What Are Atoms Made Of?
TLDRThe video script from Stated Clearly explores the composition of atoms, debunking the early belief that they are indivisible. It explains that atoms consist of subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus, with protons determining the element's identity. Electrons, which are equal in number to protons in a neutral atom, orbit the nucleus. The video also touches on the concept of ions and the importance of the number of protons in defining an element. The script highlights the work of the National Science Foundation and the Casal Research Center, emphasizing the educational value of their research and resources, including a video game that simulates atomic interactions.
Takeaways
- 📜 The concept of atoms was first introduced by John Dalton, who believed they were uncuttable and the smallest bits of matter.
- 🔬 Atoms are actually divisible and consist of subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- 🔍 The discovery of subatomic particles challenged the early notion that atoms were fundamental and indivisible.
- 🌈 An actual scan of a nitrogen atom reveals the electron cloud, with the nucleus hidden underneath the electrons.
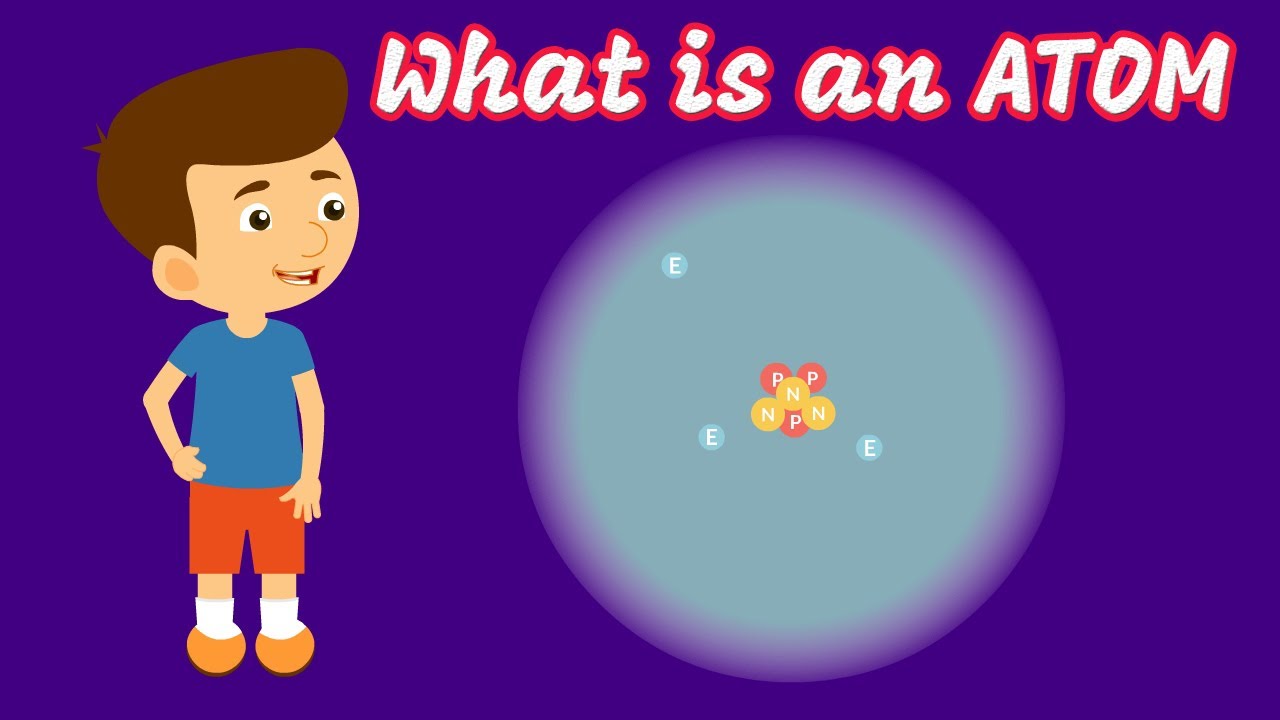
- 📊 The Bohr model is a simplified representation of an atom, with the nucleus enlarged for visibility, though not to scale.
- 🔴 The nucleus of an atom contains protons and typically neutrons, giving the atom most of its mass.
- ⚖️ The number of protons in an atom determines its identity and place in the periodic table.
- 🔝 Adding or removing protons from an atom changes its chemical properties and transforms it into a different element.
- 🔀 Isotopes of an element can vary in the number of neutrons, which can affect the atom's weight but not its chemical properties.
- 💫 Electrons are negatively charged and typically depicted as particles in orbit around the nucleus, although this is a simplified model.
- 🎮 The Castle Research Center at UC Irvine developed a video game called 'Bond Breaker' to educate on the interactions of atoms and subatomic particles.
Q & A
What is the original meaning of the word 'atom'?
-The word 'atom' originally means 'uncuttable', as it was first used by John Dalton who believed that atoms were the smallest, indivisible bits of matter.
What did John Dalton discover about atoms?
-John Dalton discovered evidence that atoms exist, and he named them 'atom' because he thought they were uncuttable and fundamental particles.
What are the subatomic particles that make up an atom?
-Atoms are made up of subatomic particles, most importantly electrons, protons, and neutrons.
What is the significance of the electron cloud in the context of an atom?
-The electron cloud represents the outer edges of the atom where electrons are found. It is the region around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be.
What is the Bohr model of an atom?
-The Bohr model is a simplified model of an atom, named after physicist Niels Bohr, which depicts electrons orbiting around the nucleus in certain paths or energy levels.
What does the nucleus of an atom consist of?
-The nucleus of an atom consists of one or more protons and, in most atoms, a collection of neutrons. It is the core of the atom and contains most of its mass.
How does the number of protons in an atom determine its identity?
-The number of protons in an atom determines the type of atom it is. For example, hydrogen has one proton, nitrogen has seven, and gold has 79. This number is also referred to as the atomic number and is found on the periodic table.
What is the relationship between the number of protons and electrons in an atom?
-In general, the number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Each positively charged proton attracts one negatively charged electron.
What happens when the number of electrons in an atom changes?
-If an electron is removed or added to an atom, the atom becomes an ion. The chemical properties of the atom can change, and the atom may become more reactive or unstable.
How can the mass of an atom be affected by the number of neutrons?
-The mass of an atom is mostly determined by the protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Changing the number of neutrons can make the atom slightly heavier or lighter, but it does not change the atom's chemical properties significantly.
What is the significance of the periodic table in relation to atoms?
-The periodic table organizes elements based on the number of protons in their atoms. Each element has a unique atomic number that corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus, which determines the element's identity and chemical properties.
Outlines
🔬 Understanding Atoms and Subatomic Particles
This paragraph delves into the fundamental concepts of atomic structure, explaining the discovery and nature of atoms, and the revelation that they are not indivisible as once believed. It introduces the concept of subatomic particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons—as the constituents of atoms. The importance of the nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, and the role of electrons in orbiting the nucleus are highlighted. The paragraph also touches on the significance of the number of protons in determining the type of element and the impact of altering this number on the atom's chemical properties. The use of the Bohr model as a simplified representation of atomic structure is mentioned, along with the actual shape and appearance of a nitrogen atom as captured by advanced imaging techniques.
📝 Recap and Further Exploration of Atomic Structure
The second paragraph serves as a recap and conclusion to the discussion on atomic structure, summarizing the key points and providing a clear overview. It reiterates the central role of protons in defining the type of atom and the balance between protons and electrons that results in a neutral atom. The paragraph also introduces the concept of ions, which are atoms that have gained or lost electrons. The speaker, John Perry, signs off by acknowledging the support of funding bodies and encourages viewers to engage with the content by subscribing to the YouTube channel and exploring additional resources like the Bond Breaker game, which offers an interactive way to learn about atomic interactions.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atoms
💡Subatomic Particles
💡Electron Cloud
💡Bohr Model
💡Nucleus
💡Protons
💡Neutrons
💡Electrons
💡Ions
💡Periodic Table
💡Chemical Reactions
Highlights
Atoms were initially thought to be uncuttable, as the word 'atom' means uncuttable.
John Dalton named atoms based on the belief they were fundamental, uncuttable particles.
Atoms can be split into subatomic particles, proving Dalton's theory of indivisibility wrong.
An atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons as its main subatomic particles.
Protons and neutrons might be composed of even smaller particles; there may be no end to smallness.
The image of a nitrogen atom was created from data collected during an actual scan.
The electron cloud represents the outer edges of the atom, with colors being artificial for visualization.
The Bohr model is a simplified representation of an atom, useful for introductory chemistry.
The nucleus is the core of the atom, containing protons and usually neutrons, and is enlarged in models for visibility.
The mass of an atom is primarily due to protons and neutrons, with the number of neutrons varying among isotopes.
Changing the number of protons in an atom fundamentally changes its chemical properties and identity.
The number of protons in an atom determines its place and identity in the periodic table.
Electrons are negatively charged and typically orbit the nucleus, though their true nature is more complex.
The number of electrons in an atom is usually equal to the number of protons, forming a neutral charge.
Ions are atoms that have gained or lost electrons, changing their chemical behavior.
The video provides a basic overview of atomic anatomy, supported by the National Science Foundation and the Casal Research Center.
Castle researchers have captured images of atoms and molecules, and developed an educational game called 'Bond Breaker'.
The 'Bond Breaker' game helps players understand the interactions between atoms and subatomic particles.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Inside Atoms: The Proton Numbers

What Is An Atom - Part 1 | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

GCSE Chemistry - Elements, Isotopes & Relative Atomic Mass #2

Basic Atomic Structure: A Look Inside the Atom

How to find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons from the periodic table
What is an Atom? - Structure of an Atom - Atom video for kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: