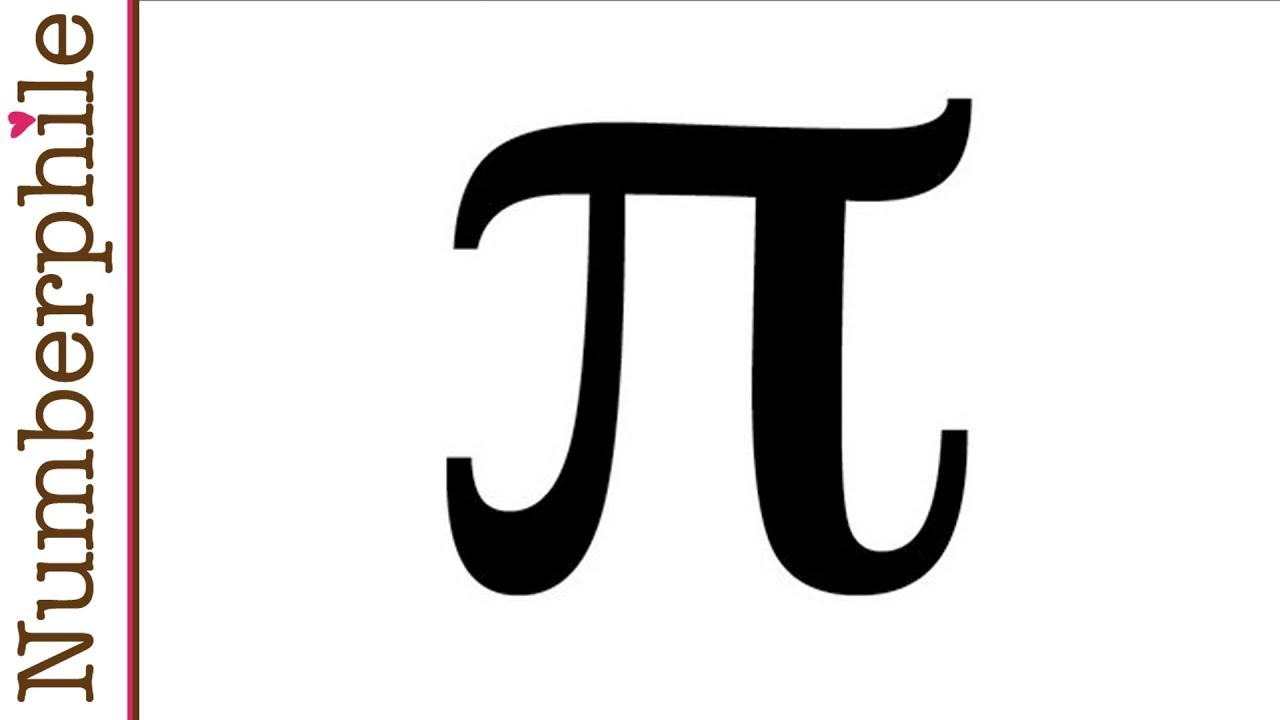
A Brief History of Pi
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating history of pi, a mathematical constant that has intrigued civilizations for millennia. From ancient Egypt and Babylon to modern-day computer calculations, the quest for pi's value reflects the evolution of mathematical thought. The script delves into methods like the method of exhaustion and infinite series, highlighting the contributions of Archimedes, Chinese mathematicians, and the Persian algebraic system. It also touches on the significance of pi in testing computational accuracy and generating random numbers, emphasizing the human drive to understand and explore the natural world.
Takeaways
- 🍕 Pi is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- 📚 The history of pi's understanding spans across various civilizations including the Middle East, Europe, China, India, and America.
- 📏 Ancient Egyptians and Babylonians were among the first to investigate pi, with the Babylonians estimating it to be 3.125, which is accurate to 1% of its true value.
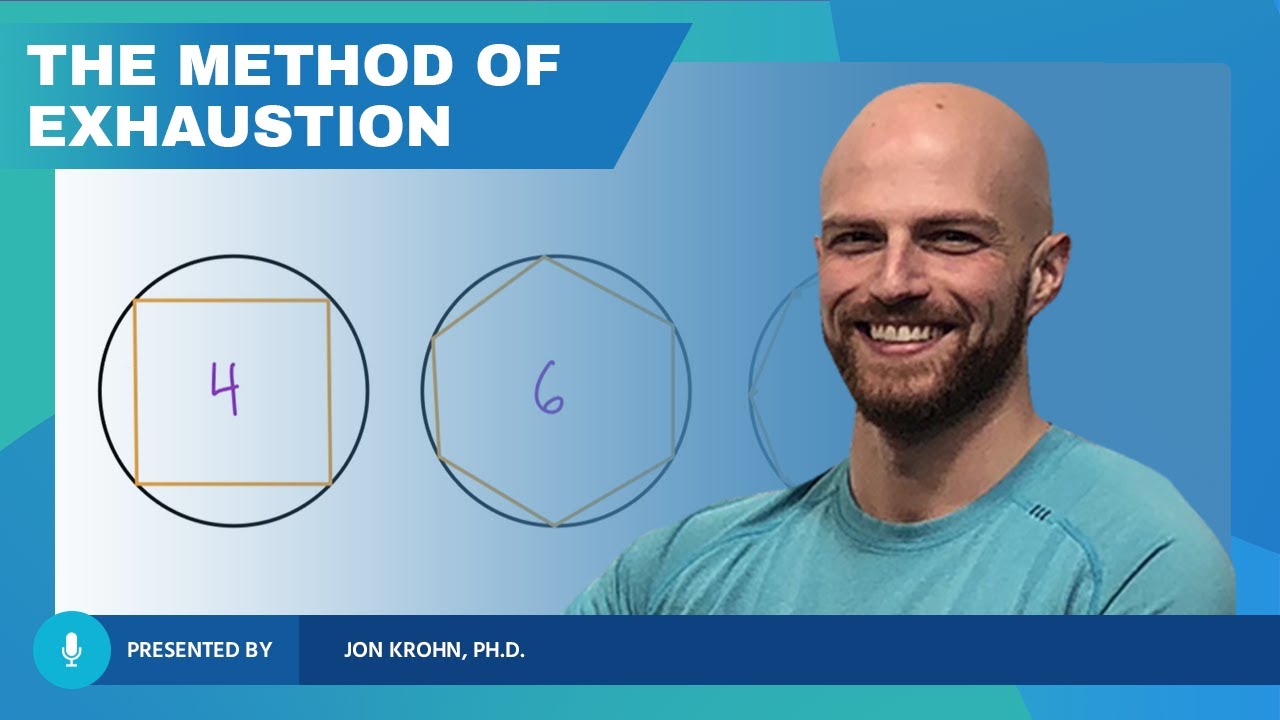
- 📐 Archimedes used the method of exhaustion to estimate pi by approximating circles with polygons, leading to an estimate accurate to two decimal places.
- 🌐 Chinese mathematicians used a similar method of exhaustion but focused on the areas of polygons to calculate pi to five decimal places.
- 🔢 The development of decimal notation in India and algebra in Persia revolutionized the ease of mathematical calculations.
- 🌍 The spread of decimal notation and algebra to Europe allowed for more advanced calculations of pi, with Christiaan Huygens calculating it to 38 decimal places.
- 📈 The use of infinite series to calculate pi was pioneered in India and later rediscovered in Europe, leading to rapid advancements in pi's estimation.
- 💻 The advent of mechanical and electronic computers in the 20th century dramatically increased the number of digits of pi that could be calculated.
- 🏆 The current world record for the most digits of pi calculated is held by Peter Trueb, with nearly 22.5 trillion digits.
- 🎯 People continue to calculate more digits of pi for various reasons, including testing new computers, generating random numbers, and the human desire to explore and understand the world.
Q & A
What is the mathematical constant pi, and how is it defined?
-Pi is a mathematical constant represented by the Greek letter 'π'. It is defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. This ratio is approximately 3.1415926 and is used in various mathematical and scientific calculations.
How did the Babylonians estimate the value of pi around 4000 years ago?
-The Babylonians estimated the value of pi to be 3 and 1/8, or 3.125, which is accurate to 1% of its true value. This estimation was quite remarkable considering the time period when this estimation was made.
What method did Archimedes use to estimate the value of pi?
-Archimedes used the method of exhaustion, where he approximated pi by measuring the perimeters of polygons inscribed and circumscribed around a circle, with an increasing number of sides to refine the estimate.
What is the significance of the method of exhaustion in the history of pi?
-The method of exhaustion was significant as it allowed for more accurate estimations of pi by using polygons with more sides, effectively getting closer to the shape of a circle and thus narrowing the range of possible values for pi.
How did Chinese mathematicians contribute to the calculation of pi?
-Chinese mathematicians used a method similar to the method of exhaustion but focused on the areas of polygons instead of their perimeters. They used polygons with a large number of sides to obtain pi to five decimal places, and later extended this to six decimal places, setting a world record that stood for 800 years.
What are the two world-changing mathematical ideas that simplified arithmetic calculations?
-The two world-changing mathematical ideas are the decimal notation system, which allows any number to be written using just ten symbols and a place value notation, and algebra, which involves representing unknowns with symbols and manipulating equations.
Who was the Persian mathematician that established algebra and how did it impact the calculation of pi?
-The Persian mathematician Mohammed ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi established algebra. This allowed for easier and more efficient calculations across all of mathematics, including the calculation of pi, by enabling mathematicians to use infinite series to estimate pi to greater accuracy.
What is an infinite series and how is it used in calculating pi?
-An infinite series is an expression made up of terms added together in succession. If the contributions of the terms keep getting smaller, the series converges to a particular value. In the case of pi, mathematicians use infinite series that converge on pi to calculate its value to many decimal places.
Why do people continue to calculate more digits of pi even though it is known to be a transcendental number?
-People continue to calculate more digits of pi for several reasons: to test the capabilities of new computers, as pi serves as a good random number generator useful in fields like cryptography, and simply because of human curiosity and the desire to push the boundaries of knowledge.
What is the current world record for the number of digits of pi calculated and who holds it?
-The current world record for the number of digits of pi calculated is held by Peter Trueb, with a shade under twenty-two and a half trillion digits.
How did the sponsor of the video, Squarespace, contribute to the creation of the video?
-Squarespace sponsored the video and provided an easy-to-use platform for the video creator to build his website. The platform allowed for customization and setup for selling merchandise, requiring no web development experience.
Outlines
📚 The Historical Quest for Pi
This paragraph delves into the historical journey of understanding the mathematical constant pi. It starts with the ancient civilizations of Egypt and Babylon, which estimated the value of pi around 4000 years ago, and then moves on to the Greeks, particularly Archimedes, who used the method of exhaustion to approximate pi's value. The paragraph also touches on the significance of pi in the broader history of mathematics, highlighting its connection to various cultures and the evolution of mathematical thought.
🌐 The Global Pursuit of Pi's Precision
This section highlights the global efforts to calculate pi with increasing accuracy. It mentions Chinese mathematicians who used polygons with a large number of sides to refine pi's value to five decimal places, and later, a father-son team who extended this to six decimal places. The paragraph also discusses the introduction of decimal notation and algebra from India and Persia, which revolutionized the way calculations were performed, paving the way for more precise calculations of pi in the future.
🔍 The Infinite Series and Pi's Calculation
This paragraph explores the shift in the method of calculating pi from geometric approximations to using infinite series, a significant leap in mathematical methodology. It discusses the contributions of Indian mathematician Madhava and the later independent rediscovery of his methods in Europe by James Gregory and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. The narrative then moves to the 17th century, where the adoption of algebra and decimal notation in Europe led to rapid advancements in pi's calculation, culminating in the use of increasingly efficient infinite series.
🏆 The Competitive Spirit in Pi's Computation
This section examines the competitive aspect of calculating pi, where mathematicians strove to outdo each other by using faster converging infinite series. It describes the race to calculate more digits of pi, leading to the use of mechanical and electronic computers, which drastically increased the number of digits computed. The paragraph also reflects on the reasons for continuing to calculate pi, such as testing computational capabilities, generating random numbers, and the human spirit of exploration and achievement.
🌟 The Launch of a New Website and Sponsorship Acknowledgement
In the final paragraph, the speaker announces the launch of their new website and acknowledges the sponsorship of the video by Squarespace. They share their experience of building the website with ease using Squarespace's templates and tools, and they highlight the platform's benefits, such as ease of use, automatic updates, and the ability to sell merchandise. The speaker also provides a discount offer for viewers interested in using Squarespace for their own projects.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Pi (π)
💡Archimedes
💡Method of Exhaustion
💡Decimal Notation
💡Algebra
💡Infinite Series
💡Scientific Revolution
💡Age of Enlightenment
💡Electronic Computers
💡Transcendental Numbers
💡Random Number Generation
Highlights
Sponsorship by Squarespace for creating websites, domains, and online stores.
Pi (π) is a mathematical constant with a rich history, studied for thousands of years.
The ancient Egyptians and Babylonians were among the first to investigate pi, with the Babylonians estimating it to be 3.125.
Archimedes used the method of exhaustion to estimate pi, introducing the concept of approximating a circle with polygons.
Chinese mathematicians used polygons with 3072 sides to obtain pi to five decimal places.
Decimal notation and algebra were key to simplifying calculations and advancing the study of pi.
Christiaan Huygens achieved the most accurate estimate of pi using polygons with 10 to the 40 sides.
The Enlightenment movement emphasized reason over tradition, influencing new approaches to calculating pi.
Infinite series were used to calculate pi, with Madhava of Sangamagrama being the first to write mathematical functions as infinite series.
Competition among mathematicians led to the development of faster converging infinite series for pi.
Srinivasa Ramanujan developed an efficient infinite series for pi calculation, which is still used today.
Mechanical and electronic computers revolutionized the calculation of pi, with records continually being broken.
Calculating pi serves as a test for new computers and a source of random numbers for cryptography.
The pursuit of calculating more digits of pi is driven by human curiosity and the desire to understand the world.
The presenter launched a website built with Squarespace, showcasing the ease of use and customization.
Squarespace offers a free trial and a discount for first-time users, emphasizing its user-friendly platform for building websites.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: