Energy intro (kinetic & potential) | Work & Energy | Physics | Khan Academy
TLDRThe video script delves into the scientific concept of energy, explaining that it is the capacity to do work. It differentiates between kinetic and potential energy, with kinetic energy being associated with the motion of objects and potential energy being the energy stored due to an object's position or configuration. The script uses relatable examples, such as a moving ball, a compressed spring, and the force of gravity, to illustrate these concepts. It also touches on other forms of energy like light, heat, sound, electrical, and chemical energy, suggesting that they are combinations of kinetic and potential energy. The video concludes with a brief mention of dark energy, a mysterious force thought to be responsible for the universe's expansion. The script effectively simplifies complex physics concepts, making them accessible to a broader audience.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Energy is the scientific term for the capacity to do work, which is a fundamental concept in physics.
- 💡 Work in physics is defined as the force acting on an object multiplied by the displacement of the object.
- 🏃♀️ Living things, by their nature of being able to do work, inherently possess energy.
- 🏀 Non-living objects can also have energy, such as a thrown cricket ball or a dropped hammer, which can do work on other objects.
- 🏃 Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion, and it increases with the speed of the object.
- 🔕 Potential energy is the energy that is waiting to become kinetic, and it can be found in objects due to their position or configuration.
- 🌱 Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands are examples of objects with elastic potential energy, which can do work when released.
- 🌐 Gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object, with higher positions holding more energy due to increased work potential.
- 💥 Other forms of energy include light energy, heat energy, sound energy, electrical energy, and chemical energy, which can be combinations of kinetic and potential energies.
- 🌌 Dark energy is a hypothesized form of energy related to the expansion of the universe, although it remains a mystery and is not yet fully understood.
Q & A
What is the scientific meaning of energy?
-In physics, energy is the capacity to do work. It is the ability of an object or a system to perform work upon another object, which can be expressed as the force applied to an object times the distance the object moves in the direction of the force.
What is work in physics?
-Work in physics is the product of the force acting on an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force. It is a measure of energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved by a force over a distance.
How is energy related to work?
-Energy is directly related to work in that anything capable of doing work possesses energy. The more work an object can do, the more energy it has. This relationship is fundamental in understanding the concept of energy as it highlights the connection between the potential to cause change (energy) and the actual process of causing change (work).
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of an object due to its motion. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. It is a form of mechanical energy and can be calculated using the formula KE = 0.5 * m * v^2, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
Can non-living things have energy?
-Yes, non-living things can have energy. Energy is not exclusive to living organisms. For example, a compressed spring or a stretched rubber band possesses potential energy due to its configuration, even though it is not moving. This energy can be converted into kinetic energy when the object is released and allowed to move.
Potential energy is the stored energy of an object or system that has the potential to be converted into kinetic energy. It depends on the object's position or configuration. For instance, a ball held at a certain height has gravitational potential energy, and a compressed spring or stretched rubber band has elastic potential energy.
-Potential energy is the energy that is waiting to become kinetic. It is stored in an object or system due to its position or configuration. For example, a ball at a height has gravitational potential energy, and a compressed spring or stretched rubber band has elastic potential energy. The amount of potential energy depends on factors such as the height of the ball or the degree of compression or stretching of the spring or rubber band.
What factors affect the amount of potential energy an object has?
-The amount of potential energy an object has depends on its position or configuration. For gravitational potential energy, the higher the object is lifted, the more potential energy it has. For elastic potential energy, the more an object like a spring or rubber band is compressed or stretched, the more potential energy it stores.
How can you increase the potential energy of a compressed spring?
-You can increase the potential energy of a compressed spring by compressing it more. The more you compress the spring, the greater the potential energy it stores, because it can do more work when released.
What is the relationship between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object?
-The gravitational potential energy of an object is directly proportional to its height. The higher the object is lifted, the more gravitational potential energy it has, because it can do more work when it is allowed to fall under the influence of gravity.
What are some examples of potential energy?
-Examples of potential energy include a stretched rubber band, a compressed spring, and a ball lifted to a certain height. These objects have elastic potential energy and gravitational potential energy, respectively, due to their configuration or position.
What other forms of energy are mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions light energy, heat energy, sound energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, and dark energy. Light energy can potentially do work by pushing objects, while heat, sound, electrical, and chemical energies are forms of energy that we might encounter in our daily lives. Dark energy is a theoretical form of energy associated with the expansion of the universe.
How are kinetic and potential energies related?
-Kinetic and potential energies are two forms of mechanical energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is the stored energy that has the potential to become kinetic energy. All forms of energy can be seen as combinations of kinetic and potential energies, which is why understanding these two concepts is crucial in the study of energy.
Outlines
🔋 Understanding Energy and Work
This paragraph introduces the scientific concept of energy, defining it as the capacity to do work. It explains that work in physics is the product of force acting on an object and its displacement. The paragraph uses examples such as a person pushing a cart, a ball hitting stumps, and a hammer dropping on a pin to illustrate how objects that can do work possess energy. It further distinguishes between living and non-living things, emphasizing that both possess energy. The concept of kinetic energy is introduced, relating it to the motion of objects and their capacity to do work. The paragraph also discusses the correlation between the speed of an object and its energy, establishing that faster moving objects have more kinetic energy due to their increased ability to do work.
🌐 Potential Energy and its Varieties
This paragraph delves into the concept of potential energy, which is energy that is waiting to become kinetic. It explains that potential energy can exist without motion and provides examples of a compressed spring and a stretched rubber band to illustrate this point. The paragraph also introduces gravitational potential energy, explaining how raising an object to a height increases its potential energy due to gravity. It further discusses how the energy of an object depends on its position or configuration. The paragraph concludes by mentioning other forms of energy such as light, heat, sound, electrical, and chemical energy, and touches upon the concept of dark energy, which is still a mystery to scientists.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Energy
💡Work (Physics)
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Displacement
💡Force
💡Elastic Potential Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Configuration
💡Light
💡Dark Energy
Highlights
Energy is defined scientifically as the capacity to do work.
In physics, work is calculated as the force acting on an object multiplied by the displacement of the object.
Anything that can do work possesses energy.
Living things, due to their ability to do work, inherently possess energy.
Non-living things can also have energy, as demonstrated by a thrown cricket ball doing work on stumps.
Kinetic energy is the name given to the energy a moving object possesses due to its motion.
Examples of kinetic energy include moving air (wind) and waves in water.
Energy can exist without motion, such as in a compressed spring or a stretched rubber band.
Potential energy is the energy that is waiting to become kinetic.
The energy of a compressed or stretched object depends on its configuration.
Gravitational potential energy depends on the height or position of an object.
Light is a form of energy that can potentially do work by pushing objects and causing them to move.
Other forms of energy include heat, sound, electrical, and chemical energy.
Kinetic and potential energies are fundamental as other energy forms are combinations of these two.
Dark energy is a theoretical form of energy that is thought to be responsible for the expansion of the universe.
The video summarizes that anything capable of doing work has energy, which is primarily categorized into kinetic and potential energies.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
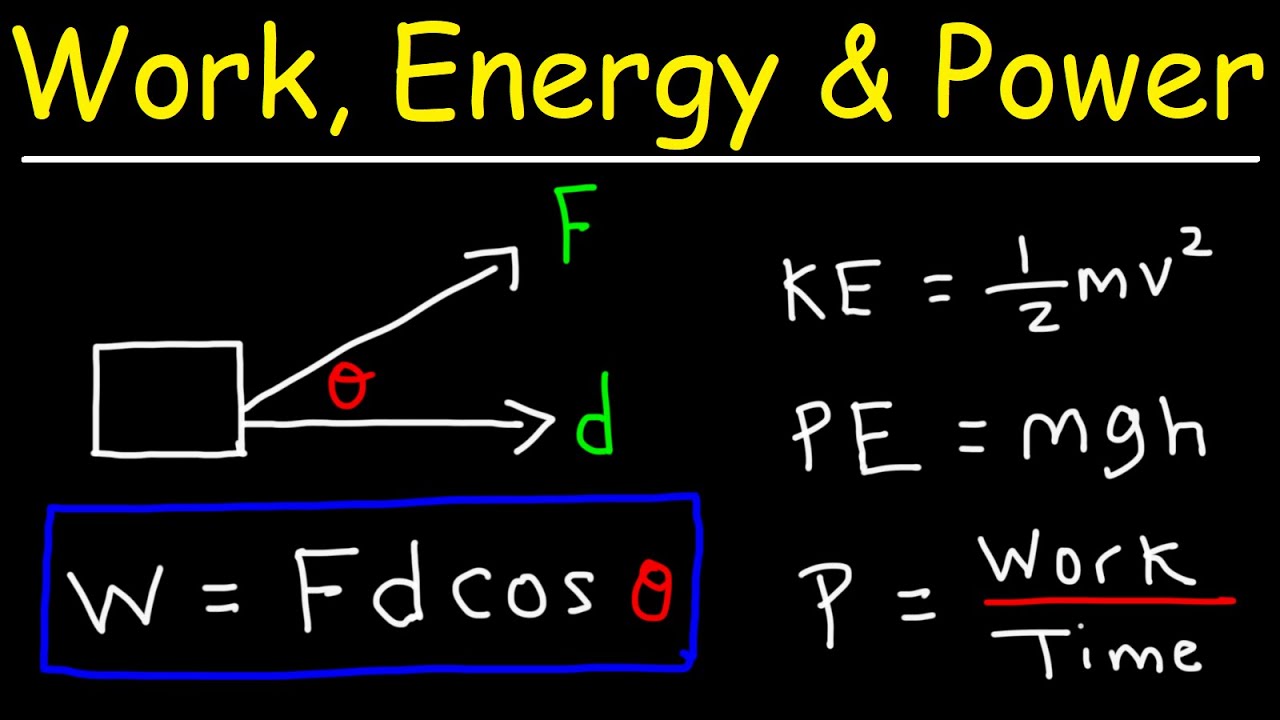
Work, Energy, and Power - Basic Introduction
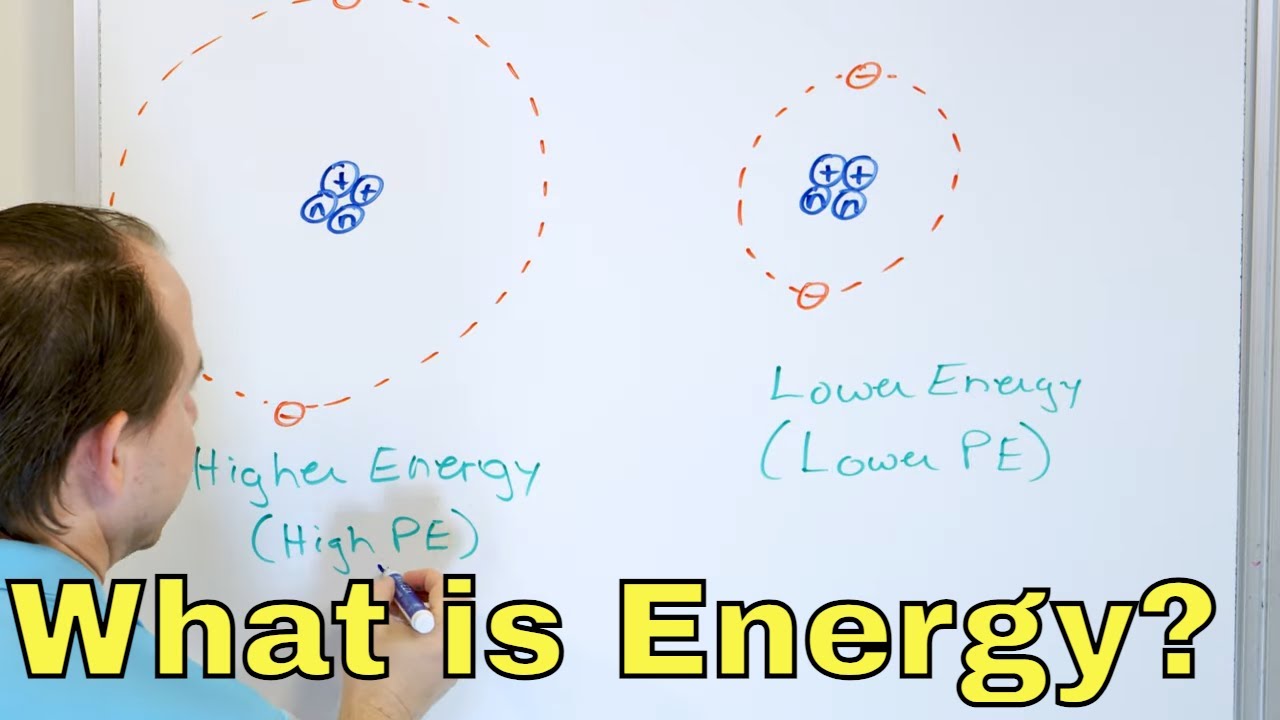
What is Energy & Work in Chemistry & Physics? - [1-1-6]

Different Forms Of Energy | Physics

The Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy
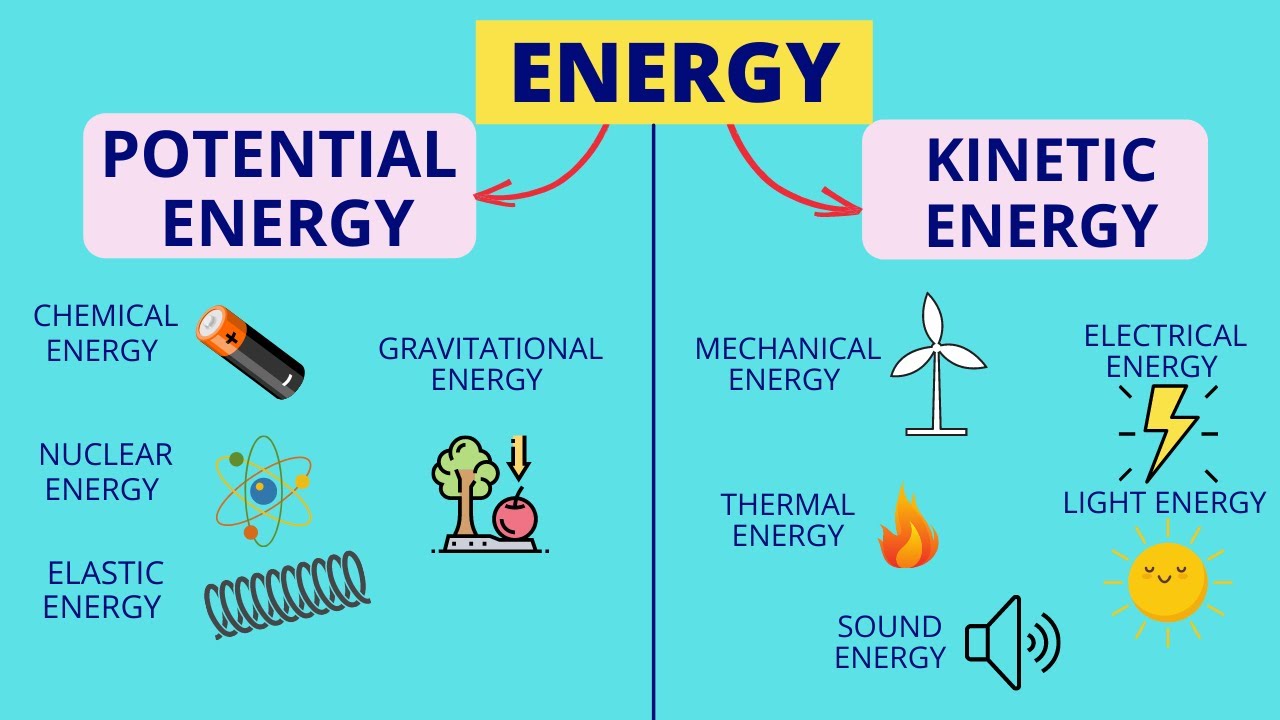
Energy | Forms of Energy | Law of Conservation of Energy | Science Lesson for Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: