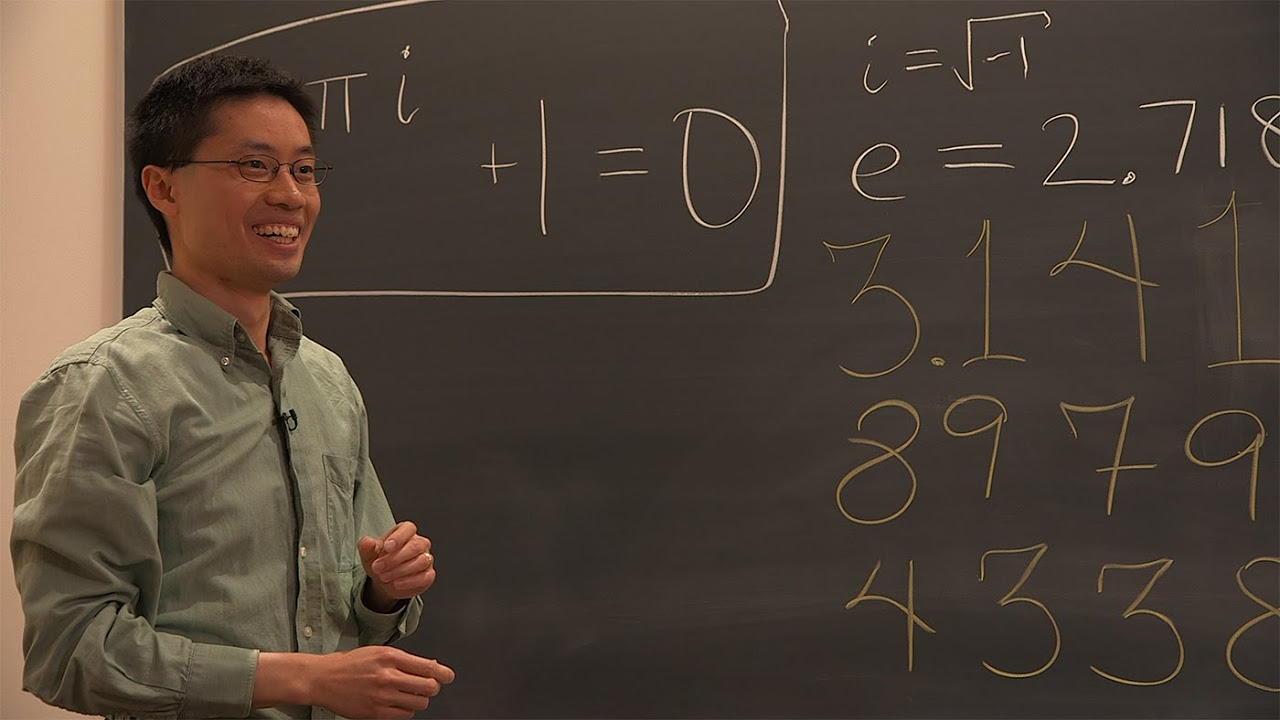Number Tier List
TLDRThis script humorously ranks numbers from best to worst, starting with the iconic '1' for its simplicity and victory, moving through the significance of '2' as the first even prime number, and exploring cultural and religious importance of '3' and '4'. It touches on superstitions around '13' and '666', praises '7' for its lucky connotations, and acknowledges the game-changing introduction of '0' by Brahmagupta. The script also delves into the importance of '10' in our base-10 system and ends with a playful look at special numbers like '42', 'π', and '∞', all while maintaining a light-hearted and engaging tone.
Takeaways
- 📝 The script discusses the historical development of numerical systems, starting from tally marks and evolving into more complex systems like the Babylonian base 60 system.
- 🔢 The concept of zero was a significant innovation, credited to the Indian mathematician Brahmagupta, which revolutionized how we keep track of numbers.
- 🥇 The number one is described as iconic and simple, representing the epitome of simplicity and victory.
- 👫 The number two is the first even number and the first prime number, signifying duality and pairs, such as in the case of eyes, arms, and bike wheels.
- 🔺 The number three is significant in many cultures and religions, often associated with opposition and dynamics.
- 🔲 The number four is associated with stability and is used to make squares, which are solid objects, and is also related to the 4/4 time signature in music.
- 🚫 The number 13 is considered unlucky in many cultures, with its origins in Norse mythology and reinforced by various superstitions.
- 🌌 The number six is the first combination of even and odd numbers, and is seen as aesthetically pleasing.
- 🌟 The number seven is significant in various cultural and religious contexts, including the Babylonian's original seven-day week and the seven wonders of the world.
- 🔢 The script humorously ranks numbers from best to worst, with a subjective perspective on their significance and symbolism.
- 🎲 The number 42 is mentioned as the 'meaning of life' in a reference to 'The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy,' but the script suggests that life's meaning is subjective.
Q & A
What was the original method of counting used by early humans?
-Early humans originally counted by looking at their fingers and using the number of them to represent quantities of other things.
How did the Alpha stages of the counting system evolve?
-The Alpha stages of the counting system evolved from using little rocks to keep track of things like sheep to carving tally marks in written forms.
What significant contribution did the Babylonians make to the development of numbers?
-The Babylonians contributed to the organization of the counting system, similar to how other cultures had their own ways of doing things.
How did the concept of the base 10 system originate?
-The concept of the base 10 system originated from the Egyptians who figured out the whole base 10 thing.
What is the significance of the number zero in the history of numbers?
-The number zero, invented by the Indian mathematician Brahma Gupta, was significant because it changed the way we keep track of things and marked the full release of the number system.
Why is the number one considered iconic and what does it symbolize?
-The number one is considered iconic because it represents the first place, the epitome of simplicity, and victory. It's also the first letter in the alphabet.
What makes the number two special in the script?
-The number two is special because it's the first even number on the list, the first prime number, and it signifies duality, such as light and dark, good and bad.
How is the number three significant in various cultures and mythologies?
-The number three is significant in many cultures and mythologies, often representing opposition or differing dynamics, such as in the case of Zeus, Poseidon, and Hades.
Why is the number four considered sturdy and reliable?
-The number four is considered sturdy and reliable because it is used to make squares, which are solid objects, and it represents stability and absolute sturdiness.
What is the cultural significance of the number 13, and how did it become associated with bad luck?
-The number 13 is considered unlucky in many cultures due to its association with the Norse myth where Loki, the 13th guest at a party, caused disaster. This association was further reinforced by the French play and the concept of Friday the 13th.
Why is the number six considered to have a nice connection to the speaker's childhood?
-The speaker has a personal connection to the number six from their childhood, and it is the first combination of even and odd numbers that form a swirly pattern, which they find appealing.
What is the significance of the number seven in various cultural and historical contexts?
-The number seven is significant because it was thought to represent the number of planets by the Babylonians, it's part of the seven-day week, and is associated with the seven wonders of the world and the seven seas.
What is the meaning of the number 666 in religious contexts, and how is it viewed in the script?
-In religious contexts, the number 666 is associated with the Beast and the Devil, making it an unlucky number. The script mentions it as having a 'fun phobia name' and views it as cool personally.
Why is the number eight associated with the octopus and the month of October?
-The number eight is associated with the octopus due to the eight-legged creature, and with October because it is the eighth month in the Gregorian calendar.
What is the significance of the number nine being an upside-down six?
-The number nine being an upside-down six is a visual observation that the speaker finds interesting and uses to place it on the opposite side of six in their tier list.
How did the concept of zero change the way we think about numbers?
-The concept of zero changed the way we think about numbers by providing a way to represent the absence of quantity and allowing for the development of the modern base 10 number system.
What is the significance of the number 10 in our modern number system?
-The number 10 is significant in our modern number system because it is the base of the system, and we divide things into tens in various aspects of life, such as money and time.
What is the cultural significance of the number 100, and how does it relate to the concept of a percent?
-The number 100 is culturally significant as it represents a greater extent of completion and is the basis for the concept of a percent, which is a way of expressing a ratio or a fraction of 100.
What is the meaning of the number 42 in the context of the script, and how is it viewed?
-In the script, the number 42 is mentioned as 'the meaning of life' in a humorous context, but the speaker personally finds life's meaning to be subjective and not a fixed number.
What is the significance of the number 5040 in the script, and how is it viewed?
-The number 5040 is significant in the script because it allows for the formation of perfectly formed groups out of the first 11 numbers, but the speaker finds it too normal and not extraordinary.
What is the script's view on the number Pi and its significance?
-The script views the number Pi as cool-looking and significant for its contribution to circle-related mathematics and physics.
What is the script's view on the number representing gravity, and how is it associated with staying grounded?
-The script humorously mentions the number representing gravity as a force that holds us back from space, using it as a metaphor for staying grounded in life.
What are the bonus numbers mentioned in the script, and how are they categorized?
-The bonus numbers mentioned in the script are tally marks, the kanji character for one, imaginary numbers, Infinity, and Omega. They are categorized into different tiers based on their uniqueness and significance.
How does the script view the ancient Egyptian number for 'one' and its writing style?
-The script views the ancient Egyptian number for 'one' as quick to write and efficient, following the natural flow of pencil movement, and categorizes it as S-tier.
Outlines
🔢 The Evolution and Significance of Numbers
The script begins by exploring the origins of numerical systems, starting from the use of fingers to tally objects like sheep. It discusses the transition from physical methods like tally marks to written forms, highlighting the contributions of various cultures such as the Babylonians and Egyptians. The script emphasizes the pivotal role of the Indian mathematician Brahma Gupta in inventing the concept of zero. It then humorously ranks numbers from best to worst, starting with the iconic 'one' for its simplicity and victory symbolism, followed by the significance of 'two' as the first even and prime number, and 'three' for its cultural and religious importance. The paragraph also touches on the superstitions around 'four' and 'thirteen', considering their impact on perception but not necessarily their value.
🎲 Cultural and Mathematical Perspectives on Numbers
Continuing the numerical theme, this paragraph delves into the cultural and mathematical significance of numbers six through infinity. It describes 'six' as the first combination of even and odd numbers, evoking nostalgia and a sense of harmony. 'Seven' is noted for its prevalence in Babylonian astronomy and the subsequent seven-day week, as well as its association with luck and the 'angel number' 777. The paragraph humorously addresses 'eight' and 'nine' with their visual and conceptual connections to other numbers and shapes. It also revisits the importance of 'zero' in transforming numerical systems. The script then moves on to discuss 'ten' and 'one hundred' in the context of base-10 systems and their psychological impact. It briefly mentions '42' as a cultural reference to the meaning of life, 'pi' for its mathematical significance, and 'gravity' as a physical constant. The paragraph concludes with a playful look at tally marks, kanji, imaginary numbers, infinity, and omega, categorizing them into different tiers based on their perceived importance and fascination.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Numerals
💡Tally Marks
💡Babylonians
💡Base 10
💡Zero
💡Prime Numbers
💡Duality
💡Religious Significance
💡Unlucky Numbers
💡Angel Numbers
💡Infinity
Highlights
Numbers originated from counting physical objects like fingers, which led to the development of counting systems.
Early stages of numerical systems involved using rocks and tally marks for tracking quantities.
Babylonians and Egyptians contributed to early numerical systems, with the latter introducing the base 10 system.
The concept of zero was invented by Indian mathematician Brahma Gupta, revolutionizing the way numbers are used.
The speaker ranks numbers based on their significance and cultural impact, starting with number one as the epitome of simplicity and victory.
Number two is highlighted as the first even and prime number, symbolizing duality and pairs.
Number three is associated with religious and mythological significance, often representing opposition or dynamics.
Four is noted for its role in creating squares and its prevalence in modern music with the 4/4 time signature.
Number 13 is considered unlucky in many cultures, with its origins tied to Norse mythology and the French play.
Number six is praised for being the first combination of even and odd numbers, creating a visually appealing swirl.
Seven is significant for its associations with the seven-day week, seven wonders of the world, and angel numbers.
Number 666 is considered unlucky and associated with religious taboos, such as the number of the Beast.
Eight is likened to an octopus and the shape of an octagon, with a unique swirly factor.
Nine is simply an upside-down six, offering a playful perspective on its relationship with the number six.
The importance of zero is reiterated, emphasizing its role in changing the way we track and understand quantities.
Number 10 is celebrated as the foundation of our base 10 number system, delivering joy through completion.
The number 100 is highlighted for its use in percentages and as a symbol of greater extent of the base 10 system.
The number 42 is humorously mentioned as the 'meaning of life', but the speaker encourages personal interpretations of life's meaning.
The number Pi is acknowledged for its significance in mathematics, particularly in relation to circles.
Bonus numbers like tally marks, kanji characters, imaginary numbers, and infinity are given unique recognition for their distinct roles.
The s-tier ranking is introduced as the highest level of significance among the numbers discussed.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: