Cómo hacer CARBONATO DE SODIO a partir de BICARBONATO DE SODIO
TLDRThe video script delves into the chemistry and applications of sodium carbonate, a common inorganic salt with the chemical formula Na2CO3. It covers its use in everyday life, such as increasing pH levels in pool water and as a cleaning agent, and its historical role in soap-making. The script also explains the process of converting sodium bicarbonate to sodium carbonate through heating and the importance of stoichiometry in calculating reactants and yields. It concludes with a safety reminder about the proper use of gloves and goggles in the lab, emphasizing the need for knowledge and caution when handling chemicals.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The script discusses the chemical properties and uses of sodium carbonate, including its role as a basic salt that can neutralize acidity in various applications.
- 📚 The chemical formula of sodium carbonate is Na2CO3, highlighting the need for two sodium ions (Na+) to balance the charge of the carbonate ion (CO3^2-).
- 🏊♂️ Sodium carbonate is commonly used as a pH increaser in swimming pool water to prevent the dissolution of pool tiles.
- 🧼 It is also used as a detergent due to its strong base properties, effectively cleaning greases through a chemical process that can be utilized in soap making.
- 🍞 In cooking, sodium carbonate helps regulate acidity and stabilize the pH of certain products, such as ramen and pasta doughs, and is listed as additive E501.
- 🔍 The script describes a process of making sodium carbonate from sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) by heating it to decompose and form sodium carbonate, CO2, and water.
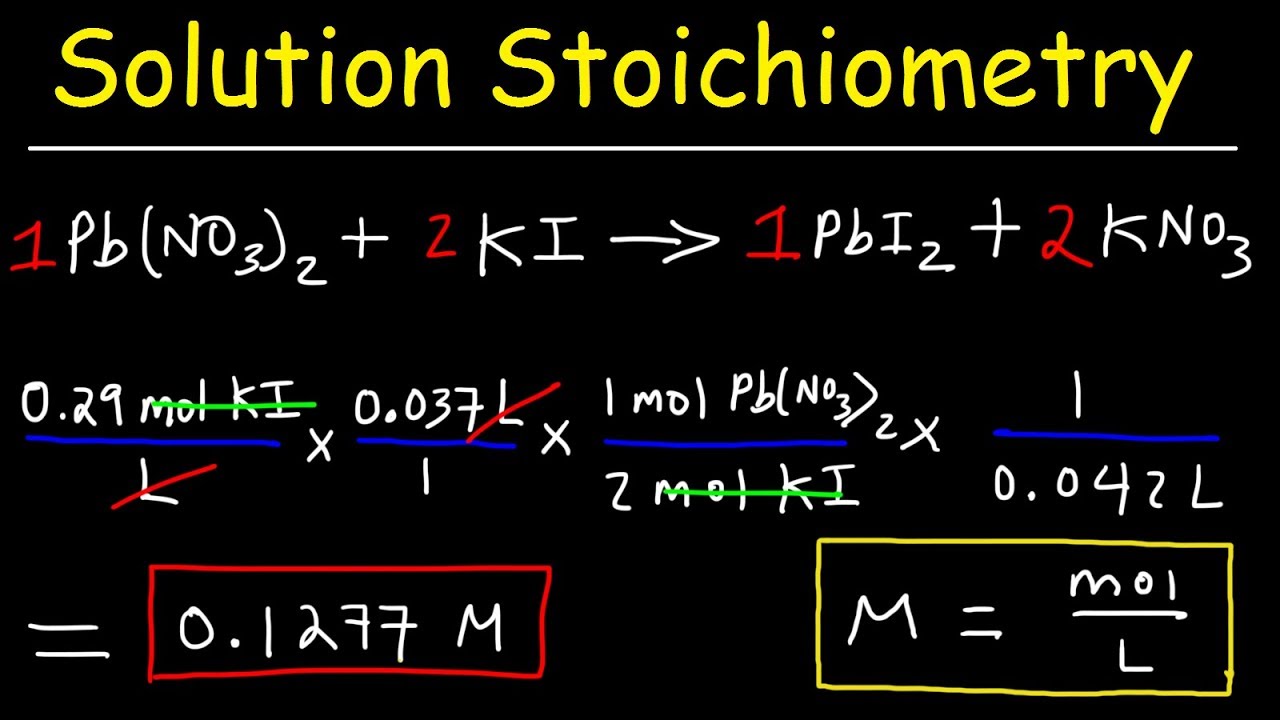
- 🔬 The importance of accurate measurement in chemistry is emphasized, including the weighing of reactants and the calculation of moles to predict product yields.
- 🧊 A recrystallization technique is introduced for purifying compounds, which involves dissolving the compound in hot solvent and allowing it to cool and crystallize, leaving impurities in solution.
- 🌡️ The solubility of sodium carbonate in water is temperature-dependent, with the script noting an unusual decrease in solubility as temperature increases from 35°C to 100°C.
- ⏱️ The script provides a detailed account of the time and process involved in the reaction and recrystallization of sodium carbonate, including the challenges of ensuring complete reaction and effective filtration.
- 👀 Safety precautions in the laboratory are discussed, emphasizing the importance of understanding the risks associated with chemicals and the appropriate use of protective equipment like gloves and safety glasses.
Q & A
What is sodium carbonate and what is its chemical formula?
-Sodium carbonate is the sodium salt of carbonic acid. Its chemical formula is Na2CO3.
Why does sodium carbonate have the chemical formula Na2CO3?
-Sodium carbonate has the chemical formula Na2CO3 because the carbonate ion (CO3) has a 2- charge, and each sodium ion (Na) has a 1+ charge. Two sodium ions are needed to balance the charge of one carbonate ion.
What are some common uses of sodium carbonate in everyday life?
-Sodium carbonate is commonly used as a pH increaser for pool water, as a detergent to clean grease, and in the manufacturing of glass to lower the melting point of silica.
How does sodium carbonate help in cleaning and making soap?
-Sodium carbonate is a strong base and effective in cleaning grease. It is used in soap making, sometimes with caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) or potash (potassium hydroxide), which reacts with fats to produce soap.
What role does sodium carbonate play in the manufacturing of glass?
-In glass manufacturing, sodium carbonate is used to lower the melting point of silica, making the glass easier to work with.
How can sodium carbonate be obtained from sodium bicarbonate?
-Sodium carbonate can be obtained by heating sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), which decomposes to release carbon dioxide and water, leaving behind sodium carbonate.
Why is sodium carbonate considered a basic compound?
-Sodium carbonate is considered a basic compound because it can neutralize acids, thus increasing the pH of solutions.
How can the purity of sodium carbonate be increased through recrystallization?
-Purity of sodium carbonate can be increased through recrystallization by dissolving the impure product in a hot solvent and then letting it cool so that pure crystals form while impurities remain dissolved.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling sodium carbonate?
-When handling sodium carbonate, it's important to wear gloves and goggles, as it is a strong base and can be irritating to the skin and eyes. It should be handled with care to avoid ingestion and inhalation.
What is the difference between sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate?
-Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is a stronger base than sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), which is also known as baking soda. Sodium bicarbonate is used for baking and as a leavening agent, while sodium carbonate is used for more aggressive cleaning and pH adjustment.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate, known as soda ash or washing soda, is a sodium salt of carbonic acid. Its chemical formula is Na2CO3, and it's a white solid commonly used to increase the pH of swimming pool water. It also acts as a detergent and can be used to make soap. Historically, it was derived from wood ash. Sodium carbonate is utilized in glass making to lower the melting point of silica and has culinary applications to regulate acidity.
⚗️ Preparing Sodium Carbonate from Baking Soda
This section explains the process of converting sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) into sodium carbonate by heating. Sodium bicarbonate decomposes into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water when heated above 100 degrees Celsius. The importance of accurate measurements and safe handling of chemicals is emphasized, including weighing reactants and ensuring complete decomposition by heating.
🧪 Crystallization and Purification
After heating, the resulting sodium carbonate is purified through recrystallization. This involves dissolving the product in hot water and then allowing it to cool, causing the pure compound to crystallize out of the solution. The procedure includes filtering to remove impurities and ensuring the purity of the final product.
🔍 Filtering and Drying the Product
The filtration process is detailed, including the use of hot filtration to remove insoluble impurities. Safety precautions are highlighted, such as avoiding the use of broken glassware. The sodium carbonate is then dried, with discussions on its hygroscopic nature and techniques to ensure thorough drying without decomposing the product.
🧤 Safety Precautions in Handling Chemicals
The final section discusses the safety measures for handling sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate. It emphasizes the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and safety glasses, understanding the properties and hazards of chemicals, and proper laboratory practices to prevent accidents.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Sodium carbonate
💡Chemical formula
💡pH adjuster
💡Detergent
💡Soap making
💡Sodium bicarbonate
💡Decomposition reaction
💡Recrystallization
💡Stoichiometry
💡Yield
💡Safety precautions
Highlights
Sodium carbonate is a salt of sodium derived from carbonic acid, with the chemical formula Na2CO3.
Sodium carbonate is a white solid, commonly used in everyday life as a pH increaser for pool water.
It acts as a basic salt capable of neutralizing acidity in water, preventing the dissolution of pool tiles.
Sodium carbonate is also used as a detergent due to its strong base properties, effectively cleaning greases.
The chemical process by which bases clean greases can be utilized in soap-making with lye and animal fat.
Historically, wood ash containing soluble carbonates was used to make soap before the availability of potassium hydroxide.
Wood ash reacts with acid to produce carbon dioxide, mainly from insoluble calcium carbonate and soluble sodium and potassium carbonates.
Sodium carbonate is used in glass manufacturing to lower the melting point of silica, making glass easier to work with.
In cooking, it is used to regulate acidity and stabilize the pH of certain products, such as ramen and pasta dough.
Sodium carbonate affects gluten, improving the quality of homemade bread and certain types of pasta.
Sodium bicarbonate, also known as sodium hydrogen carbonate, is used in cooking and baking for its leavening properties.
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acidic ingredients to produce carbon dioxide, creating the sponginess in cakes.
By heating sodium bicarbonate, it decomposes to form sodium carbonate, a simple reaction used to illustrate chemical processes.
The video explains the mathematical calculations behind chemical reactions, including molar measurements and yields.
Sodium carbonate's hygroscopic nature is tested by leaving it exposed to air to check for weight changes.
The recrystallization process is demonstrated to purify sodium carbonate by dissolving it in hot water and allowing it to cool and crystallize.
The solubility of sodium carbonate in water decreases with temperature, contrary to the usual trend for salts.
Safety precautions are emphasized, highlighting the importance of understanding the properties of compounds before handling them.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: