Different Forms Of Energy | Physics
TLDRThis educational video explores the diverse forms of energy, including potential, kinetic, heat, chemical, light, sound, and electrical energy. It explains potential energy through examples like lifting a hammer or compressing a spring. Kinetic energy is associated with motion, while heat energy is measured in calories. Chemical energy is found in fuels and food, with a distinction made between food calories (kcal) and heat calories. Light and sound energy are essential for vision and hearing, respectively. Electrical energy, crucial for modern life, is supplied through power stations. The video concludes with practical examples and a science detective activity to identify energy forms in everyday objects.
Takeaways
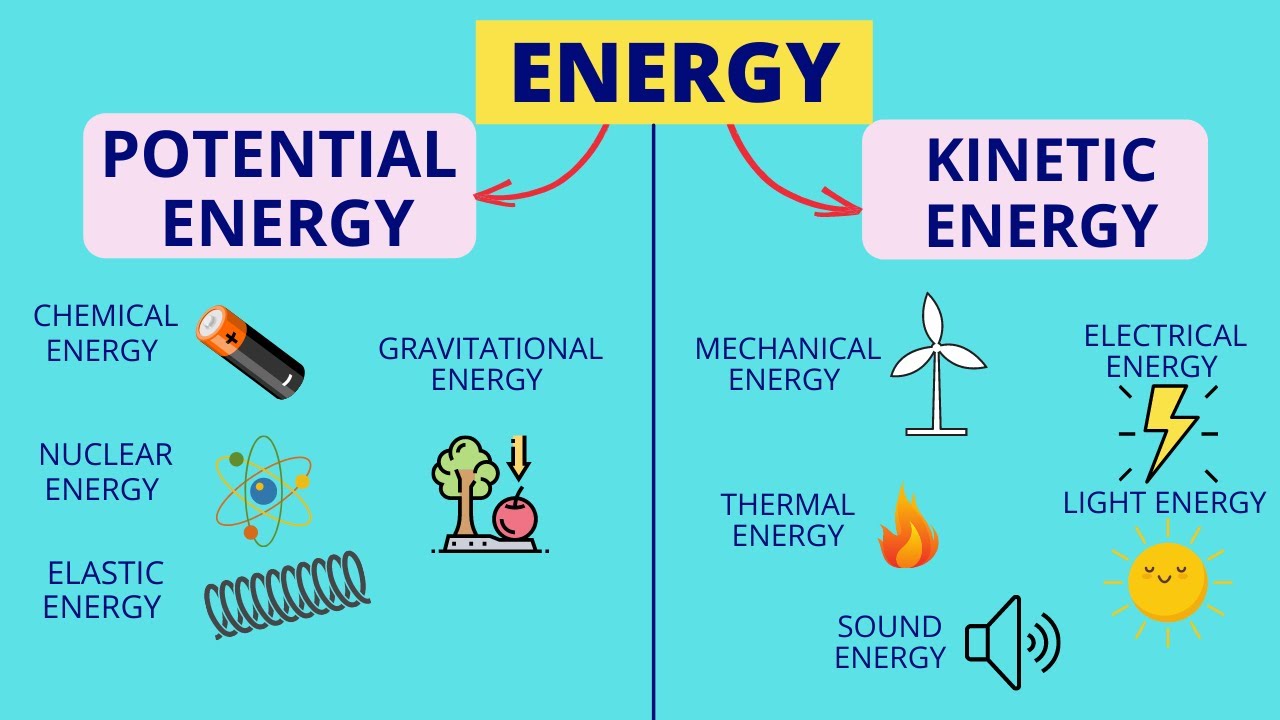
- 🌌 The universe is composed of matter and energy, with energy existing in various forms such as potential, kinetic, heat, chemical, light, sound, and electrical energy.
- 🔨 Potential energy is the stored energy due to an object's position or configuration, like lifting a hammer or compressing a spring.
- 🏃 Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, possessed by moving objects like a running person or a flying bird, which also has potential energy due to its height.
- 🔥 Heat energy is associated with an object's temperature, measured in calories, where 1 calorie is the energy needed to raise 1 gram of water's temperature by 1°C.
- 🍌 Chemical energy is the energy stored in substances and released through chemical reactions, such as burning fuels or the energy from food we consume.
- 💡 Light energy comes from sources like the Sun, bulbs, and candles, and is essential for vision.
- 🔊 Sound energy is produced by vibrations and is what allows us to hear, such as when speaking or listening to music.
- ⚡ Electrical energy is crucial for modern life, powering devices in our homes and is billed based on consumption.
- 🔋 A battery stores chemical energy and supplies electrical energy when in use, with the potential for leakage if old and not replaced.
- 🕵️♂️ The script encourages viewers to identify different forms of energy in everyday activities, such as turning on a lamp or drinking juice.
- 📚 The video aims to educate on the various forms of energy, emphasizing their presence and importance in daily life.
Q & A
What are the two fundamental components that make up the universe?
-The two fundamental components that make up the universe are matter and energy.
What is potential energy and how is it related to an object's position or configuration?
-Potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration, such as lifting a hammer to a height or compressing a spring.
How is kinetic energy different from potential energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, whereas potential energy is the energy stored due to position or configuration. A moving ball has kinetic energy, while a stationary ball does not.
What is the sum of kinetic and potential energy known as?
-The sum of kinetic and potential energy is known as mechanical energy.
How is heat energy different from a glass of cold water to a glass of hot water?
-Heat energy is associated with the temperature of an object. A glass of hot water has more heat energy than a glass of cold water.
What is the definition of one calorie of heat energy?
-One calorie of heat energy is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree centigrade, and it is equivalent to 4.2 joules.
What is the difference between the calories of heat and the calories of food?
-The calories of heat (small C) are a small amount of energy, while food calories (capital C) are much larger, with one food calorie being equivalent to one thousand calories of heat, often written as kilocalories or kcal.
What is chemical energy and how is it related to food and fuel?
-Chemical energy is the energy stored in a substance that is released during a chemical reaction. It is present in fuels like coal, petrol, and diesel, and in food, which provides energy to our bodies.
What is the source of light energy and how does it help us?
-Sources of light energy include the Sun, bulbs, LED lights, and candles. Light energy helps us see the world around us.
How is sound energy produced and what role does it play in our daily lives?
-Sound energy is produced by vibrations, such as when we speak or when a music system plays. It enables us to hear.
Why is electrical energy important in our daily lives and how can we reduce its consumption?
-Electrical energy powers many devices in our homes, such as lights, fans, TVs, and computers. To reduce consumption and save on the electricity bill, we can turn off devices when they are not in use.
What form of energy is stored in a cell or a battery and what happens when it is used?
-A cell or battery stores chemical energy, which is converted into electrical energy through a chemical reaction when the battery is in use.
Outlines
🚀 Introduction to Energy Forms
This paragraph introduces the concept of energy, emphasizing that the universe is composed of matter and energy. It outlines various forms of energy, including potential, kinetic, heat, chemical, light, sound, and electrical energy. The speaker promises to delve into these forms in detail and mentions that potential energy is due to an object's position or configuration, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Mechanical energy is introduced as the sum of potential and kinetic energy.
🔥 Understanding Heat and Chemical Energy
The second paragraph focuses on heat and chemical energy. It explains heat energy as the energy associated with an object's temperature, measured in calories, where 1 calorie equals 4.2 joules. Chemical energy is described as the energy stored in substances and released during chemical reactions, with fuels like coal, petrol, and diesel as examples. The paragraph also clarifies the difference between 'calories' of heat and 'Calories' of food, noting that food calories, often referred to as kilocalories, are much larger units of energy.
💡 Exploring Light, Sound, and Electrical Energy
This paragraph explores light, sound, and electrical energy. Light energy is essential for vision and comes from sources like the Sun, bulbs, and candles. Sound energy, produced by vibrations, enables hearing and is exemplified by speaking and music systems. Electrical energy, crucial for modern life, is supplied through power stations and cables, with the cost of electricity based on consumption. The paragraph also includes a summary of the energy forms discussed and transitions into a set of top three exam-oriented questions.
🔍 Detecting Energy in Everyday Objects
The final paragraph presents a practical application of the energy concepts discussed in the video. It challenges the viewer to identify different forms of energy in various everyday activities and objects, such as a lamp receiving electrical energy, a ball possessing potential and kinetic energy, and a bouncing ball demonstrating mechanical energy. The paragraph also touches on sound energy from the ball's bounce and chemical energy from food and drink. It concludes with an encouragement to observe and recognize the omnipresence of energy in daily life.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Mechanical Energy
💡Heat Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Light Energy
💡Sound Energy
💡Electrical Energy
Highlights
The universe is composed of matter and energy.
Energy exists in various forms such as potential, kinetic, heat, chemical, light, sound, and electrical energy.
Potential energy is stored due to an object's position or configuration.
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, possessed by moving objects.
Mechanical energy is the sum of potential and kinetic energy.
Heat energy is associated with an object's temperature, measured in calories.
One calorie of heat energy is defined as the amount needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree centigrade.
Chemical energy is stored in substances and released through chemical reactions.
Fuels like coal, petrol, and diesel, as well as food, are sources of chemical energy.
Food calories are measured in kilocalories, which are larger units than heat calories.
Light energy is emitted by sources like the Sun, bulbs, and candles, aiding in visibility.
Sound energy is produced by vibrations and enables hearing.
Electrical energy is crucial for daily life, powering devices in homes and businesses.
Electrical energy is supplied through power stations and electric cables.
Batteries store chemical energy and supply electrical energy through chemical reactions.
An aeroplane in flight possesses both potential and kinetic energy.
The energy of a flying aeroplane can be described as mechanical energy.
Cells or batteries store chemical energy and are used in various devices.
Encouragement to observe and identify different forms of energy in everyday life.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: