Magnetic flux explained in 3 minutes
TLDRIn this educational video, Paul from Physics High explains the concept of magnetic flux, which is the measure of the magnetic field in a specific area. He uses a visual representation to demonstrate how the number of magnetic field lines passing through a loop changes with the loop's size and orientation. Paul also covers how to calculate magnetic flux mathematically, introducing the formula Φ = B * A * cos(θ), where Φ is the magnetic flux, B is the magnetic field strength, A is the area perpendicular to the field, and θ is the angle between the normal to the surface and the magnetic field. The unit for magnetic flux is the Weber (Wb), equated to Tesla meters squared.
Takeaways
- 🧲 Magnetic flux is a measure of the magnetic field in a specific area, represented by the symbol B.
- 🔍 The strength of the magnetic field can be visualized by the number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area.
- 🔄 The magnetic flux can be altered by changing the area or the orientation of the loop within the magnetic field.
- 📏 Reducing the area of the loop decreases the number of magnetic field lines passing through, thus reducing the flux.
- 🔄 Rotating the loop can also reduce the number of field lines passing through, reaching zero when perpendicular to the field.
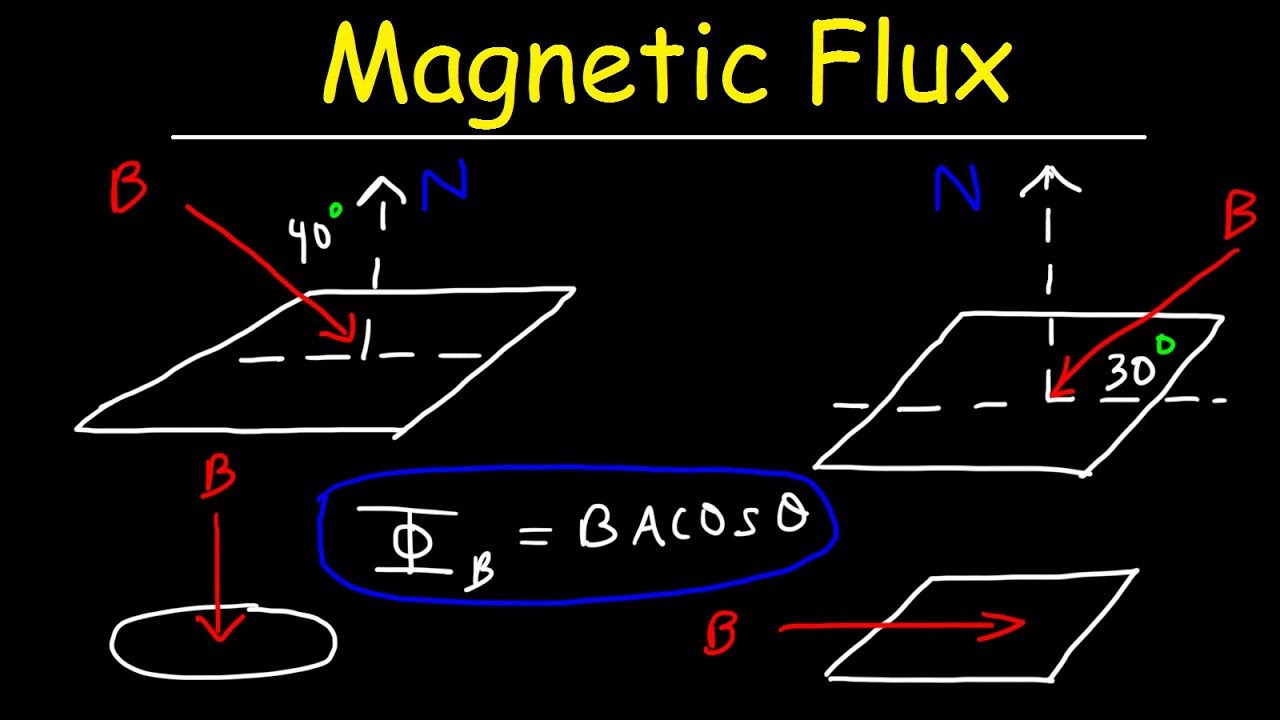
- 📚 The mathematical expression for magnetic flux, denoted by Φ, involves the product of the magnetic field strength, the area, and the cosine of the angle (θ) between the field and the area.
- 📐 The area considered in the calculation of magnetic flux is only the component that is parallel to the magnetic field.
- 📈 The cosine function determines the contribution of the area to the flux, being 1 when parallel (θ=0) and 0 when perpendicular (θ=90°).
- 🔢 The unit of magnetic flux is the Weber (Wb), which is equivalent to Tesla meters squared (Tm²).
- 👋 The script is part of a quick review series by Paul from Physics High, who encourages viewers to subscribe, share, and support his content.
- ☕️ The video includes a call to action for viewers to support the creator by buying him a coffee through a provided link.
Q & A
What is magnetic flux?
-Magnetic flux is the measurement of the magnetic field in a particular area, represented by the symbol B, and it quantifies the number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area.
How can you visualize magnetic flux?
-Magnetic flux can be visualized as magnetic field lines entering or leaving a surface area, with the number of lines indicating the strength of the magnetic field in that area.
What factors can change the magnetic flux through a loop?
-The magnetic flux can be changed by altering the area of the loop, the strength of the magnetic field, or the orientation of the loop relative to the magnetic field.
What happens to the magnetic flux when the loop is rotated?
-When the loop is rotated, the number of magnetic field lines passing through it can decrease, potentially reaching zero if the loop is perpendicular to the magnetic field lines.
What is the mathematical formula for calculating magnetic flux?
-The mathematical formula for magnetic flux is Φ = B * A * cos(θ), where Φ is the magnetic flux, B is the magnetic field strength, A is the area perpendicular to the magnetic field, and θ is the angle between the normal to the area and the direction of the magnetic field.
What is the unit of measurement for magnetic flux?
-The unit of measurement for magnetic flux is the Weber (Wb), which is equivalent to one Tesla meter squared.
How does the direction of the loop affect the magnetic flux?
-The direction of the loop, represented by the normal vector, affects the magnetic flux because only the component of the area that is parallel to the magnetic field contributes to the flux.
What is the relationship between the angle θ and the magnetic flux?
-The relationship between the angle θ and the magnetic flux is given by the cosine function in the formula Φ = B * A * cos(θ). When θ is 0 degrees, cos(θ) is 1, and the magnetic flux is at its maximum. When θ is 90 degrees, cos(θ) is 0, and the magnetic flux is zero.
What does it mean when the magnetic flux is zero?
-A magnetic flux of zero indicates that there are no magnetic field lines passing through the loop or surface area, which can occur when the loop is oriented perpendicular to the magnetic field lines.
Who is the presenter of the video and what is the purpose of the series?
-The presenter of the video is Paul from Physics High, and the purpose of the series is to provide quick reviews on various physics topics, including the calculation of magnetic flux.
Outlines
🧲 Understanding Magnetic Flux
This paragraph introduces the concept of magnetic flux as part of a quick review series. The speaker explains that magnetic flux is a measure of the magnetic field in a specific area, represented by the symbol B. They use a visual representation to illustrate how the number of magnetic field lines passing through a loop can indicate the flux. The speaker then discusses how changing the area or the orientation of the loop can affect the number of field lines passing through, and hence the magnetic flux. The paragraph concludes with a brief introduction to the mathematical representation of magnetic flux, involving the normal to the surface area and the direction of the magnetic field.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Magnetic Flux
💡Magnetic Field
💡Magnetic Field Lines
💡Area
💡Flux Density
💡Loop
💡Rotation
💡Normal
💡Cosine Theta
💡Weber
💡Tesla
Highlights
Magnetic flux is the measurement of the magnetic field in a particular area.
The symbol B is used to represent the magnetic field strength.
Magnetic flux can be visualized by the number of magnetic field lines passing through a loop.
Changing the area of the loop can alter the magnetic flux.
Rotation of the loop can reduce the number of magnetic field lines passing through, affecting the flux.
Magnetic flux can be zero when the loop is positioned such that no magnetic field lines pass through it.
The direction of the loop is important and is represented by a normal vector.
The mathematical formula for magnetic flux involves the magnetic field strength, area, and the cosine of the angle between them.
The Greek letter Phi (Φ) is used to denote magnetic flux.
Only the component of the area parallel to the magnetic field contributes to the magnetic flux.
The unit for magnetic flux is the Weber (Wb), equivalent to Tesla meters squared.
The video is part of a quick review series on physics concepts.
The speaker encourages viewers to subscribe and support the channel.
A coffee support link is provided in the video description for viewers to contribute.
The video features a visual representation of magnetic field lines and their interaction with a loop.
The impact of the loop's orientation on the calculation of magnetic flux is discussed.
The video concludes with a reminder to like, share, and subscribe for more physics content.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: