Potential Energy | Science for Kids
TLDRIn this educational video, viewers are introduced to the concept of potential energy, the hidden energy stored due to an object's position or condition. It explains two main types: gravitational potential energy, which is the energy an object possesses due to its height, and elastic potential energy, found in objects like stretched rubber bands. The video illustrates how potential energy can transform into kinetic energy, the energy of motion, using examples like a falling ball and a roller coaster. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of potential energy as the energy of possibilities.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video introduces the concept of potential energy, which is energy stored in an object due to its position or condition.
- 🌐 Gravitational potential energy is a type of potential energy that an object possesses because of its position relative to Earth's gravity.
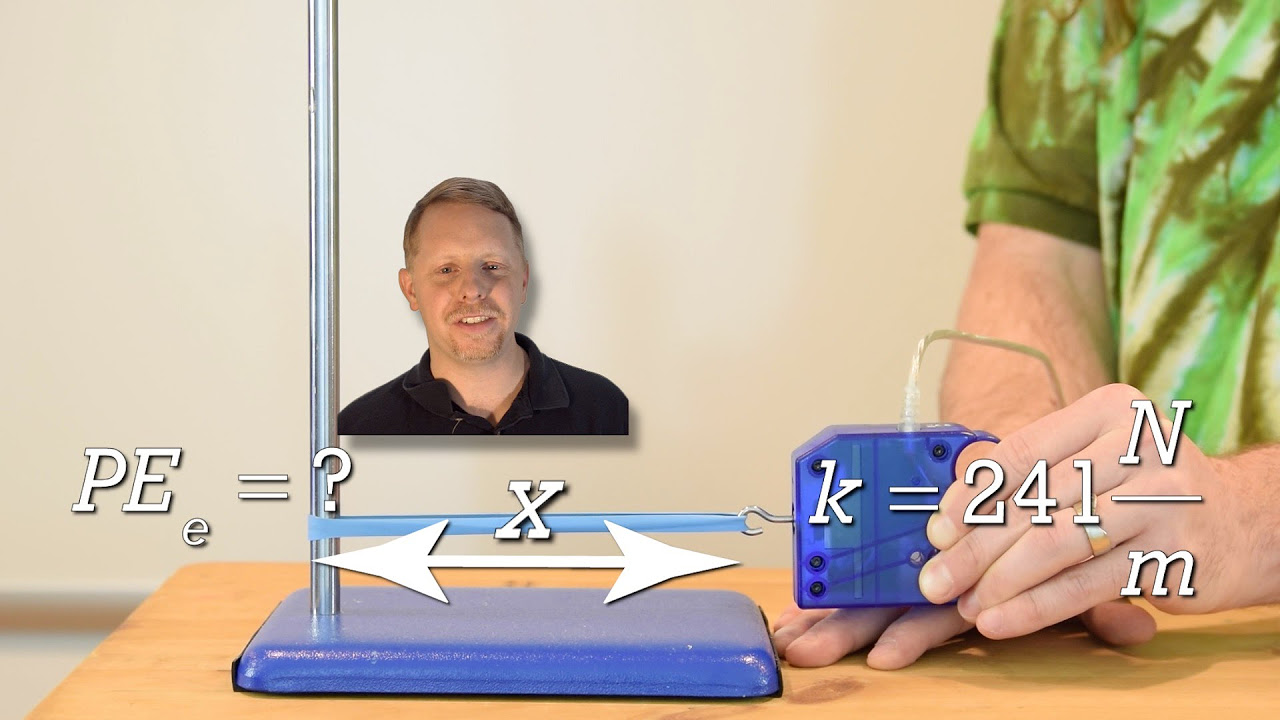
- 🏹 Elastic potential energy is another type of potential energy, which is stored in objects like stretched rubber bands or pulled bow strings.
- 📚 Potential energy is described as 'hidden' or 'stored' energy, indicating that it is not immediately apparent but can be released under the right conditions.
- 🔍 The script uses the example of a book on a shelf to illustrate gravitational potential energy, highlighting how the book has the potential to fall due to gravity.
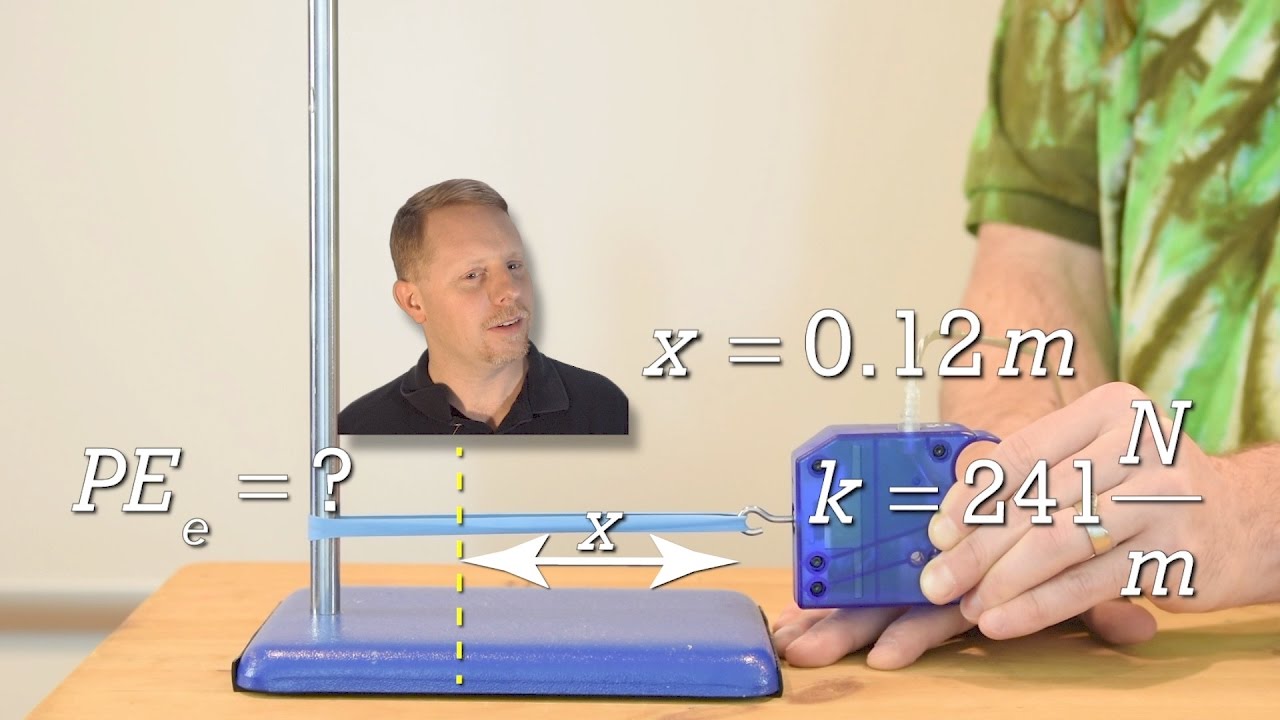
- 🎯 The concept of elastic potential energy is explained using a stretched rubber band, which has the potential to snap back to its original shape.
- 🏋️♂️ Lifting an object, like a ball, increases its gravitational potential energy, with the height of the lift directly affecting the amount of energy stored.
- 🏹 Pulling a bow string stores elastic potential energy, with the extent of the pull determining the amount of energy that can be released.
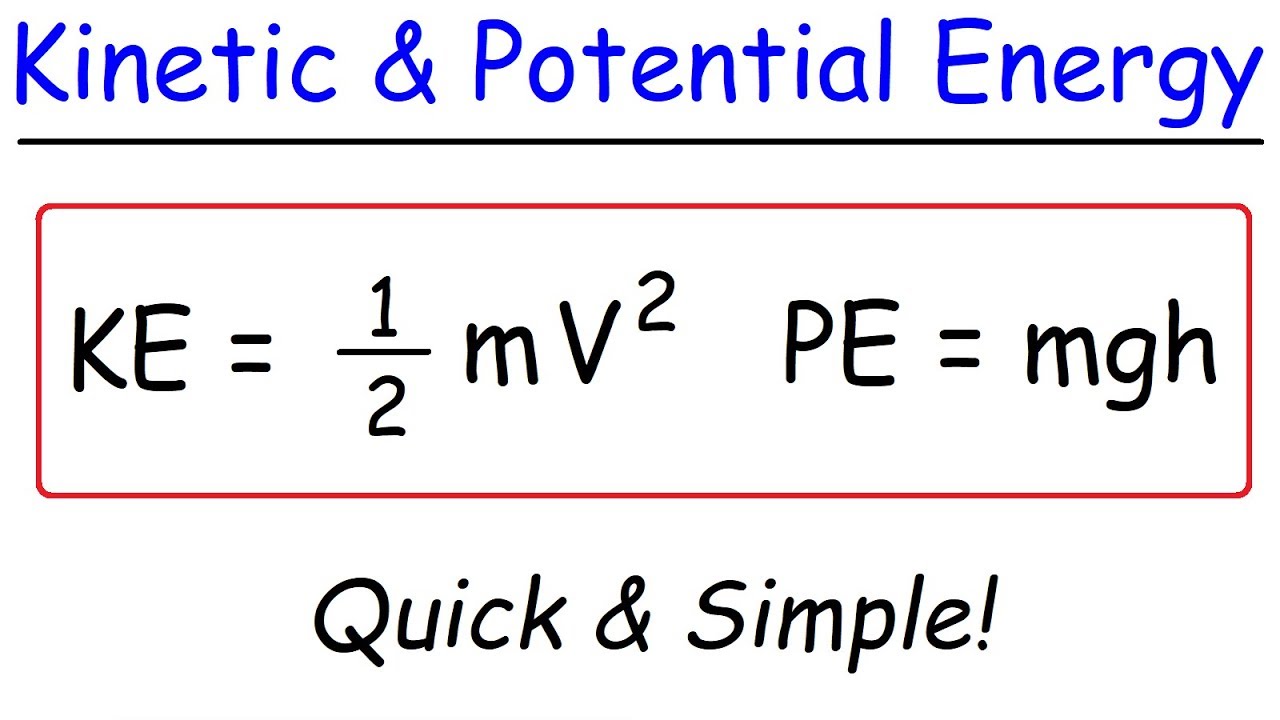
- 🏎️ Potential energy can be transformed into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. This is demonstrated by a ball falling or a roller coaster descending a hill.
- 🏁 The video concludes by emphasizing that potential energy represents the 'energy of possibilities,' suggesting its role in various physical phenomena and applications.
- 👍 The video encourages viewers to subscribe and like the content for more educational videos on similar topics.
Q & A
What is potential energy?
-Potential energy is the hidden or stored energy that an object has because of its position or condition, such as being raised to a height or being stretched.
Why does a ball sitting on a shelf have the potential to fall down?
-A ball sitting on a shelf has the potential to fall down due to gravitational potential energy, which is influenced by gravity pulling it towards the ground.
What is elastic potential energy?
-Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object, like a rubber band, when it is stretched or compressed and has the potential to return to its original shape.
How is potential energy related to the height of an object?
-The higher an object is lifted, the more gravitational potential energy it has, as it has further to fall due to the force of gravity.
What happens to the potential energy when you release a stretched rubber band?
-When a stretched rubber band is released, its elastic potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing it to snap back to its original shape.
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. An object in motion has kinetic energy, which is dependent on its mass and velocity.
How does a roller coaster demonstrate the transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy?
-A roller coaster at the top of a hill has a lot of gravitational potential energy. As it descends, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing the roller coaster to move faster.
What happens to the potential energy of a ball when it is dropped?
-When a ball is dropped, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing the ball to start moving and gain speed as it falls.
Can potential energy be converted into other forms of energy besides kinetic energy?
-While the script primarily discusses the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy, potential energy can also be converted into other forms of energy depending on the situation, such as thermal energy or sound energy.
Why is it important to understand potential energy in everyday life?
-Understanding potential energy is important as it helps explain various phenomena in everyday life, such as why objects fall, how springs work, and the principles behind various mechanical devices.
What is the conclusion of the video about potential energy?
-The conclusion of the video is that potential energy represents the energy of possibilities, emphasizing its role as a stored form of energy that can be converted into motion or other forms of energy.
Outlines
🚀 Introduction to Potential Energy
The video begins with an introduction to potential energy, a concept that explains why objects in certain positions or conditions have stored energy. The script uses the example of a ball on a shelf and a stretched rubber band to illustrate the concept. It sets the stage for a deeper exploration of potential energy types and their transformation into kinetic energy.
📚 Types of Potential Energy Explained
This section delves into the two main types of potential energy: gravitational and elastic. Gravitational potential energy is exemplified by a book that could fall due to gravity, while elastic potential energy is likened to a rubber band that can snap back to its original shape. The script provides everyday examples to help viewers understand how these energies manifest in real-life situations, such as lifting a ball to gain gravitational potential energy and pulling a bow string to store elastic potential energy.
🔄 Transformation of Potential to Kinetic Energy
The script explains the transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. It uses the analogy of a dropped ball and a roller coaster at the top of a hill to demonstrate how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as objects move. This section highlights the dynamic relationship between these two forms of energy and their importance in various physical phenomena.
🌟 Conclusion and Call to Action
The video concludes by emphasizing the significance of potential energy as the 'energy of possibilities.' The host encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content and to like the video to support the channel. This final paragraph serves as a summary and a prompt for viewers to engage with the content and the creators.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Potential Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Elastic Potential Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Position
💡Condition
💡Conversion
💡Stored Energy
💡Motion
💡Roller Coaster
💡Energy of Possibilities
Highlights
Introduction to the concept of potential energy in the video.
Potential energy is like hidden or stored energy due to an object's position or condition.
Gravitational potential energy explained with the example of a book that can fall due to gravity.
Elastic potential energy is described using the example of a stretched rubber band.
Everyday examples of potential energy include lifting a ball to gain gravitational potential energy.
The relationship between the height of a lifted object and its gravitational potential energy.
Elastic potential energy is stored when a bow string is pulled and its potential to shoot an arrow.
Transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy, the energy of motion.
Demonstration of kinetic energy through the example of a falling ball.
Roller coasters as an example of potential energy turning into kinetic energy for speed.
Potential energy described as the energy of possibilities.
Conclusion summarizing the importance of potential energy.
Encouragement for viewers to subscribe for more educational content.
Request for likes to support the channel.
Gratitude expressed to viewers for their support and interest in the videos.
Anticipation of future video content and a prompt for viewers to stay tuned.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: