Work, Force & Energy | What Is Force? | Science For Kids | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
TLDRThis educational script introduces the concepts of work, force, and energy, emphasizing their relevance in everyday life. It differentiates between contact and non-contact forces, providing examples for each and explaining how force can set an object in motion or change its state. The script further explores the idea of work as the application of force leading to movement, detailing the calculation and measurement of work in joules. Finally, it highlights the importance of energy, necessary for performing work, and suggests that regular intake of energy through food is crucial for maintaining health and wisdom.
Takeaways
- 📚 The subject matter is work, force, and energy, and their relevance in daily life activities.
- 🏃♂️ Daily tasks like cleaning, working in a factory, or playing involve forces that can set objects in motion or change their state.
- 🔧 Force is the interaction causing an object to move, and it can be categorized into contact and non-contact forces.
- 🤜 Contact force occurs when objects touch each other, like pushing a box or friction when skating.
- 🔌 Non-contact force happens without physical touch, such as gravitational pull or magnetic attraction.
- ⚖️ Force is measured in Newtons and is differentiated based on its type and application.
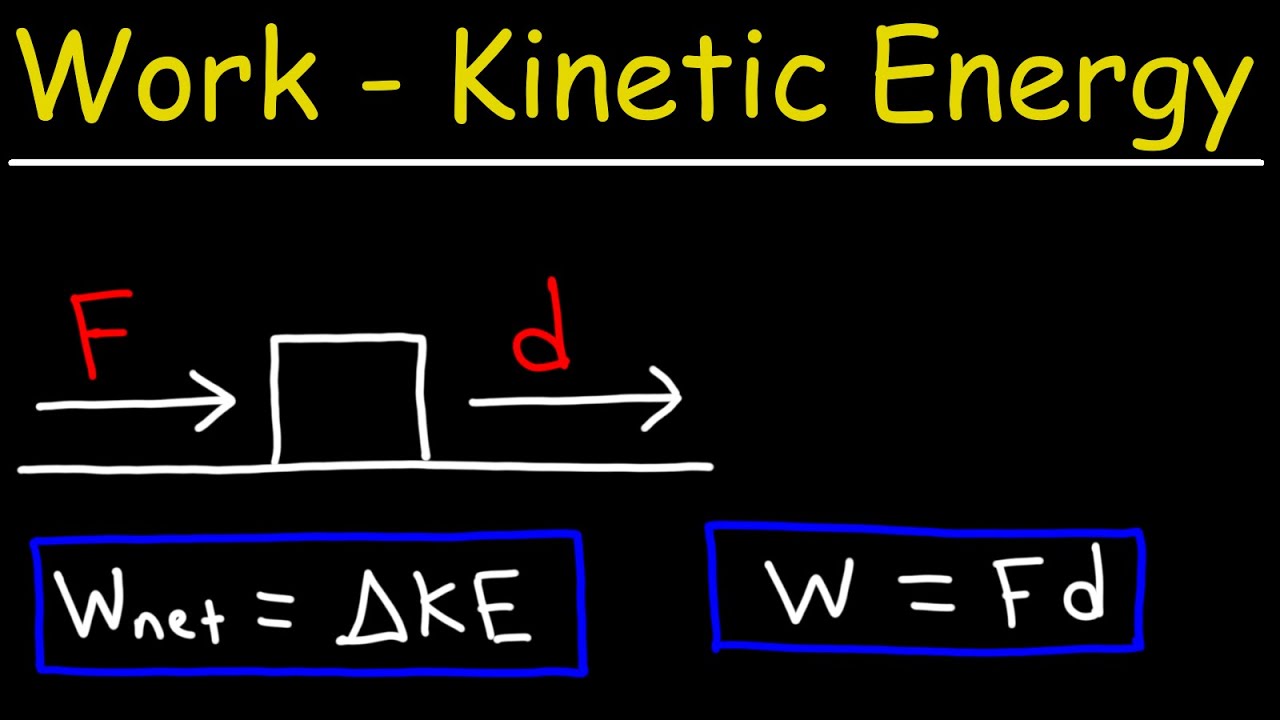
- 🔄 Work is done when a force causes an object to move, and it can be positive, negative, or zero based on the direction of force and displacement.
- 📊 Work is calculated using the formula work = force × distance, and it's measured in Joules.
- 💪 Energy is the ability to do work, which is essential for performing tasks and maintaining health.
- 🍏 Regular intake of energy from food like vegetables, fruits, and nuts is crucial for strength and health.
- 🌍 Gravitational force keeps the Earth in orbit around the Sun, and Earth's magnetic field influences compass needles.
- 📚 The episode aims to educate audiences on the academic and practical aspects of force, work, and energy.
Q & A
What is the main subject of the transcript?
-The main subject of the transcript is the concept of work, force, and energy, and how they relate to our daily lives.
What are the two categories of force mentioned in the transcript?
-The two categories of force mentioned are contact force and non-contact force.
Can you provide an example of a contact force?
-An example of a contact force is a person pushing a huge wooden box.
What are some types of non-contact forces?
-Some types of non-contact forces include gravitational, electrostatic, and magnetic forces.
How is the force measured quantitatively?
-Force is measured quantitatively in the unit Newton.
What is the standard unit of measurement for work?
-The standard unit of measurement for work is the joule.
What is the role of energy in performing work?
-Energy is the ability to perform work; without it, even the simplest tasks cannot be completed.
How can one obtain the required energy for daily tasks?
-One can obtain the required energy from food, such as green vegetables, fruits, and nuts.
What does the gravitational force do in the context mentioned?
-In the context mentioned, the gravitational force keeps the Earth orbiting around the Sun.
How is the Earth described in terms of magnetism in the transcript?
-The Earth is described as a strong bar magnet with a magnetic north and south, which is represented by the needle on a compass.
What is the significance of understanding the concepts of force, work, and energy?
-Understanding these concepts is significant as it helps us comprehend the physical interactions in our daily activities and the energy required to perform them.
Outlines
💡 Introduction to Workforce and Energy
This paragraph introduces the topic of workforce and energy, emphasizing the importance of understanding the concept of force and its role in our daily activities. It explains that force is the interaction that causes objects to move, change direction, shape, or return to rest. The paragraph categorizes force into contact and non-contact forces, providing examples for each and highlighting the significance of force in performing work. It also introduces the concept of work as the application of force leading to movement and differentiates between positive, negative, and zero work. The unit of force, the Newton, and the unit of work, the Joule, are mentioned, leading to the discussion of energy as the ability to perform work, which is essential for completing tasks and maintaining health.
🌿 Energy Sources and Gravitational Force
The second paragraph delves into the sources of energy for humans, such as food, and its role in providing the strength needed for daily activities. It also touches on the broader concept of energy in the universe, specifically mentioning gravitational force as the reason Earth orbits the Sun. Additionally, the paragraph discusses Earth's magnetic properties, with references to the magnetic north and south poles. The segment concludes with a reminder that learning about these forces and energy is vital for understanding the world around us, and the speaker, Dr. Bynox, signs off with a hint of humor.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Work
💡Force
💡Energy
💡Contact Force
💡Non-Contact Force
💡Friction
💡Newton
💡Joule
💡Gravitational Force
💡Magnetic Force
💡Electrostatic Force
Highlights
The subject of the episode is work, force, and energy, aiming to educate audiences on these academic topics.
Daily tasks such as cleaning, working in a factory, or playing in a field involve forces that can set objects in motion or change their state.
Force is the interaction that causes an object to move, change direction, shape, or return to rest.
Forces are categorized into contact force and non-contact force, depending on whether objects physically interact.
Contact forces occur when objects touch each other and include applied force, frictional force, and normal force.
Examples of contact force include pushing a wooden box, friction stopping a skater, and a table supporting a vase.
Non-contact forces involve gravitational, electrostatic, and magnetic forces that act without direct physical contact.
Non-contact force examples include an apple falling from a tree, a football falling to Earth, and an iron nail attracted to a magnet.
Force is measured in newtons, and understanding it quantitatively helps in studying the effects of different forces.
Work is done when a force causes an object to move, and it can be positive, negative, or zero based on the direction of force and displacement.
Work is calculated using the formula work equals force times distance, and it is measured in joules.
Energy is the ability to perform work, which is essential for completing tasks and is derived from food intake.
Gravitational force keeps the Earth orbiting the Sun, and Earth's magnetic field influences compass needles.
The episode concludes with a reminder that understanding these concepts is crucial for health and wisdom.
The importance of a regular supply of energy from food for maintaining the ability to perform daily tasks is emphasized.
The episode is designed to teach and expand the audience's knowledge on workforce and energy in an engaging manner.
The concept of force and its application in work is introduced with real-world examples to enhance understanding.
The episode provides a comprehensive overview of the principles of force, work, and energy, and their relevance to everyday life.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: