What is Energy?
TLDRThis video explores the concept of energy, its omnipresence, and its forms. It discusses kinetic and potential energy, explaining how they power our world, from lighting homes to fueling life processes. The script also illustrates energy conversion, such as chemical energy in fuels and gravitational potential energy, highlighting the dynamic nature of energy in everyday life.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Energy is omnipresent and defined as the capacity to do work or cause change.
- 🔧 We can't see energy itself, but we observe its effects, such as movement and power generation.
- 🏡 Energy is crucial for lighting homes and cities and for powering vehicles.
- 🌱 All living organisms require energy for growth, reproduction, and life processes.
- 🌞 Plants harness sunlight to produce food, converting light energy into chemical energy.
- 🍃 Animals obtain energy by consuming plants and other animals, transferring energy through the food chain.
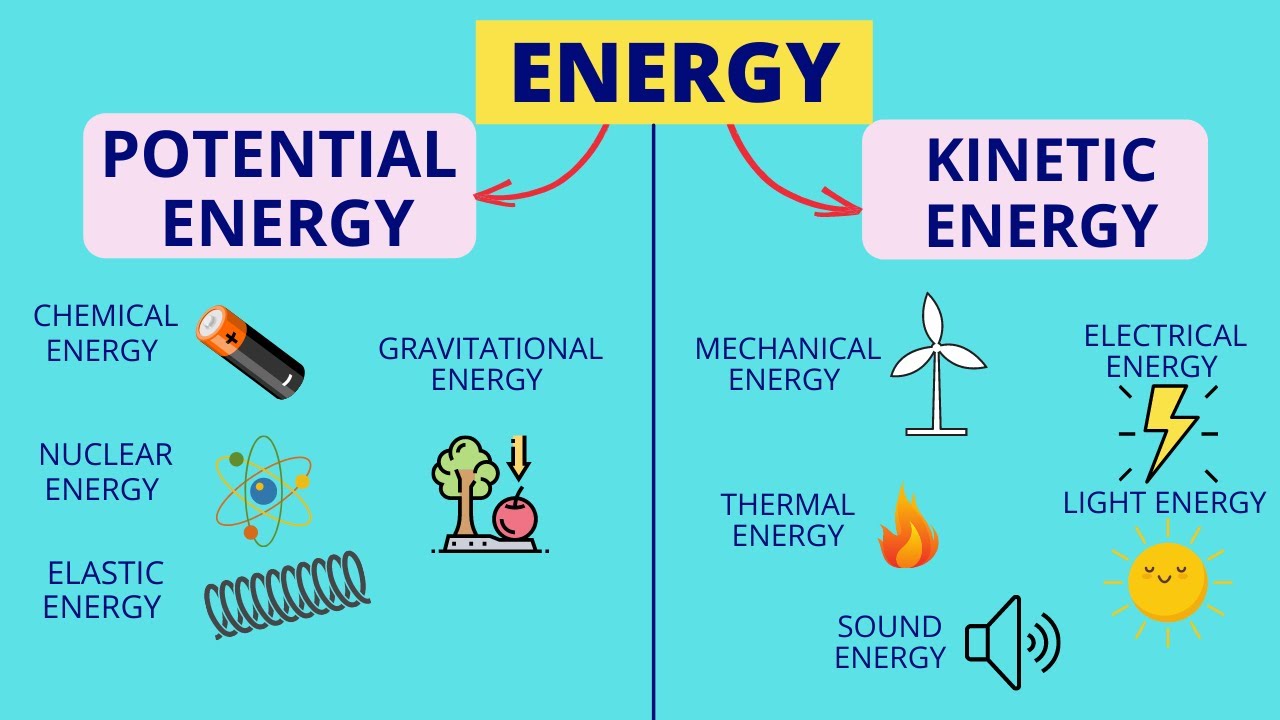
- 🏋️♂️ Kinetic energy is associated with movement and includes mechanical, sound, light, heat, and electrical energy.
- 🔋 Potential energy is stored energy due to an object's position, composition, or state and can be converted into kinetic energy.
- 🔥 Chemical energy, found in fuels like petroleum, gas, and wood, is a form of potential energy that converts to light and heat upon combustion.
- 🪨 Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its elevated position and is converted to kinetic energy as it falls.
- 🏹 Elastic potential energy is stored in objects like a drawn bow and is released as kinetic energy when the object is propelled.
Q & A
What is energy defined as by scientists?
-Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change.
How do we perceive energy if we cannot see it?
-We perceive energy through the effects it has, such as making things move, powering machines, lighting up homes and cities, and enabling life processes.
What are the primary uses of energy in our daily lives?
-Energy is used to power machines, light up homes and cities, power vehicles, and support the growth and reproduction of organisms.
How do plants utilize energy from the sun?
-Plants use light energy from the sun to make food in the form of sugar through a process called photosynthesis.
What are the two main forms of energy mentioned in the script?
-The two main forms of energy are kinetic energy and potential energy.
What is kinetic energy and what are some examples?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Examples include mechanical energy, sound, light, heat, and electrical energy.
What is potential energy and how can it be converted?
-Potential energy is the stored energy something has due to its position, composition, or state. It can be converted into various types of kinetic energy.
What is chemical energy and how is it related to fuels like petroleum, gas, and wood?
-Chemical energy is a form of potential energy contained in fuels. When these fuels are burned, the chemical energy is converted into light and heat.
What is gravitational potential energy and how is it converted into kinetic energy?
-Gravitational potential energy is the potential energy due to an object's position above the ground. As the object falls, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
What is elastic potential energy and how does it relate to a bow and arrow?
-Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its elastic deformation, like a drawn bowstring. When the string is released, the elastic potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, propelling the arrow forward.
What does the script suggest for further learning about different forms of energy and their conversions?
-The script suggests checking out related videos to learn more about different forms of energy and their conversions.
Outlines
🌟 Energy and Its Forms
This paragraph introduces the concept of energy, defining it as the capacity to do work or cause change. It highlights energy's omnipresence in our daily lives, from powering machines to lighting homes and cities, and its essential role in biological processes. The paragraph distinguishes between two primary forms of energy: kinetic, which includes movement, mechanical, sound, light, heat, and electrical energy, and potential, which is stored energy that can be converted into kinetic energy. Examples of potential energy include chemical energy in fuels and gravitational potential energy in objects positioned above the ground. The script invites viewers to explore related videos for a deeper understanding of these energy forms and their transformations.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Elastic Potential Energy
💡Light Energy
💡Heat Energy
💡Mechanical Energy
💡Photosynthesis
Highlights
Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change.
We cannot see energy, but we can observe its effects through movement, heat, light, and sound.
Energy powers machines, lights up homes and cities, and fuels vehicles.
All living organisms require energy for growth, reproduction, and life processes.
Plants convert sunlight into food through photosynthesis, storing it as chemical energy.
Animals obtain energy by consuming plants and other animals.
There are two main forms of energy: kinetic and potential energy.
Kinetic energy is associated with movement and includes mechanical, sound, light, heat, and electrical energy.
Potential energy is due to an object's position, composition, or state and can be converted into kinetic energy.
Fuels like petroleum, gas, and wood contain chemical potential energy.
Burning fuels converts chemical energy into light and heat.
Gravitational potential energy is due to an object's position above the ground.
A rock on a hill has gravitational potential energy that converts to kinetic energy as it rolls down.
Elastic potential energy is stored in objects like a drawn bowstring.
The more a string is drawn back, the greater the elastic potential energy.
When released, elastic potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, as seen with a flying arrow.
The video encourages viewers to explore related videos for more information on energy forms and conversions.
The video concludes with a reminder to subscribe for more content.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: