Polarization of light, linear and circular | Light waves | Physics | Khan Academy
TLDRThis script delves into the concept of light polarization, explaining how light waves, consisting of electric and magnetic fields, can be polarized in various orientations. It discusses the use of polarizers to filter light and the practical applications of polarization in reducing glare with sunglasses, enhancing visibility for fishermen, and enabling 3D movie experiences. The script also introduces circular polarization, highlighting its advantage in maintaining 3D image clarity even when head position changes.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Light waves are electromagnetic waves composed of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other.
- 🔄 Polarization refers to light where the electric field oscillates in a single direction, either vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
- 👀 Our eyes can only perceive the electric field component of light, which is why we see polarized light as having a specific orientation.
- 🌞 Most natural light sources like the sun emit unpolarized light, where the electric field can oscillate in any direction.
- 🕶 Polarized sunglasses work by using a polarizer to block certain orientations of light, reducing glare from reflective surfaces.
- 🎣 Fishermen benefit from polarized lenses as they reduce glare from water, allowing for clearer visibility of fish below the surface.
- 🎬 3D movies use polarized light to send different images to each eye, creating the perception of depth and a three-dimensional effect.
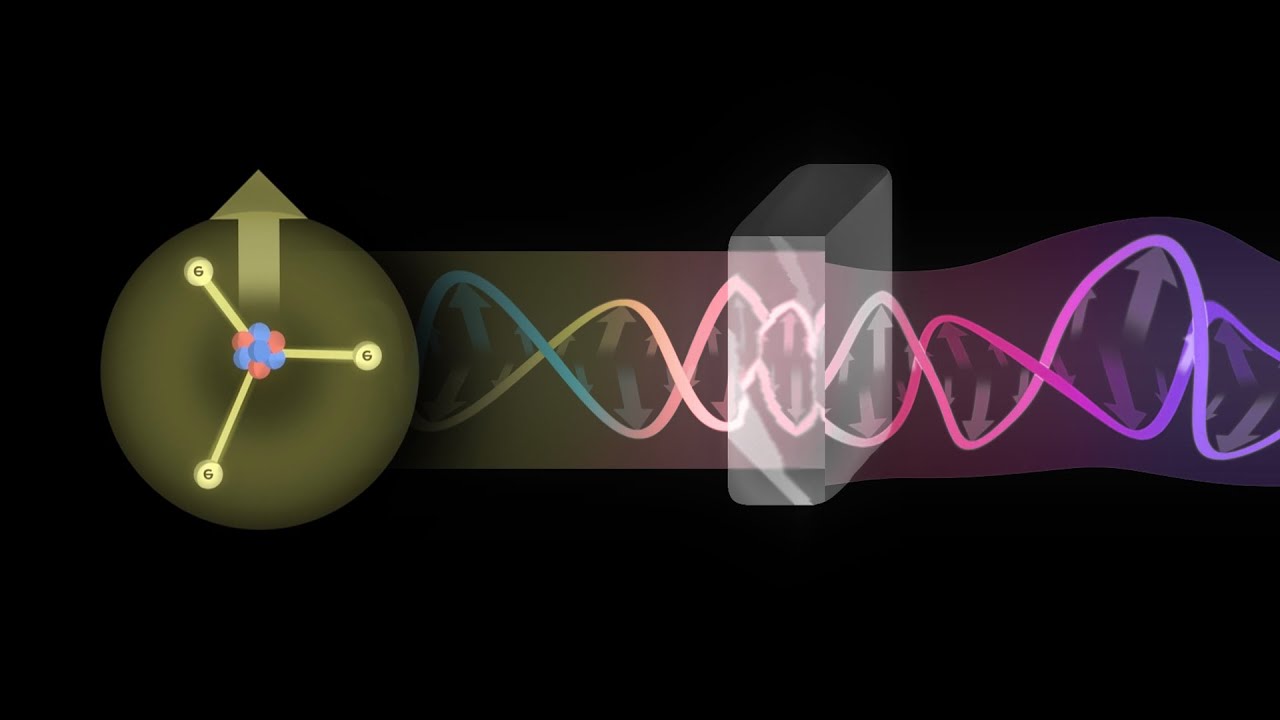
- 🔄 Linear polarization is characterized by the electric field oscillating in a single plane, while circular polarization involves the electric field rotating around the direction of propagation.
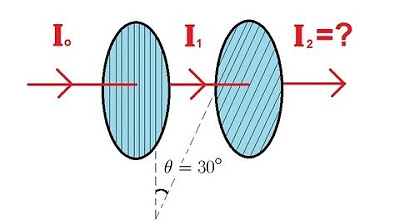
- 📚 A polarizer is a material that allows light of only one orientation to pass through, effectively polarizing the light.
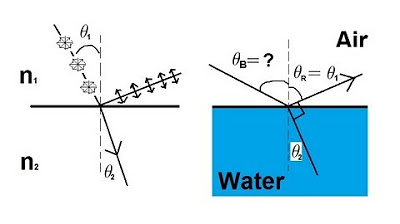
- 🔄 Reflected light often becomes partially polarized, with the polarization direction defined by the plane of the reflecting surface.
- 🎥 Circular polarization is used in some 3D movie systems to provide a better viewing experience even when the viewer's head is tilted.
Q & A
What are the primary components of light waves?
-Light waves are electromagnetic waves composed of electric fields and magnetic fields, which are perpendicular to each other.
Why do we often focus on the electric field when discussing polarization?
-Focusing on the electric field simplifies the explanation since the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular, and knowing the direction of the electric field is often sufficient.
What does it mean for light to be polarized?
-Polarized light means that the electric field of the light wave oscillates in only one direction, such as vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
How is light from common sources like the sun or a light bulb typically polarized?
-Light from sources like the sun or incandescent light bulbs is typically not polarized. It has electric fields oscillating in all directions.
What is a polarizer and how does it work?
-A polarizer is a material that only lets light through in one orientation. It can filter out all other orientations of light, allowing only light with a specific polarization direction to pass through.
How do polarized sunglasses reduce glare?
-Polarized sunglasses reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light, which is common in reflections off horizontal surfaces like water or roads, thereby reducing the intensity of the reflected light that reaches the eyes.
Why are polarized sunglasses particularly useful for activities like fishing?
-Polarized sunglasses are useful for fishing because they reduce glare from the water surface, allowing fishermen to see beneath the surface more clearly by blocking horizontally polarized reflected light.
How can polarization be used to create a 3D effect in movies?
-In 3D movies, two different images are projected with different polarizations (one for each eye). By wearing glasses with lenses polarized in corresponding directions, each eye receives only the intended image, creating a 3D effect.
What is circular polarization and how is it different from linear polarization?
-Circular polarization occurs when the angle of polarization rotates smoothly in a circular pattern as the light ray propagates. Linear polarization has the electric field oscillating in a single direction. Circular polarization involves a combination of two perpendicular linear polarizations with a phase shift.
Why might circular polarization be preferred in movie theaters over linear polarization?
-Circular polarization is preferred in movie theaters because it ensures that each eye receives the correct image even if the viewer tilts their head. This reduces the risk of the image becoming blurry due to head movement.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Light Polarization
This paragraph introduces the concept of light polarization, explaining that light waves are electromagnetic waves consisting of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicularly to each other. It clarifies that polarization refers to light where the electric field oscillates in a single direction, which can be vertical, horizontal, or diagonal. The paragraph contrasts polarized light with natural light from sources like the sun or incandescent bulbs, which is typically not polarized, as it has electric fields in all directions. It also introduces the use of a polarizer to achieve polarized light in experiments or applications like polarized sunglasses to reduce glare.
🕶️ Polarization in Sunglasses and its Applications
This paragraph delves into the practical applications of light polarization, particularly in sunglasses. It explains how reflected light, such as from water or other surfaces, becomes partially polarized, with the electric field predominantly in the plane of the reflecting surface. The paragraph describes how polarized sunglasses can block this glare by only allowing light with a vertical orientation to pass through, enhancing visual comfort and clarity. It also touches on the use of polarization in fishing to see through water and in 3D movie theaters to deliver separate images to each eye for a three-dimensional effect.
🔄 Exploring Circular Polarization
The final paragraph explores the concept of circular polarization, which occurs when two perpendicular light waves with a phase difference of 90 degrees are combined. It demonstrates how the resulting light wave's electric field rotates, creating circular polarization. This type of polarization is useful in situations where linear polarization might be affected by orientation changes, such as tilting one's head during a 3D movie. Circular polarization ensures a consistent 3D viewing experience regardless of head position, making it a valuable technology in modern entertainment and other applications.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Polarization
💡Light Waves
💡Electric Field
💡Magnetic Field
💡Polarizer
💡Glare
💡Incandescent Light Bulb
💡3D Movies
💡Circular Polarization
💡Reflection
💡Phase
Highlights
Light waves are electromagnetic waves composed of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other.
Polarization is the phenomenon where the electric field of light oscillates in a single direction, such as vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
Unpolarized light, such as sunlight or light from an incandescent bulb, has electric fields oscillating in all directions.
A polarizer is a material that allows light through in only one orientation, useful for creating polarized light.
Polarized sunglasses reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light, which is common in reflected light from surfaces like water.
Fishermen benefit from polarized sunglasses to see through water by reducing glare from the sun.
3D movie technology uses polarized light to send different images to each eye, creating a three-dimensional effect.
Linear polarization is characterized by the electric field oscillating in a single, straight line direction.
Circular polarization occurs when two perpendicular light waves with a phase difference of 90 degrees combine, resulting in a rotating electric field.
Circular polarized glasses are used in 3D movies to allow for head movement without image blurriness.
Understanding polarization helps in the practical application of reducing glare in various scenarios, such as driving or outdoor activities.
Polarization can be fully or partially achieved, with complete polarization being rare in natural light sources.
The orientation of polarization is defined by the plane of the reflecting surface, influencing the direction of the electric field.
Polarization can be manipulated and observed through the use of polarizing filters, which have practical applications in imaging and vision.
The concept of polarization is fundamental in the study of optics and has implications in various scientific and technological fields.
Combining two light waves with different polarizations can result in various polarization states, including diagonal and circular polarization.
The polarization state of light can be visualized and understood through the use of diagrams and the Pythagorean theorem.
Polarization plays a crucial role in the functionality of liquid crystal displays and other optical devices.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: