Acid and Base | Acids, Bases & pH | Video for Kids
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the concepts of acids and bases, explaining their chemical properties and the role of hydrogen and hydroxide ions in determining their nature. It delves into the pH scale, highlighting the distinction between strong and weak acids and bases, and their applications in everyday life, such as in antacids, digestion, and household products. The script also touches on the presence of acids and bases in plants and the practical implications of their properties, such as the slipperiness of bases in cleaners.
Takeaways
- 🍊 Acids and bases are two types of chemicals characterized by the presence of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-), respectively.
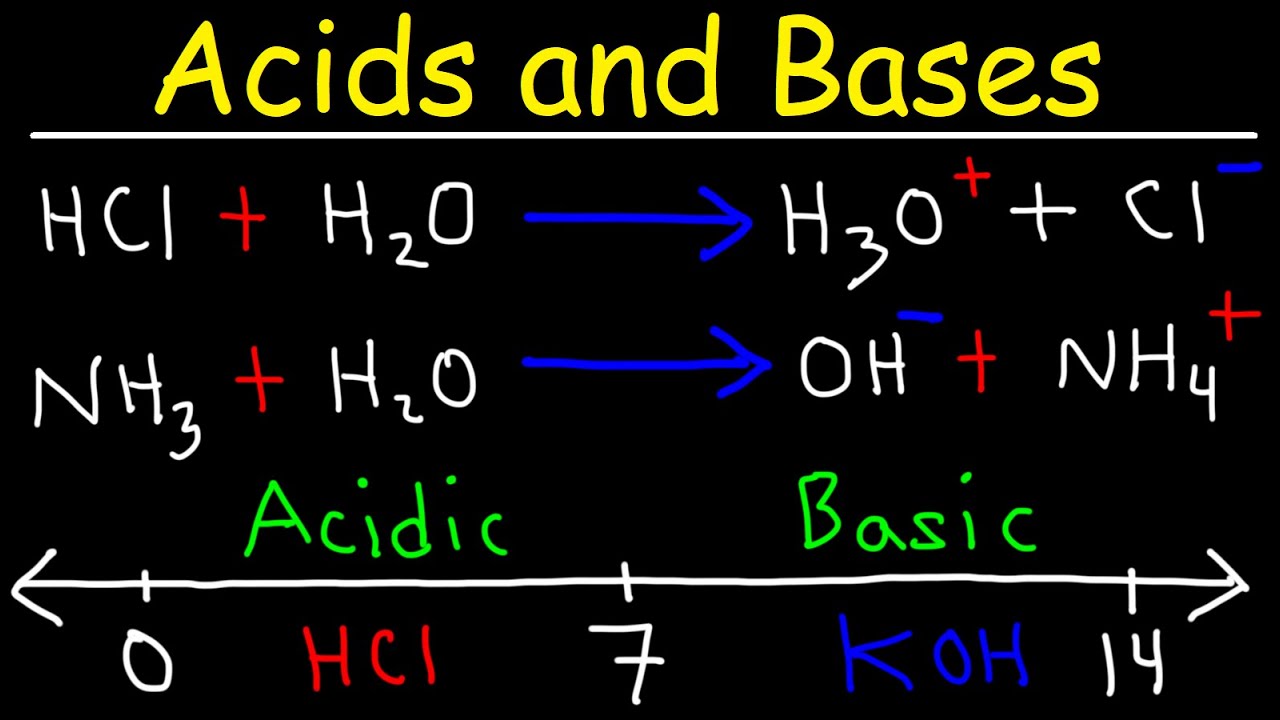
- 🧪 The pH scale is used to measure how acidic or basic a liquid is, with a range from 0 to 14, where 0 is the most acidic and 14 is the most basic.
- 💧 A liquid is considered neutral if it has a pH value of 7, indicating an equal concentration of H+ and OH- ions.
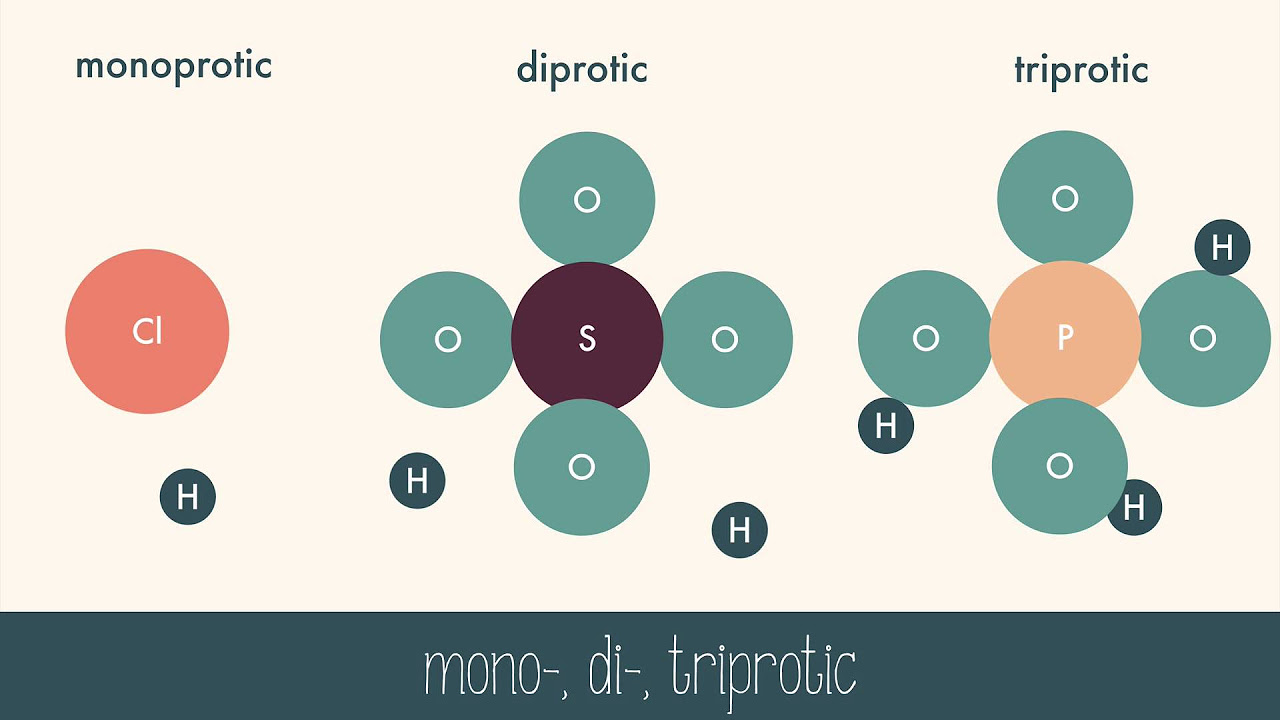
- 🌟 Strong acids are those that dissociate 100% into ions, while weak acids do not dissociate completely.
- 🌿 Many plants contain acids and bases in their seeds and leaves, such as citric acid in citrus fruits like lemons.
- 🛡 Antacids, which include sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate, are bases used to neutralize stomach acids and relieve upset stomachs.
- 🍽 The stomach uses hydrochloric acid for digestion and to kill bacteria, maintaining health.
- 🏃♂️ During exercise, muscles can produce lactic acid, which can cause discomfort.
- 🧼 Bases can feel slippery, which is why substances like sodium hydroxide are used in cleaners to create a soapy texture.
- 🏠 Common household items containing bases include baking soda, drain cleaner, washing powder, and toothpaste.
- 🍶 Household items that contain acids include yogurt, vinegar, lemon juice, and batteries.
Q & A
What are acids and bases?
-Acids and bases are two specific types of chemicals that can be identified by the presence of hydrogen ions (H+) for acids and hydroxide ions (OH-) for bases.
How can we determine if a liquid is acidic or basic?
-The presence of a high concentration of hydrogen ions indicates an acid, while a high concentration of hydroxide ions indicates a base.
What is the pH scale used for?
-The pH scale is used to measure how acidic or basic a liquid is, with numbers ranging from 0 to 14.
What is the significance of the number 7 on the pH scale?
-A pH value of 7 indicates a neutral liquid, which is neither acidic nor basic.
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
-A strong acid dissociates 100% into ions, while a weak acid does not dissociate completely.
Can you give an example of a strong acid found in nature?
-Hydrochloric acid is an example of a strong acid found in nature and is used in various applications, including the human stomach for digestion.
What are some uses of acids and bases in everyday life?
-Acids and bases are used in various household items such as antacids, cleaners, baking soda, drain cleaner, washing powder, toothpaste, yogurt, vinegar, lemon juice, and batteries.
Why do some plants have acids and bases in their seeds and leaves?
-Plants contain acids and bases for various biological processes, including defense mechanisms and aiding in digestion for herbivores.
What is citric acid and where is it found?
-Citric acid is a weak organic acid found in citrus fruits like oranges, grapes, and lemons, which gives them their sour taste.
How do antacids work to alleviate an upset stomach?
-Antacids, which include bases like sodium bicarbonate or baking soda, work by neutralizing stomach acids, converting them to water and carbon dioxide gas.
Why do bases feel slippery?
-Bases feel slippery because they are soapy in nature, which is why some of them, like sodium hydroxide, are used in cleaners.
Outlines
🍋 Introduction to Acids and Bases
This paragraph introduces the concept of acids and bases as specific types of chemicals, explaining that all liquids are either acidic or basic based on the presence of hydrogen or hydroxide ions. It introduces the pH scale as a tool to measure a liquid's acidity or alkalinity, ranging from 0 to 14, with 0 being the strongest acid and 14 the strongest base. The paragraph also distinguishes between strong and weak acids based on their degree of ion dissociation and mentions the presence of acids and bases in nature, including in plants and everyday items like lemons.
💊 Uses of Acids and Bases in Everyday Life
This section delves into the practical applications of acids and bases, highlighting their roles in various household and health-related scenarios. It discusses how antacids, which are bases, are used to neutralize stomach acids, aiding digestion and reducing discomfort after consuming junk food. The paragraph also touches on the role of hydrochloric acid in the stomach for digestion and bacterial control. Additionally, it mentions the production of lactic acid during exercise and the slipperiness of bases, exemplified by cleaners containing sodium hydroxide. Common household items containing acids and bases, such as baking soda, drain cleaner, washing powder, toothpaste, yogurt, vinegar, lemon juice, and batteries, are also listed.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acid
💡Base
💡pH Scale
💡Hydrogen Ions
💡Hydroxide Ions
💡Strong Acid
💡Weak Acid
💡Antacids
💡Citric Acid
💡Lactic Acid
💡Household Items
Highlights
Acids and bases are two specific types of chemicals distinguished by the type of ions present.
Liquids can be categorized as acids or bases based on their hydrogen and hydroxide ion concentrations.
The pH scale is a chemical detector for hydronium and hydrogen ions, ranging from 0 to 14.
Acids are on the pH scale from 0 to 7, with 0 being the strongest.
Bases are on the pH scale from 7 to 14, with 14 being the most powerful.
A liquid is neutral if it has a pH value of 7.
Strong acids are those that dissociate 100 percent into ions.
Weak acids do not dissociate completely and are less ionized.
Strong acids and bases have various applications in nature, some being used in insecticides.
Hydrochloric acid is a dangerous but useful strong acid.
Plants contain acids and bases in their seeds and leaves.
Citrus fruits contain citric acid, which gives them a sour taste.
Antacids, such as sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate, are bases used to neutralize stomach acids.
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach aids digestion and kills bacteria.
Exercise can lead to the production of lactic acid in muscles.
Bases can feel slippery, which is why some are used in cleaners.
Sodium hydroxide is a base used in cleaning products.
Common household items containing bases include baking soda, drain cleaner, washing powder, and toothpaste.
Household items with acids include yogurt, vinegar, lemon juice, and batteries.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: