Electrical conductance | periodic properties | ch.no.1 | 12th class chemistry
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of electrical conductivity, emphasizing the importance of free electrons for conduction. It discusses the role of charge particles and the process of electrical conduction through various substances, highlighting the significance of factors like atomic structure and electron movement. The script also touches on the periodic table, differentiating between conductors and non-conductors, and explains how the arrangement and properties of elements affect their electrical conductivity, providing a foundational understanding of the principles behind electronic devices and materials.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Electrical Conductivity: The script discusses the concept of electrical conductivity, emphasizing the importance of understanding what makes a material a good conductor or insulator.
- 🔋 Charged Particles: It mentions that the presence of charged particles within a material is crucial for electrical conductivity, indicating that free electrons are key for conductors.
- 💡 Conductors and Insulators: The script explains the difference between conductors and insulators, highlighting that conductors allow for the easy flow of electricity while insulators resist it.
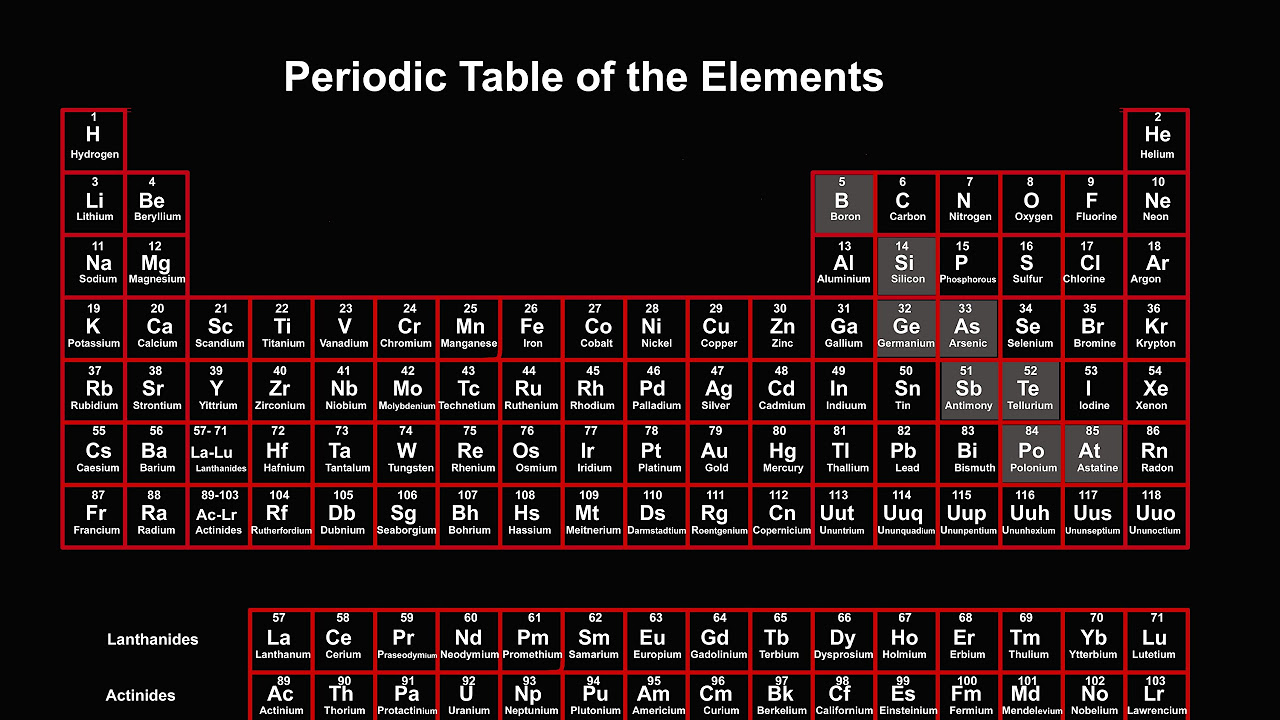
- 📚 Periodic Table: Reference to the periodic table is made, indicating that elements on the left side are metals and typically good conductors, while those on the right are non-metals and often insulators.
- ⚙️ Atomic Structure: The script touches on atomic structure, particularly how the arrangement of electrons in shells influences a material's electrical properties.
- 🔬 Electron Mobility: It is pointed out that the mobility of electrons within a material is a significant factor in determining its conductivity, with metals having high electron mobility.
- 💎 Diamond and Graphite: The properties of diamond and graphite are contrasted, with diamond being a poor conductor due to its rigid structure, while graphite, with its free-moving electrons, is a good conductor.
- 🔄 Electron Flow: The script explains how the flow of electrons is facilitated in conductors, and how this flow can be impeded in insulators, affecting the material's conductivity.
- 🌐 Current and Voltage: The relationship between current and voltage is briefly discussed, indicating that voltage is the driving force that pushes electrons through a conductor.
- 🛠️ Applications: The script hints at practical applications of electrical conductivity, such as in the design of electronic devices and the selection of materials for wires and circuits.
- 🔄 Environmental Impact: There is a mention of environmental trends, suggesting that the choice of materials in products can have implications for sustainability and environmental impact.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is electrical conductivity, focusing on the factors that affect it and the properties of various materials in relation to electrical conduction.
What is the significance of 'free electrons' in the context of electrical conductivity?
-Free electrons are crucial for electrical conductivity as they facilitate the flow of electric charge through a material. The presence of free electrons indicates a higher potential for electrical conductivity.
What does the script imply about the relationship between atomic structure and electrical conductivity?
-The script implies that the atomic structure, specifically the availability of valence electrons, plays a significant role in determining a material's electrical conductivity.
What is the role of the 'Predic Table' in understanding electrical conductivity?
-The 'Predic Table', likely referring to the Periodic Table, helps in understanding the electrical conductivity of elements by showing their electron configurations and positions in the table.
How does the script describe the process of electrical conduction in terms of electron movement?
-The script describes electrical conduction as a process where free electrons move through a material, facilitated by the presence of charge particles within the material.
What is the term used in the script to describe a material that does not conduct electricity?
-The term used in the script to describe a material that does not conduct electricity is 'electrical insulator'.
What is the significance of 'sp3 hybridization' in the context of the script?
-The 'sp3 hybridization' is significant as it relates to the bonding and structure of materials like diamond, which affects their electrical conductivity properties.
How does the script differentiate between conductors and insulators of electricity?
-The script differentiates between conductors and insulators based on their ability to allow the flow of electric charge, with conductors having high electrical conductivity and insulators having low or no electrical conductivity.
What is the role of 'graphite' in the script's discussion on electrical conductivity?
-Graphite is mentioned as an example of a good conductor of electricity due to its structure, which allows for the easy movement of electrons.
How does the script relate the size of atoms to electrical conductivity?
-The script suggests that as the size of atoms increases, the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus, making it easier for them to move and contribute to electrical conductivity.
Outlines
🔌 Understanding Electrical Conductivity
The first paragraph discusses the concept of electrical conductivity, emphasizing the importance of remembering that certain materials are insulators, while others are conductors. It explains the process of electrical conduction through substances, mentioning the flow of current and the role of charged particles. The paragraph also touches on the idea of electrical conductivity being free from any material, highlighting the need to understand the basic principles of conductors and insulators.
🔗 Factors Influencing Electrical Conductivity
The second paragraph delves into the factors that affect electrical conductivity, such as the presence of elements on the right side of the periodic table, which are more conductive or have higher electrical conductivity. It discusses the decrease in conductivity with the increase in elements and the concept of non-conductivity. The paragraph also mentions the importance of understanding the properties of elements to predict their electrical behavior, including the balance between conductors and insulators.
💎 The Role of Diamond and Graphite in Conductivity
This paragraph explores the electrical conductivity properties of diamond and graphite, highlighting their atomic structures and how they influence conductivity. Diamond, with its sp3 hybridization, is an insulator, while graphite, with sp2 hybridization, is a good conductor due to the free movement of electrons. The discussion includes the reasons behind graphite's superior conductivity and the role of hybridization in determining the electrical properties of these carbon allotropes.
🌐 Applications and Comparison of Conductive Materials
The final paragraph discusses the practical applications of different conductive materials, comparing their electrical conductivity. It mentions metals like copper, silver, and gold as common conductors and their uses in various industries. The paragraph also touches on the importance of selecting the right material for specific applications based on their conductivity levels, concluding with a note on the high conductivity of gold among other elements.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electrical Conductance
💡Charge Particles
💡Atomic Number
💡Hybridization
💡Periodic Table
💡Electron Cloud
💡Non-conductors of Electricity
💡Graphite
💡Diamond
💡Conductors of Electricity
💡Electrical Resistance
Highlights
Electrical conductivity is dependent on the presence of free electrons in a material.
The importance of remembering that for electrical conductivity, the material must have charged particles inside.
The concept of electrical conductivity is explained using the process of a pump, transferring current through substances.
Presence of free electrons is crucial for a material to act as an electrical conductor.
The discussion of the periodic table and its role in understanding the properties of elements, especially their electrical conductivity.
Elements with higher atomic numbers on the right side of the periodic table tend to be better conductors of electricity.
The increase in electrical conductivity as elements move from left to right across the periodic table.
The explanation of how the size of atoms and the availability of valence electrons affect electrical conductivity.
The mention of non-conductors of electricity, such as insulators, and their role in preventing the flow of electric current.
The significance of the valence electrons' ability to move easily in conductors, contributing to their conductivity.
The role of hybridization, such as sp3, in the electronic structure of elements and its impact on electrical conductivity.
The comparison between diamond and graphite, highlighting their different electrical properties due to their atomic structure.
Graphite is identified as a good conductor of electricity due to its structure, which allows electrons to move freely.
The practical applications of understanding electrical conductivity, such as in the selection of materials for electronic devices.
The impact of environmental factors on the electrical conductivity of materials.
The mention of metals like copper, silver, and gold as high electrical conductors and their uses in various applications.
The concept of electrical resistance and its relation to the properties of conductors.
The importance of understanding the electrical properties of materials for the development of new technologies and innovations.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: