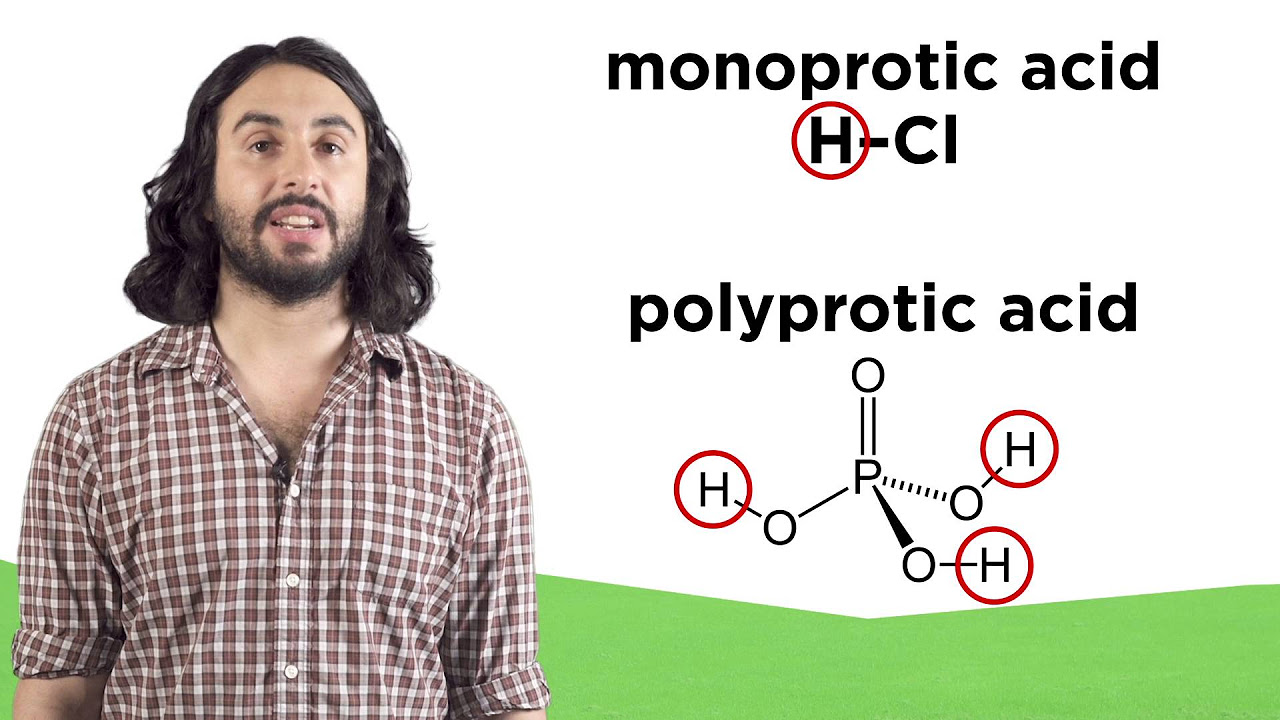
Ranking Acidity, Using pKa, and Drawing Arrows in Acid-Base Reactions
TLDRThe transcript captures a comprehensive study session focused on understanding the concepts of acids and bases in organic chemistry. The discussion delves into the factors affecting acidity, such as electronegativity, size, and resonance, and how these can be used to predict the order of decreasing acidity among various chemical species. The session also explores the use of pKa values as a tool for comparison and the importance of recognizing exceptions to general rules. The conversation further illustrates the process of acid-base reactions, emphasizing the role of electron movement and the formation of conjugate acids and bases. The transcript aims to demystify organic chemistry concepts, making them accessible and 'easy' by breaking down complex topics into understandable segments.
Takeaways
- 📚 The session is aimed at helping students understand organic chemistry, specifically acids and bases, and achieving good grades in the subject.
- 💡 Importance of practice problems is emphasized, encouraging students to download and try them out for better understanding of the concepts.
- 📈 The significance of PKA values in determining the acidity of compounds and how it can guide the study and comparison of different acids.
- 🔍 The discussion highlights the factors affecting acidity such as electronegativity, size, resonance, inductive effect, and hybridization, and their role in the study of organic chemistry.
- 🧪 The session addresses common fears and misconceptions about acids and bases from general chemistry, providing clarity and new perspectives.
- 📊 The use of PKA values as a study tool is discussed, with a reminder that they should not be solely relied upon as there might be exceptions.
- 🤔 The importance of understanding the underlying rules and concepts, rather than just memorizing them, is stressed for truly grasping the subject matter.
- 🌟 The session showcases how understanding the factors influencing acidity can help predict the behavior of compounds in reactions and their relative strengths.
- ⚖️ The process of determining the weakest acid or strongest base among given species is outlined, highlighting the need to consider charge, electronegativity, and other factors.
- 🔄 The concept of equilibrium in acid-base reactions is introduced, explaining how it favors the formation of the weaker acid or stronger base.
- 🎯 The session concludes with an exercise to rank hydrogens in order of increasing acidity, encouraging active participation and application of the learned concepts.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the study session mentioned in the transcript?
-The main topic of the study session is organic chemistry, specifically focusing on understanding acids and bases.
What was the student's score on the recent quiz?
-The student scored 10 out of 10 on the recent quiz.
What factors are used to determine the order of decreasing acidity in the examples provided?
-The factors used to determine the order of decreasing acidity are electronegativity and size (specifically, the size of the central atom in the given examples).
What is the significance of the pKa value in determining acidity?
-The pKa value is significant because the smaller the pKa value, the more acidic the substance is. This is because a lower pKa indicates a higher concentration of the acid in its dissociated form.
Why might one not always be able to depend on pKa values?
-One might not always be able to depend on pKa values because sometimes the necessary pKa information might not be provided, or the specific compound might not be listed in the pKa table.
What is the exception mentioned when discussing the acidity of sulfur and oxygen?
-The exception mentioned is that despite oxygen being more electronegative, sulfur is more acidic due to its larger size, which can make a difference in certain cases.
How does the presence of a double bond affect the acidity of a molecule?
-The presence of a double bond can increase the acidity of a molecule because it allows for resonance, which can stabilize the conjugate base, making the molecule more likely to donate a proton and thus more acidic.
What is the role of inductive effect in determining acidity?
-The inductive effect plays a role in determining acidity by considering how close electronegative atoms are to each other and how many there are. The closer these atoms are, the more acidic the compound tends to be due to the influence on electron distribution.
What is the general approach to identifying the acid and base in an acid-base reaction?
-The general approach is to identify the acid as the species that donates a proton (usually has a hydrogen atom that it can lose) and the base as the species that accepts a proton (usually has a lone pair of electrons and a negative charge).
How does the concept of equilibrium relate to the strength of acids in an acid-base reaction?
-Equilibrium favors the formation of the weaker acid. In an acid-base reaction, the product side is favored at equilibrium if the conjugate acid formed is weaker than the original acid, meaning it donates protons less readily.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Acid-Base Concepts
The paragraph introduces the topic of organic chemistry with a focus on acids and bases. It discusses the importance of understanding the rules and concepts to excel in the subject. The speaker shares their personal experience of acing a quiz on the topic, emphasizing that despite initial fears, the rules and examples make the subject much easier to grasp. The conversation then shifts to a more technical discussion about the ordering of acids by decreasing acidity, using the PKA values and understanding the factors that influence acidity levels, such as electronegativity and size.
🧪 Analyzing Acidic Strength through PKA and Atomic Properties
This paragraph delves deeper into the analysis of acidic strength by comparing different chemical groups. The discussion revolves around using PKA values as a reference but also highlights the limitations of relying solely on these values. The speaker introduces the concept of electronegativity and atomic size as key factors in determining acidity. The conversation includes a comparison of different functional groups, such as carboxylic acids, alcohols, and amines, and how their properties contribute to their relative acidity levels.
🔬 Understanding the Influence of Charges and Electronegativity
The focus of this paragraph is on the influence of charges and electronegativity on the acidity of compounds. The speaker explains the process of categorizing compounds based on their charge and then using electronegativity as a tiebreaker. The discussion includes the identification of the most acidic compounds and the reasoning behind their classification. The speaker also emphasizes the importance of considering resonance and inductive effects, as well as hybridization, in determining the acidity of a compound.
🧬 Application of Acid-Base Principles in Organic Chemistry
This paragraph discusses the application of acid-base principles in organic chemistry, particularly in the context of the ACS exam. The speaker guides through the process of identifying the weakest acid or the strongest base among given species. The conversation involves analyzing the electronegativity of atoms, the presence of resonance structures, and the impact of functional groups on the basicity or acidity of compounds. The speaker also explains how to use PKA values effectively when available and how to approach problems when such values are not provided.
📝 Breakdown of an Acid-Base Reaction and Equilibrium
The paragraph provides a detailed breakdown of an acid-base reaction, focusing on identifying the acid and base, and predicting the products and their favorability at equilibrium. The speaker explains the concept of conjugate acids and bases, and how to represent the movement of electrons during the reaction using curved arrows. The discussion includes the analysis of the strength of the conjugate acid and how it influences the position of equilibrium. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for success in organic chemistry.
🌟 Advanced Analysis of Acidity and Reaction Dynamics
In this paragraph, the speaker increases the complexity by ranking hydrogens in order of increasing acidity. The discussion involves a detailed analysis of different chemical environments and their relative acidities. The speaker encourages a deep understanding of the underlying principles, such as electronegativity and resonance, to correctly predict the order of acidity. The conversation is geared towards a deeper understanding of organic chemistry and the ability to apply these concepts to more complex problems.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Organic Chemistry
💡Acids and Bases
💡pKa
💡Electronegativity
💡Resonance
💡Inductive Effect
💡Conjugate Acid and Base
💡Acid-Base Reaction
💡Equilibrium
💡Curvature Arrows
Highlights
Introduction to the study of organic chemistry and its importance for achieving good grades.
Discussion on the experience of students with acids and bases, and how overcoming initial fears leads to understanding.
Explanation of the concept of decreasing acidity and how to rank substances from most to least acidic.
Importance of electronegativity in determining the acidity of substances and how it affects the ranking.
Role of size and volume in the acidity of substances, specifically how a larger size can increase acidity.
Use of PKA values in determining the acidity of substances and how it can be a reliable method.
Exception to the rule with sulfur being more acidic than oxygen due to its larger size.
Explanation of how to rank substances in decreasing order of acidity using both PKA values and electronegativity.
Discussion on the acidity of different functional groups like sulfide, alcohol, and amine.
Understanding the concept of inductive effect and its impact on the acidity of substances.
Explanation of how to approach ranking the acidity of charged and neutral species.
Use of electronegativity as a deciding factor in the acidity of substances when other factors are equal.
Discussion on the application of these concepts to real-world organic chemistry problems.
Explanation of the acid-base reaction, identification of acids and bases, and the formation of conjugate acid-base pairs.
Understanding of equilibrium in acid-base reactions and how to determine which side is favored.
Practical application of these concepts in ranking the acidity of different hydrogens in a molecule.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: