential because it allows the scientific community to build upon discoveries, facilitates collaboration, and ensures that knowledge is not lost if a researcher's work is not widely known. It also enables scientists to inform the public and policymakers about their work and its implications.
What is the structure of a scientific article, and why is each part important?
-A scientific article typically includes an abstract, introduction, experimental section, results, discussion, and conclusion. Each part is important: the abstract provides a brief overview, the introduction provides context and rationale, the experimental section details the methods, the results present the data, the discussion interprets the results, and the conclusion summarizes the findings.
Why is it important to not round numbers when dealing with atomic mass units (AMU) and energy calculations in nuclear engineering?
-Rounding numbers in AMU and energy calculations can lead to significant errors, as even small differences in mass can correspond to large amounts of energy. Maintaining precision is crucial for accurate calculations and understanding the outcomes of nuclear reactions.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Nuclear Science and Chadwick's Discovery
The video introduces the course on ionizing radiation, with a focus on the historical context of nuclear engineering and the discovery of the neutron by James Chadwick. It discusses the importance of the neutron in nuclear reactions and the educational journey from classical physics to modern nuclear physics.
🔬 Chadwick's Experiment and the Neutron Hypothesis
The paragraph details Chadwick's experiment involving beryllium and alpha particles, leading to the discovery of the neutron. It explains the experimental observations, the discrepancy with existing theories, and Chadwick's hypothesis that a neutral particle, the neutron, was responsible for the unexplained phenomena.
🧮 The Conservation Laws and Nuclear Reactions
This section emphasizes the importance of conservation laws in physics, particularly in the context of nuclear reactions. It discusses the concept of mass and energy conservation, and how Chadwick used these principles to support the existence of the neutron, including the formulation of nuclear reactions and the calculation of mass defects.
📉 Penetrating Power and Range of Neutrons
The discussion moves on to the penetrating power of neutrons and how Chadwick's experiments with aluminum foil helped deduce the range of the radiation. It contrasts the behavior of neutrons with charged particles and explains the concept of mass defect and binding energy in the context of nuclear reactions.
📝 Documentation and Communication in Science
The speaker stresses the importance of scientific communication, outlining how to write scientific articles effectively. It covers the structure of a scientific paper, from abstract to conclusion, and the necessity of clear and accurate reporting of experimental results and analysis.
🎓 Course Structure and Assignment Expectations
The paragraph outlines the course structure, including the types of assignments, grading policies, and expectations for student work. It also discusses the importance of academic honesty and the consequences of plagiarism or cheating, as well as the resources available for students to improve their scientific communication skills.
🏆 Incentives and Interactive Learning
The video concludes with a discussion on incentives for students to perform well in the course, such as the opportunity to operate advanced scientific equipment. It also mentions a final class activity involving irradiated fruit to dispel myths about food irradiation, emphasizing the application of nuclear science in everyday life.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Creative Commons license
💡Ionizing Radiation
💡Neutron
💡Nuclear Reaction
💡Binding Energy
💡Mass Defect
💡X-rays
💡Chadwick's Experiment
💡Nuclear Engineering
💡Half-Life
💡Plasma Sputtering
Highlights
Introduction to MIT OpenCourseWare and the course 22.01, Introduction to Ionizing Radiation.
Instructor Mike Short and TA Amelia Trainer's introduction, along with the course's hands-on approach.
The significance of the discovery of the neutron in nuclear engineering and its role in differentiating it from high energy physics.
Chadwick's experiment that led to the discovery of the neutron, using basic conservation of energy principles.
The historical context of nuclear discoveries, including the electron, alpha, beta, and gamma rays.
The explanation of the penetrating power of radiations and the distinction between gamma rays and other photons.
Chadwick's paper and its impact on proving the existence of neutrons through experimental observation.
The importance of mass, momentum, and energy conservation in nuclear reactions and physics.
The process of balancing nuclear reactions using the q equation and the concept of mass defect.
The discovery of the neutron's properties, such as its lack of charge and high penetrating power.
The use of the Learning Module site for course materials, assignments, and useful resources.
The importance of accurate and precise scientific communication, including writing scientific articles.
Course structure, assignments, and expectations, including problem sets, quizzes, and a final exam.
The role of the Comm Lab in enhancing scientific communication skills and the benefits of using it.
Discussion on the definition of science and the critical nature of communication in the scientific process.
The practical aspects of the course, including laboratory assignments and the use of technology.
The significance of food irradiation and its impact on importing agricultural products, to be discussed with a fruit party at the end of the class.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

25. Review of All Nuclear Interactions and Problem Set 7 Help

7. Q-Equation Continued and Examples

2. Radiation Utilizing Technology

10. Radioactive Decay Continued

3. Nuclear Mass and Stability, Nuclear Reactions and Notation, Introduction to Cross Section
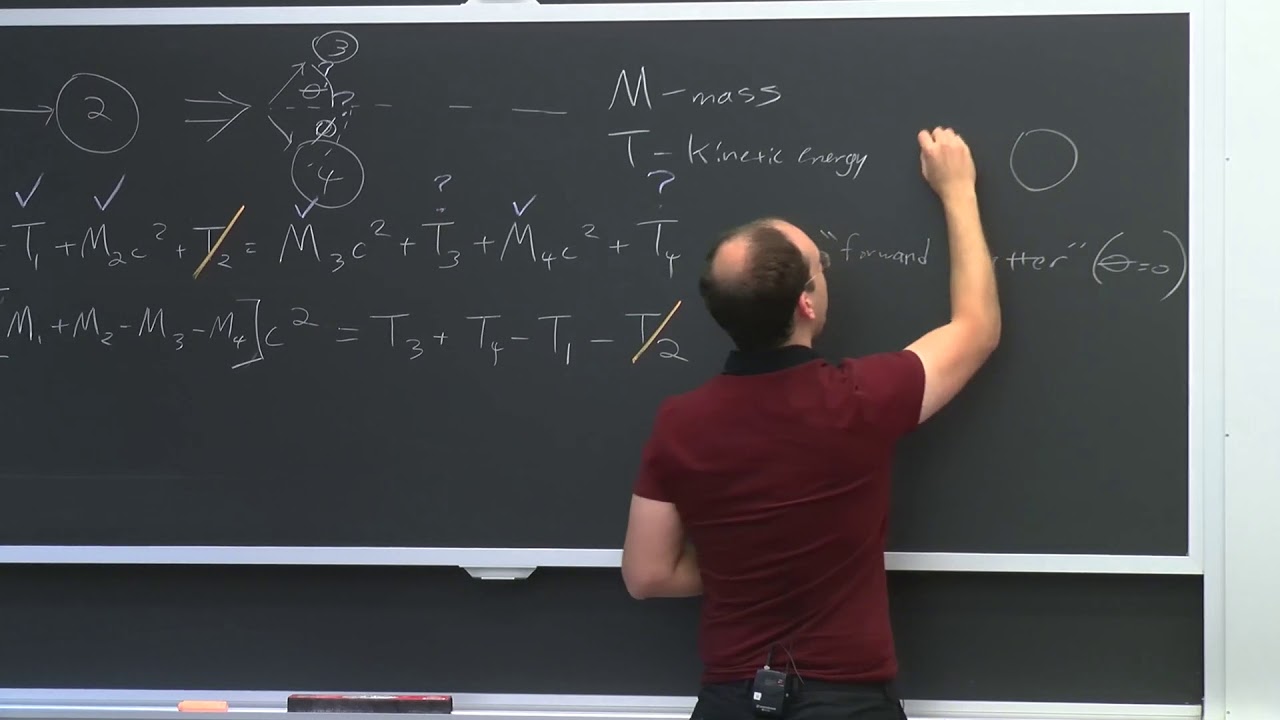
6. The Q-Equation — The Most General Nuclear Reaction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: