What Are Mixtures? | Chemistry Matters
TLDRIn this episode of 'Chemistry Matters,' the focus is on mixtures and their significance in everyday life and extreme situations, like Felix Baumgartner's record-breaking skydive. The discussion covers the distinction between pure substances and mixtures, the importance of understanding their chemical properties, and how mixtures can be separated. The video explores the concepts of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, using examples from food to alloys, and emphasizes the role of mixtures in technology and safety equipment.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Mixtures are combinations of two or more pure substances where each retains its individual chemical properties.
- 🚀 The importance of understanding mixtures and their properties was crucial for Felix Baumgartner's survival during his record-breaking skydive.
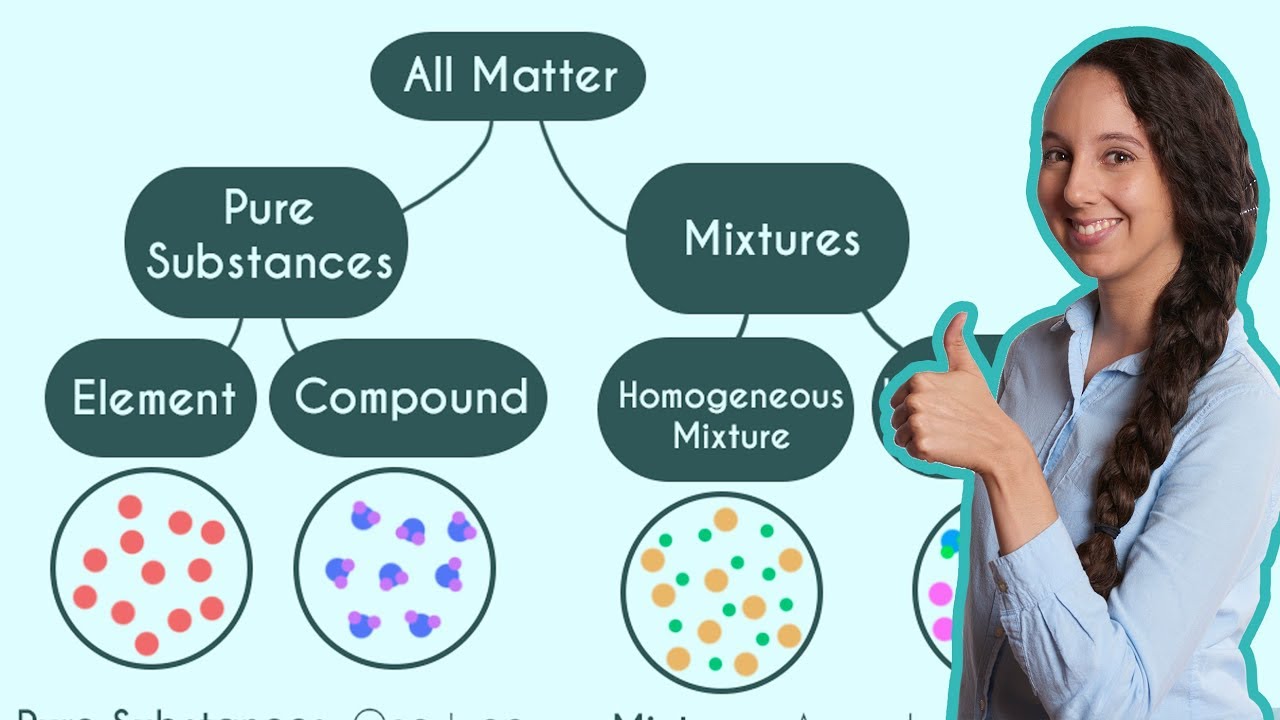
- 💨 Pure substances consist of a single chemical, either an element or a compound, whereas mixtures are made up of multiple pure substances.
- 🍦 Everyday items like ice cream are examples of heterogeneous mixtures, where the components do not fully blend together.
- 🥄 Homogeneous mixtures, or solutions, have uniform composition and chemical properties throughout, like salt dissolved in water.
- 🎨 Mixtures can be classified as either homogenous or heterogeneous based on the distribution of their components.
- 🥂 Gas-liquid solutions, such as carbonated beverages, involve gases like carbon dioxide dissolved under pressure.
- 🏺 Alloys are homogenous mixtures of metals, or a metal and a non-metal, designed to achieve specific properties like strength and durability.
- 🚗 Car manufacturers use alloys to create strong, lightweight vehicles for improved performance and safety.
- 💎 The karat system indicates the purity of gold and the presence of other metals to enhance its physical properties.
- 🔬 Understanding the structure and function of mixtures is essential for practical applications, from skydiving suits to the materials used in everyday products.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the 'Chemistry Matters' unit discussed in the transcript?
-The main topic of the 'Chemistry Matters' unit is mixtures and their characteristics, including how they can be separated.
How does the atmosphere of the Earth relate to the concept of mixtures?
-The atmosphere of the Earth is used as an example of a mixture, where nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide maintain their individual chemical properties despite being combined.
Why was understanding chemistry and mixtures crucial for Felix Baumgartner's survival during his 2012 jump?
-Felix Baumgartner needed a good understanding of chemistry and mixtures to ensure that the air in his tank had the right gas mixture for breathing, and that his suit was made of materials that could withstand extreme temperatures and pressures.
What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture?
-A pure substance is made up of one chemical, either an element alone or a group of elements chemically bonded together, while a mixture is a combination of two or more pure substances where each retains its individual chemical properties.
What are the two main types of mixtures and how do they differ?
-The two main types of mixtures are homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition and chemical properties throughout, also known as solutions. Heterogeneous mixtures consist of substances that are separated into physically distinct regions with different properties.
How does the structure of a mixture affect its function?
-The structure of a mixture, whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous, affects its function by determining its physical and chemical properties, which in turn influence how the mixture behaves and how it can be used in everyday life.
What is an alloy and how is it used in manufacturing?
-An alloy is a homogenous mixture of metals, or a mixture of a metal and a non-metal. Alloys are used in manufacturing to combine properties of various metals to achieve greater strength and durability, such as in car bodies and alloy wheels.
Why are mixtures of materials with the right intermolecular forces important in the design of a spacesuit?
-The right intermolecular forces are crucial for a spacesuit as they need to be strong enough to be heat-resistant and air-tight, yet flexible enough to allow movement. If the forces are too strong, the suit would be rigid; if they are too weak, the suit would not maintain its shape or integrity.
What is the significance of the karat system in relation to gold?
-The karat system indicates the purity of gold by referring to the amount of other metals mixed with it. Pure gold is too soft for many applications, so it is mixed with other metals to increase its hardness and durability without losing its luster and resistance to corrosion.
How does the composition of a gas-liquid solution like soda contribute to its properties?
-In a gas-liquid solution like soda, carbon dioxide is dissolved under pressure. When the soda is opened or shaken, the pressure is released, causing the carbon dioxide to form bubbles and create the characteristic fizzy texture.
What is the role of mixtures in the context of Felix Baumgartner's jump through the Earth's atmosphere?
-During Felix Baumgartner's jump, the mixture of gases in the Earth's atmosphere played a crucial role in providing the necessary conditions for his survival, such as oxygen for breathing. Additionally, the mixture of gases inside his suit was designed to maintain a comfortable and stable environment for him.
Outlines
🌍 Introduction to Mixtures and Their Importance
The video begins with the host welcoming viewers back to 'Chemistry Matters' and transitioning into the topic of mixtures. Using the example of a candy bowl representing Earth's atmosphere, the host explains how each component maintains its individual chemical properties, a concept crucial to Felix Baumgartner's survival during his record-breaking skydive. The segment emphasizes the necessity of understanding chemistry and mixtures, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of mixture characteristics and separation methods. The professor then delves into the definition of a mixture, contrasting it with pure substances, and engages students in a discussion about everyday examples of mixtures, such as ice cream and pencil lead. The importance of understanding the distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures is highlighted, with examples and student interactions that illustrate these concepts.
📚 Understanding Mixtures: Structure, Function, and Applications
This paragraph continues the educational segment on mixtures, focusing on the cross-cutting concept of 'Structure and Function.' It explains how the chemical structure of a mixture influences its behavior and practical applications. The example of Felix Baumgartner's skydive is revisited to illustrate the importance of material mixtures in creating an airtight, flexible, and heat-resistant suit. The discussion moves on to solutions, a term for homogeneous mixtures, and纠正 the common misconception that solutions are only liquids. The professor and students explore various types of solutions, including gas-gas, gas-liquid, solid-liquid, and solid-solid mixtures, with examples such as air, soda, salt water, and alloys. The practical applications of alloys in manufacturing, particularly in the automotive industry, are discussed, along with the reasons for mixing metals, such as enhancing strength and durability. The segment concludes with a look forward to the next video, which will cover the separation of materials.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mixtures
💡Chemical Properties
💡Pure Substances
💡Homogeneous Mixtures
💡Heterogeneous Mixtures
💡Structure and Function
💡Solutions
💡Alloys
💡Intermolecular Forces
💡Separation of Mixtures
Highlights
The concept of mixtures is introduced, emphasizing their importance in chemistry and everyday life.
The Earth's atmosphere is compared to a mixture, highlighting the individual chemical properties of its components.
Felix Baumgartner's record-breaking free-fall jump is discussed, illustrating the practical application of understanding mixtures.
The definition of a mixture is provided, explaining it as a combination of two or more pure substances retaining their chemical properties.
The distinction between pure substances and mixtures is clarified, with examples of elements and compounds.
The prevalence of mixtures in daily life is noted, with a challenge to identify common examples.
Ice cream is used as an example of a mixture, discussing its components and the process of making it.
Pencil lead is revealed to be a mixture of graphite and clay, correcting a common misconception.
Cymbals are explained as a mixture of copper and tin, demonstrating the concept of heterogeneous mixtures.
The classification of mixtures into homogeneous and heterogeneous is introduced, with explanations and examples.
Italian salad dressing is used to illustrate the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
The process of dissolving salt in water is described, showing the formation of a homogeneous mixture.
The structure and function concept is introduced, linking the chemical composition of mixtures to their properties and uses.
Felix Baumgartner's suit is discussed in terms of the intermolecular forces in its material mixture.
The concept of solutions is explored, expanding on the idea of homogeneous mixtures.
Examples of gas-gas solutions, gas-liquid solutions, and solid-liquid solutions are provided.
The definition and examples of alloys are given, explaining their importance in manufacturing and technology.
The use of alloys in car manufacturing and alloy wheels is discussed, highlighting their role in strength and weight reduction.
The concept of karat in gold is explained, relating to the mixture of gold with other metals for practical purposes.
The episode concludes with a teaser for the next video, which will cover the separation of materials.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: