Lec-12 I Types of Bonds I Applied Chemistry I Chemical Engineering
TLDRThis lecture series on applied chemistry introduces key concepts such as quantum theory, coordination chemistry, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. It delves into the hybridization of orbitals, chemical kinetics, and chemical bonding, highlighting the formation of molecular orbitals and the principles of LCAO. The lecture distinguishes between types of chemical bonds including ionic, covalent, coordinate covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds, providing examples and explaining their roles in forming stable molecules and compounds.
Takeaways
- 📘 Applied chemistry subject code is 3130506.
- 🌟 The chapter on quantum theory introduces Heisenberg's uncertainty principle and wave mechanics.
- 🔄 The hybridization of orbitals and chemical kinetics theories are also covered in the chapter.
- 🤖 The Ammo theory explains how atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals, influencing their shape and energy levels.
- 🌐 LCAO (Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals) theory suggests that molecular orbitals are formed by combining atomic orbitals.
- 💡 The simplest example of molecular orbital formation is the H2 molecule, with its bonding (ψMO) and non-bonding (ψ*MO) orbitals.
- 📊 The Aufbau principle dictates the order in which molecular orbitals are filled with electrons.
- 🔗 Chemical bonds are electrostatic attractions between atoms, crucial for forming stable molecules and compounds.
- ⚛️ There are five main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, coordinate covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds.
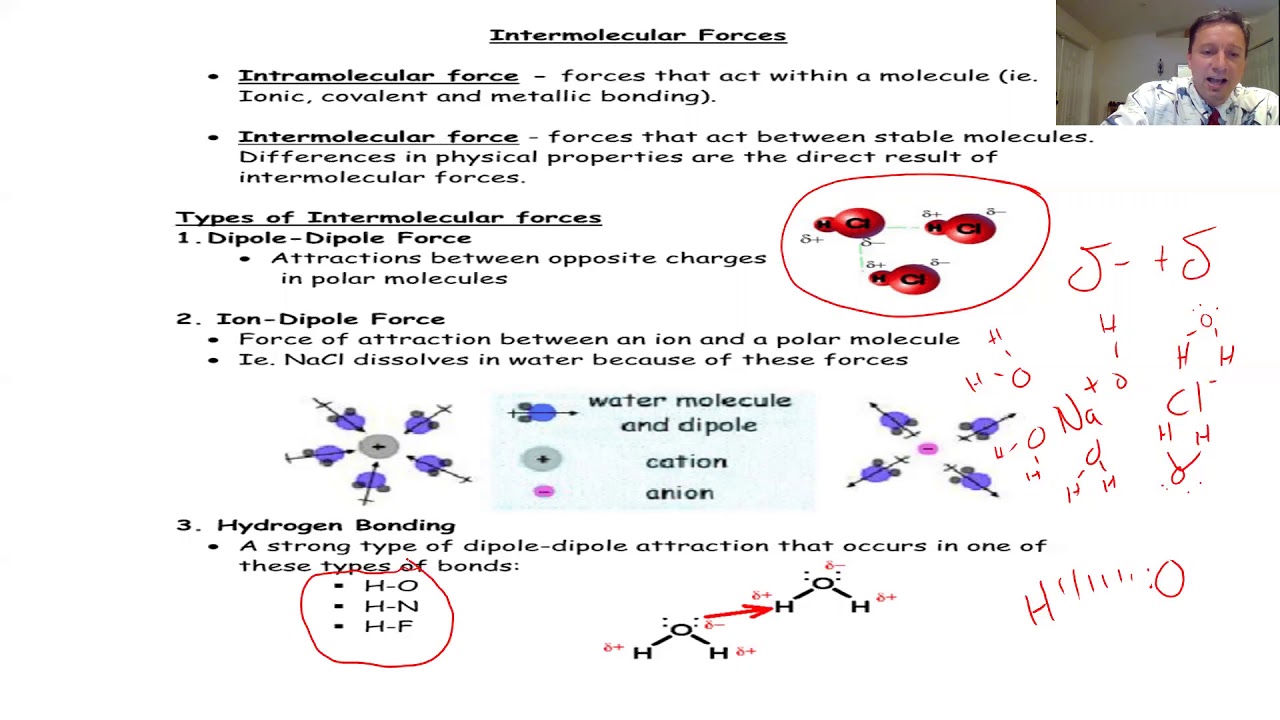
- 🔍 The script distinguishes between intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds, with examples provided for each type.
Q & A
What is the subject code for Applied Chemistry in the lecture series?
-The subject code for Applied Chemistry is 3130506.
What was the main topic discussed in the previous session of Applied Chemistry?
-The main topics discussed in the previous session were Introduction to Quantum Theory for Chemical Systems and Coordination Chemistry, including Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle and the wave mechanical concept.
What is the significance of Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle in the context of chemistry?
-Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle is significant in chemistry as it introduces the concept that we cannot simultaneously know the exact position and momentum of a particle, which has implications for understanding atomic and molecular behavior.
What are the two parts of the chapter on coordination chemistry discussed in the lecture?
-The two parts of the chapter on coordination chemistry discussed are the hybridization of orbitals and the theories involved in chemical kinetics and chemical bondings.
How does the MO Theory describe the formation of molecular orbitals?
-The MO Theory describes the formation of molecular orbitals as a result of atomic orbitals combining when atoms combine to form molecules, taking the shape of their atomic orbitals but having different energy levels and characteristics.
What is the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) theory?
-The Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) theory posits that molecular orbitals are formed by the linear combination of atomic orbitals, which can combine when they are collinear with each other.
How does the H2 molecule illustrate the concept of bonding and non-bonding (anti-bonding) orbitals?
-In the H2 molecule, the bonding orbital (sigma 1s) is formed by the addition of atomic orbitals (psi_a and psi_b), which lowers the energy and increases stability. The non-bonding (anti-bonding) orbital (sigma star 1s) is formed by the subtraction of atomic orbitals, which cannot form bonds and has higher energy.
What are the five types of chemical bonds mentioned in the lecture?
-The five types of chemical bonds mentioned are ionic or electrovalent bonds, covalent bonds, coordinate covalent bonds, metallic bonds, and hydrogen bonds.
How does an ionic bond differ from a covalent bond?
-An ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction between a cation and an anion (positive and negative charges), resulting in ionic compounds. A covalent bond involves the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms, leading to the formation of covalent compounds.
What is a coordinate covalent bond and how is it formed?
-A coordinate covalent bond is a type of covalent bond where both electrons in the shared pair come from one of the two atoms involved. It involves single-sided sharing, resulting in the formation of coordinate compounds or coordinate covalent compounds.
Can you explain the difference between intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds?
-Intermolecular hydrogen bonds form between different molecules, typically due to slightly positive and slightly negative charges. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds occur within the same molecule, involving different parts of the molecule. An example of intermolecular hydrogen bonding is between HF molecules, while intramolecular hydrogen bonding can be seen in a water (H2O) or ammonia (NH3) molecule.
Outlines
📘 Introduction to Quantum Theory and Chemical Bonding
This paragraph introduces the viewers to the video lecture series on applied chemistry, focusing on chapter four which delves into quantum theory for chemical systems, coordination chemistry, and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. It progresses to discuss the Ammonia theory and Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) theory, using the H2 molecule as an example to explain the formation of molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals. The explanation includes the concept of bonding, non-bonding, and anti-bonding orbitals, and how they contribute to the stability of a chemical system.
🌟 Understanding Bond Formation in H2 Molecule
This section continues the discussion on chemical bonding by zooming in on the H2 molecule. It explains how two hydrogen atoms, each contributing one s-orbital, form a molecule with two molecular orbitals: sigma 1s (bonding) and sigma star 1s (non-bonding). The paragraph elucidates the Aufbau principle in filling these orbitals and how the presence of two electrons in the bonding orbital leads to the formation of a stable H-H single bond. It also visually represents the concept using pink color boxes to depict 1s atomic orbitals and their electronic configuration.
🔗 Types of Chemical Bonds and Their Characteristics
The final paragraph of the script delves into the various types of chemical bonds that hold atoms together in a stable molecule. It defines a chemical bond as an electrostatic attraction and outlines five main types: ionic, covalent, coordinate covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds. Each bond type is briefly explained with examples, highlighting how they contribute to the formation of stable compounds. The ionic bond is described as the electrostatic attraction between a cation and an anion, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons. Coordinate covalent bonds are a special type of covalent bond where both electrons come from one atom. Metallic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal, and hydrogen bonds are electrostatic attractions between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom. The explanation is enriched with examples and a clear distinction between intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Applied Chemistry
💡Quantum Theory
💡Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
💡Wave Mechanics
💡Hybridization of Orbitals
💡Chemical Kinetics
💡Molecular Orbital Theory
💡Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO)
💡Bonding and Anti-Bonding Orbitals
💡Chemical Bonds
💡Ionic Bond
💡Covalent Bond
Highlights
Introduction to Quantum Theory for chemical systems
Exploration of Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
Wave mechanical concept introduction
Hybridization of orbitals in chemical systems
Theories involved in chemical kinetics and chemical bonding
Explanation of the Ammonia (AMO) theory
Formation of molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) theory
Simplest case of H2 molecule and its atomic orbitals representation
Formation of bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals
Electronic configuration and molecular orbital filling for H2 molecule
Types of chemical bonds: Ionic, Covalent, Coordinate covalent, Metallic, and Hydrogen bonds
Formation of ionic compounds through electrostatic attraction between cation and anion
Covalent bond formation through mutual sharing of electrons
Coordinate covalent bond with single-sided electron sharing
Metallic bond formation between metal and non-metal
Intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

[H2 Chemistry] 2023 Topic 2 Chemical Bonding 1

1.3 Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization | Organic Chemistry
AP Chemistry Unit 2 Review

Lec-14 I Hybridization I Applied Chemistry I Chemical Engineering

ATI TEAS 7 I Chemical Bonds I Chemistry I

Valence Bond Theory, Hybrid Orbitals, and Molecular Orbital Theory
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: