Laws of Reflection | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
TLDRThe video script delves into the Laws of Reflection, introducing the concept through the behavior of light rays in relation to mirrors. It defines the incident ray, the point of incidence, and the normal line, emphasizing the angle of incidence and its relationship to the angle of reflection. The script outlines two fundamental laws: the equality of the angle of incidence to the angle of reflection and the co-planar alignment of the incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray. This educational overview aims to clarify the principles governing light reflection, ensuring viewers understand that these angles are measured from the normal, not the mirror surface.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The topic discussed is the Laws of Reflection, which govern how light behaves when it strikes a reflective surface like a mirror.
- 📐 The incident ray is the initial ray of light that strikes the mirror, and it is essential to understanding the reflection process.
- 📍 The point of incidence is the exact point where the incident ray meets the mirror, serving as a reference for the reflection laws.
- 🔍 A normal is an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence, crucial for measuring angles of incidence and reflection.
- 🔢 The angle of incidence is the angle formed between the incident ray and the normal, and it is a key variable in the reflection laws.
- 🔄 When the incident ray hits the mirror, it bounces off, creating the reflected ray, which is the ray of light that leaves the mirror.
- 🔢 The angle of reflection is the angle formed between the reflected ray and the normal, and it mirrors the angle of incidence.
- 🔁 The first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, emphasizing the symmetrical nature of light reflection.
- 📐 The second law of reflection highlights that the incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane, ensuring consistency in the reflection process.
- 📏 Angles in the laws of reflection are measured from the normal, not from the mirror surface itself, which is an important distinction for accurate measurements.
- 📚 Remembering these laws is fundamental for understanding how light interacts with reflective surfaces in various scientific and everyday contexts.
Q & A
What is the topic of the video script?
-The topic of the video script is the Laws of Reflection.
What is the term for the ray of light that strikes a mirror?
-The ray of light that strikes a mirror is called the incident ray.
What is the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror known as?
-The point where the incident ray strikes the mirror is known as the point of incidence.
What is the line drawn perpendicular to the mirror through the point of incidence called?
-The line drawn perpendicular to the mirror through the point of incidence is called the normal.
What is the angle that the incident ray makes with the normal called?
-The angle that the incident ray makes with the normal is called the angle of incidence.
What happens when the incident ray strikes the mirror?
-When the incident ray strikes the mirror, it bounces off, creating the reflected ray.
What is the term for the ray that bounces off the mirror?
-The ray that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
What is the angle of reflection?
-The angle of reflection is the angle that the reflected ray makes with the normal.
What is the first law of reflection mentioned in the script?
-The first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
How are the angles of incidence and reflection measured in the script?
-The angles of incidence and reflection are measured from the normal, not from the mirror itself.
What is the relationship between the incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray according to the script?
-According to the script, the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Outlines
🔄 Laws of Reflection Introduction
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concept of the Laws of Reflection. It begins by describing the incident ray, which is a beam of light striking a mirror, and the point of incidence where it meets the mirror. The normal is defined as a line perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence. The angle of incidence is the angle the incident ray makes with the normal. The paragraph then explains the reflected ray, which is the light bouncing off the mirror, and the angle of reflection, which is the angle the reflected ray makes with the normal. The key takeaway is the first law of reflection, stating that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, emphasizing that these angles are measured from the normal, not the mirror surface. The paragraph concludes by noting that the incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Laws of Reflection
💡Incident Ray
💡Point of Incidence
💡Normal
💡Angle of Incidence
💡Reflected Ray
💡Angle of Reflection
💡Plane
💡Equality
💡Measurement
💡Light
Highlights
Topic introduction: Laws of Reflection
Definition of incident ray and its significance
Identification of the point of incidence on the mirror
Explanation of the normal line to the mirror
Introduction to the angle of incidence
Description of the reflected ray's behavior
Definition of the angle of reflection
Introduction of the first law of reflection
Equality of angle of incidence and reflection
Example of 30-degree angles for incidence and reflection
Emphasis on measuring angles from the normal
Clarification that angles are not measured from the mirror
Importance of the incident ray, normal, and reflected ray being in the same plane
Understanding the geometric relationship in reflection
Practical implications of the laws of reflection
Theoretical foundation for optical phenomena
Connection between the laws of reflection and real-world applications
Summary of the fundamental principles of reflection
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Law of Reflection - Geometric Optics - Physics
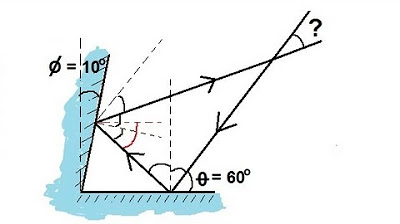
Physics 51 - Optics: Reflections (2 of 2) Inbound and Exit Ray
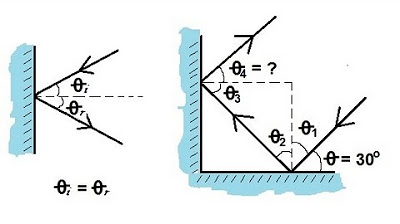
Physics 51 - Optics: Reflections (1 of 2) Introduction
Snell's Law & Index of Refraction - Wavelength, Frequency and Speed of Light

What are the Laws of Reflection of Light? | Physics | Don't Memorise

GCSE Physics - Reflection #62
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: