The Law Of Reflection. Measuring the angle of incidence and angle of reflection.
TLDRIn this educational episode, the presenter explores the law of reflection, demonstrating that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Using a light box, lens, and a plane mirror, they accurately measure angles with a paper protractor. The video also shows how curved mirrors, both concave and convex, can reflect light in various ways, creating interesting shapes. The content is designed to be informative and engaging, encouraging viewers to understand and observe the principles of light reflection.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- 💡 The presenter demonstrates the law using a light box, a lens, and a plane mirror.
- 🔍 A plastic piece with thin slits is used to narrow the light beam for more accurate angle measurements.
- 📏 A paper protractor is utilized to measure the angles of incidence and reflection.
- 📐 The angles are measured from an imaginary line called the normal, which is perpendicular to the mirror's surface.
- 🕰 The demonstration starts with the mirror perpendicular to the light source, showing 0 degrees for both angles.
- 📐 The presenter adjusts the angle of incidence and observes the corresponding angle of reflection, confirming the law of reflection.
- 📈 Different angles, from 10 to 80 degrees, are tested to demonstrate the consistency of the law of reflection.
- 🔮 Curved mirrors, both concave and convex, are also used to show how light can reflect in various interesting patterns.
- 📐 The importance of measuring angles from the normal is emphasized for accurate reflection law observations.
- 🎥 The video concludes with an encouragement to like, subscribe, and look forward to the next episode of science.
Q & A
What is the law of reflection demonstrated in the video?
-The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This principle is shown by how light rays bounce off a mirror surface.
What tools does the presenter use to demonstrate the law of reflection?
-The presenter uses a light box, a lens to adjust the beam of light, a plain mirror for reflection, a piece of plastic with thin slits to narrow the light beam, and a paper protractor to measure angles.
Why is the beam of light made narrower using the plastic with slits?
-The plastic with slits is used to make the beam of light narrower to ensure more accurate measurements of the angle of incidence and angle of reflection.
What is the normal in the context of the law of reflection?
-The normal is an imaginary line that is perpendicular (90 degrees) to the surface of the mirror. Angles of incidence and reflection are measured from this line.
How does the presenter initially align the mirror with the light source?
-The presenter initially aligns the mirror perpendicular or at 90 degrees to the incidence frame, so that the light hits the mirror and is reflected back along the normal, resulting in an angle of incidence and reflection of 0 degrees.
What happens when the presenter moves the light source to create a 10-degree angle of incidence?
-When the presenter moves the light source to create a 10-degree angle of incidence, the angle of reflection also becomes 10 degrees, demonstrating the law of reflection.
How does the presenter measure angles of incidence and reflection?
-The presenter measures angles of incidence and reflection using a paper protractor, aligning it with the light rays and the normal to the mirror surface.
What is the significance of the normal when measuring angles in the law of reflection?
-The normal is significant because it serves as the reference point from which the angles of incidence and reflection are measured.
Can the law of reflection be demonstrated with curved mirrors as well?
-Yes, the law of reflection can also be demonstrated with curved mirrors, which can produce interesting patterns of light reflection due to their shape.
What shapes can the presenter create using a curved mirror?
-The presenter can create shapes such as triangles and squares using a curved mirror, showcasing how light rays can bounce at right angles.
What happens when the presenter flips the curved mirror to use the convex side?
-When the presenter flips the curved mirror to use the convex side, the reflection pattern changes, demonstrating how the shape of the mirror affects the reflection of light.
Outlines
🔬 Demonstrating the Law of Reflection
This paragraph introduces an experiment to demonstrate the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The presenter uses a light box, a lens to adjust the light beam, and a plain mirror to reflect the light. A plastic piece with thin slits is used to narrow the light beam for more accurate angle measurements. A paper protractor is introduced to measure the angles, and the presenter shows how adjusting the mirror's position changes the angles of incidence and reflection, always maintaining equality as per the law.
📏 Measuring Angles and Exploring Curved Mirrors
The second paragraph continues the demonstration by measuring various angles of incidence and reflection, using a paper protractor, and observing that they remain equal. The presenter then transitions to using a curved mirror, explaining the difference between concave and convex sides and how they can reflect light in different ways, creating shapes like triangles and squares. The video concludes with an encouragement to like, subscribe, and look forward to the next episode, emphasizing the educational value of the content.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Law of Reflection
💡Angle of Incidence
💡Angle of Reflection
💡Light Box
💡Lens
💡Plane Mirror
💡Plastic Slit
💡Protractor
💡Normal
💡Curved Mirror
💡Concave Mirror
💡Convex Mirror
Highlights
Introduction to the law of reflection and its demonstration in the episode.
Explanation of how to measure the angle of incidence and angle of reflection.
Use of a light box connected to a power supply to create a beam of light.
Adjustable lens to modify the divergence or convergence of the light beam.
Utilization of a plain mirror for reflecting the light beam.
Narrowing the light beam with a plastic piece containing thin slits.
Importance of the normal line in measuring angles from the mirror's surface.
Demonstration of the law of reflection with the angle of incidence being equal to the angle of reflection.
Starting with a perpendicular mirror position to illustrate 0-degree angles.
Adjusting the light box to create different angles of incidence and reflection.
Use of a paper protractor for measuring angles.
Observation of the law of reflection at various angles up to 80 degrees.
Discussion of the limitations in measuring due to the print-out paper protractor and mirror flatness.
Introduction to curved mirrors and their ability to reflect light in interesting ways.
Experimentation with a concave mirror to create triangular and square shapes with light rays.
Flipping the curved mirror to use the convex side and its effect on light reflection.
Conclusion emphasizing the informative nature of the video on the law of reflection and angle measurement.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Law of Reflection - Geometric Optics - Physics

Specular Reflection
Laws of Reflection | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
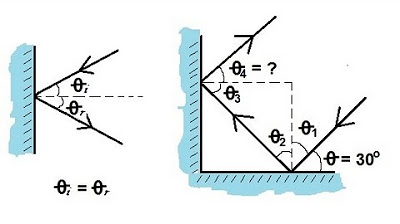
Physics 51 - Optics: Reflections (1 of 2) Introduction

Light Absorption, Reflection, and Transmission

Specular and diffuse reflection | Geometric optics | Physics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: