the concept of mass
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of mass and its representation in physics, focusing on the famous equation E=mc². It discusses the historical development and misconceptions surrounding the equation, emphasizing that mass is an intrinsic property and does not change with velocity. The script challenges common interpretations taught in schools and popular culture, advocating for the accurate equation E₀=mc² to describe the energy of a body at rest. It explores the contributions of various physicists and the evolution of understanding mass from Newtonian mechanics to Einstein's theory of relativity, ultimately arguing for clarity in physics education to avoid perpetuating misconceptions.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The video discusses the concept of mass and the historical misunderstandings surrounding Einstein's famous equation, E=mc².
- 📚 It emphasizes that the correct equation in the context of special relativity is E₀=mc², representing the energy of a body at rest.
- 👨🔬 The argument made by Soviet physicist Lev Okun is highlighted, advocating for the understanding that there is only one type of mass, not separate rest mass and relativistic mass.
- 📉 The video clarifies that Einstein's theory of relativity is not being disproven, but rather the semantics of how mass is discussed and taught are being addressed.
- 🕊️ It mentions Okun's contributions to physics, including the naming of hadrons and the clarification of the concept of vacuum in physics.
- 🌌 The script provides a historical overview of the concept of mass, from early mathematical concepts to the laws of Newton and the development of electromagnetism.
- 🔋 The video explains that mass is an intrinsic property of an object and does not change with velocity, contrary to some popular misunderstandings.
- 💡 It uses the example of cosmic rays and muons to illustrate the importance and necessity of Einstein's theory of relativity in explaining phenomena that classical mechanics cannot.
- 🚀 The script touches on the educational aspect of physics, discussing how concepts are taught at different levels and the potential for confusion and misconceptions.
- 🔬 It critiques the use of E=mc² in popular science and education, arguing for the adoption of the more accurate E₀=mc² to prevent misunderstandings about the nature of mass and energy.
- 👨🏫 The video calls for a change in how physics is communicated to the public and taught to students, advocating for clarity and precision in scientific terminology and concepts.
Q & A
What is the main argument presented by Lev Oken in the video?
-Lev Oken argues that there is only one type of mass, and the concept of 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass' should be replaced with just 'mass'. He suggests that the standard definition of 'E equals mc squared' is misleading and that 'E naught equals mc squared' is the correct equation representing the energy of a body at rest.
Why does the video emphasize that this is not a video arguing against Einstein or the theory of relativity?
-The video emphasizes this point to clarify that the argument is not about the validity of Einstein's work or the theory of relativity, but rather about the semantics of how mass is defined and taught in the context of these theories.
What is the significance of the quiz presented at the beginning of the video?
-The quiz is designed to challenge common misconceptions about Einstein's equations and to highlight the fact that not all widely recognized equations are accurate or applicable in the same way.
What is the historical significance of the equation E naught equals mc squared?
-E naught equals mc squared represents the rest energy of a body, and it is historically significant because it was first written down by Einstein as part of his theory of special relativity, emphasizing the mass-energy equivalence.
How does the video address the misconception that mass increases with velocity?
-The video clarifies that mass itself does not increase with velocity. Instead, it explains that the total energy of a body increases with velocity, which is accounted for by the full relativistic energy equation, not just E equals mc squared.
What is the role of semantics in the argument presented in the video?
-Semantics play a crucial role in the argument as the video discusses how the definitions and usage of terms like 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass' can lead to misconceptions about the theory of relativity and the nature of mass.
Why does the video mention Lev Oken's work on naming the hadron?
-The video mentions Lev Oken's work on naming the hadron to illustrate his focus on the importance of semantics in physics. His insistence on clear terminology helped to distinguish particles involved in strong interactions from those that are not.
What is the video's stance on the use of E equals mc squared in popular science and education?
-The video argues against the use of E equals mc squared in popular science and education, stating that it can lead to misconceptions about the nature of mass and its relationship to energy and velocity.
How does the video relate the concept of mass to the theory of electromagnetism?
-The video discusses the historical exploration of mass in relation to electromagnetism, including the ideas of electromagnetic mass and how these concepts were eventually integrated into the understanding of mass within the framework of relativity.
What is the video's perspective on the teaching of physics, especially regarding the concept of mass?
-The video suggests that the way physics is taught, particularly the concept of mass, can significantly impact the public's and students' understanding and perception of the theory, and it advocates for clearer and more accurate teaching methods.
Outlines
🧠 The Confusion Over Mass in Physics
The paragraph delves into the historical and conceptual misunderstandings surrounding the concept of mass in physics. It starts with a quiz about Einstein's equations and introduces Lev Oaken's argument that there's only one type of mass, challenging the common notion of 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass.' The script emphasizes that while Einstein's theory of relativity is not being disproven, the way we teach and understand mass can lead to misconceptions. It also touches on Oaken's contributions to particle physics, including naming hadrons and his work on the physics of vacuum, which is crucial for understanding the Higgs boson.
📚 A Journey Through the History of Mass Concept
This section provides a historical overview of the concept of mass, from early mathematical notions of quantity and the contributions of Archimedes and Kepler to the laws of motion and gravity by Newton. It discusses the development of the theory of gravitation, Newton's laws of dynamics, and the distinction between inertial mass and gravitational mass. The paragraph also highlights Galileo's thought experiment suggesting that physics is relative and the development of the electromagnetic force, leading up to the equations of Maxwell.
🚀 Electromagnetic Mass and the Speed of Light
The script discusses the transition from Newtonian dynamics to the theory of electromagnetism, with the discovery of the electron and the concept of electromagnetic mass. It mentions the experiments and theories that led to the understanding that the speed of light is the ultimate speed limit, and the incorrect notion that mass increases with velocity. The paragraph explores the idea that all mass could be electromagnetic in nature, leading to the development of various theories attempting to unify the concepts of mass and electromagnetism.
🌌 The Advent of Special Relativity and Mass Energy Equivalence
This section outlines the development of special relativity by Einstein, who proposed that the speed of light is constant and that the laws of physics are the same in all reference frames. It explains how Einstein derived the Lorentz transformations, time dilation, length contraction, and the mass-energy equivalence principle, expressed by the equation E=mc². The paragraph highlights the confusion that arose from Einstein's use of different forms of mass in his papers and the public's misunderstanding of the mass-energy equivalence.
🔬 The Misunderstanding of Mass and Relativity
The script addresses the misconceptions about mass and relativity that persist due to the popularization of the equation E=mc² in its simplified form. It discusses Einstein's efforts to convey the true meaning of the mass-energy equivalence and the importance of understanding the context in which the equation is applicable. The paragraph also presents a thought experiment involving two particles and a photon to illustrate the equivalence of energy and mass, emphasizing the importance of relativity in understanding phenomena like cosmic rays.
🌟 The Importance of Relativity in Modern Physics
This section highlights the significance of the theory of relativity in understanding the behavior of particles at high velocities, such as muons created by cosmic rays. It explains how classical mechanics fails to account for the observed phenomena, while relativity provides the correct explanation for why muons can reach the Earth's surface despite their short lifetimes. The paragraph also touches on the importance of the mass-energy principle in astrophysics and the development of the general theory of relativity.
📚 The Evolution of Mass Concept in Physics Education
The script discusses the evolution of the concept of mass in physics education, from the early textbooks that introduced the idea of 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass' to the modern understanding that there is only one intrinsic mass. It mentions the work of physicists like Wolfgang Pauli and the shift in teaching methods over time, leading to a clearer and more accurate understanding of mass as an intrinsic property of matter that does not change with velocity.
🌌 The Deeper Understanding of Mass in Particle Physics
This section delves into the modern understanding of mass at the particle level, discussing the composition of atoms, the role of quarks and gluons, and the concept of binding energy. It explains how the mass of a proton is largely due to the energy of the quarks and gluons within it, reflecting the deeper connection between mass and energy. The paragraph also touches on the stability of protons and the process of beta decay, further illustrating the complexity of mass at the subatomic level.
🧐 The Disparity Between Popular and Academic Physics
The script addresses the disparity between popular understanding of physics and the academic knowledge held by physicists. It discusses the prevalence of the equation E=mc² in popular culture and the confusion it can cause, contrasting it with the more accurate understanding of mass and energy equivalence used in academic and particle physics. The paragraph highlights the need for clarity in teaching physics to avoid perpetuating misconceptions.
🎓 The Journey Through Physics Education
This section outlines the journey of a physics student from introductory courses to advanced studies, illustrating how the understanding of mass evolves over time. It discusses the initial exposure to the simplified equation E=mc², the subsequent learning of relativistic mass in modern physics, and the eventual realization in graduate studies that there is only one intrinsic mass. The paragraph emphasizes the confusion that can arise from the initial teaching methods and the importance of correcting these misconceptions.
🤔 The Debate Over Teaching Relativity
The script presents a debate over how relativity should be taught, with some physicists advocating for the use of the simplified equation E=mc² for teaching purposes, despite its potential to cause misconceptions. It discusses the argument that while this equation may be helpful for introductory understanding, it can lead to a misunderstanding of the true nature of mass and energy equivalence. The paragraph calls for a more accurate and clear approach to teaching relativity to avoid confusion.
📘 The Impact of Misleading Teaching on Long-term Understanding
This section highlights the potential negative effects of teaching simplified or misleading scientific concepts, using the examples of the Bohr model and the misconceptions about evolution. It argues that while some 'lies to children' can be helpful for initial understanding, others, like the misunderstanding of mass and velocity in relativity, can lead to long-term misconceptions that are difficult to correct. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of accurate teaching to ensure a proper understanding of scientific principles.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Einstein
💡Mass
💡Energy
💡Special Relativity
💡Rest Mass
💡Relativistic Mass
💡E=mc^2
💡Momentum
💡Time Dilation
💡Length Contraction
💡Quarks
Highlights
The video starts with a quiz about Einstein's equations, emphasizing the correct equation for energy and mass is E₀ = mc², not E = mc².
Lev Oken's argument that there is only one type of mass (Mass), and the concept of 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass' is a semantic debate rather than a scientific error.
Einstein's theory of relativity is confirmed as correct and successful, and the video aims to clarify misconceptions rather than disprove any of his theories.
The importance of semantics in physics, especially in how terms are defined and taught, which can lead to different interpretations of the same theory.
Lev Oken's contributions to physics, including naming the hadron and his work on the physics of the vacuum, which became crucial for Higgs boson measurements.
A brief history of the concept of mass from ancient times to the development of the center of mass by Archimedes.
Kepler's and Galileo's early ideas on mass, leading to Newton's laws of motion and gravitation, which unified inertial and gravitational mass.
Galileo's thought experiment suggesting that the laws of physics are the same in all reference frames, a precursor to the theory of relativity.
The development of the electromagnetic force and its similarities to the gravitational force, leading to early theories of 'electromagnetic mass'.
JJ Thompson's discovery that a charged body is harder to move, suggesting a relationship between electromagnetism and mass.
The concept of length contraction and its implication on the understanding of mass, challenging the idea that electromagnetism is the sole source of mass.
Poincare's and Einstein's contributions to the mass-energy equivalence formula, E = mc², and the development of special relativity.
Einstein's thought experiment demonstrating the equivalence of energy and mass, using the emission and absorption of a photon.
The importance of relativity in explaining phenomena like the muon's ability to reach Earth's surface despite its short lifetime.
The misconception that mass increases with velocity, which is not supported by the theory of relativity or modern physics.
The unification of the concept of mass in modern physics, where 'rest mass' and 'relativistic mass' are recognized as the same intrinsic property.
The video concludes by emphasizing that mass is an intrinsic property and that the correct equation representing mass and energy is E² = (mc²)² + (pc)².
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Why light has energy, but no mass? (Understanding E = mc2)
Deriving Einstein's most famous equation: Why does energy = mass x speed of light squared?
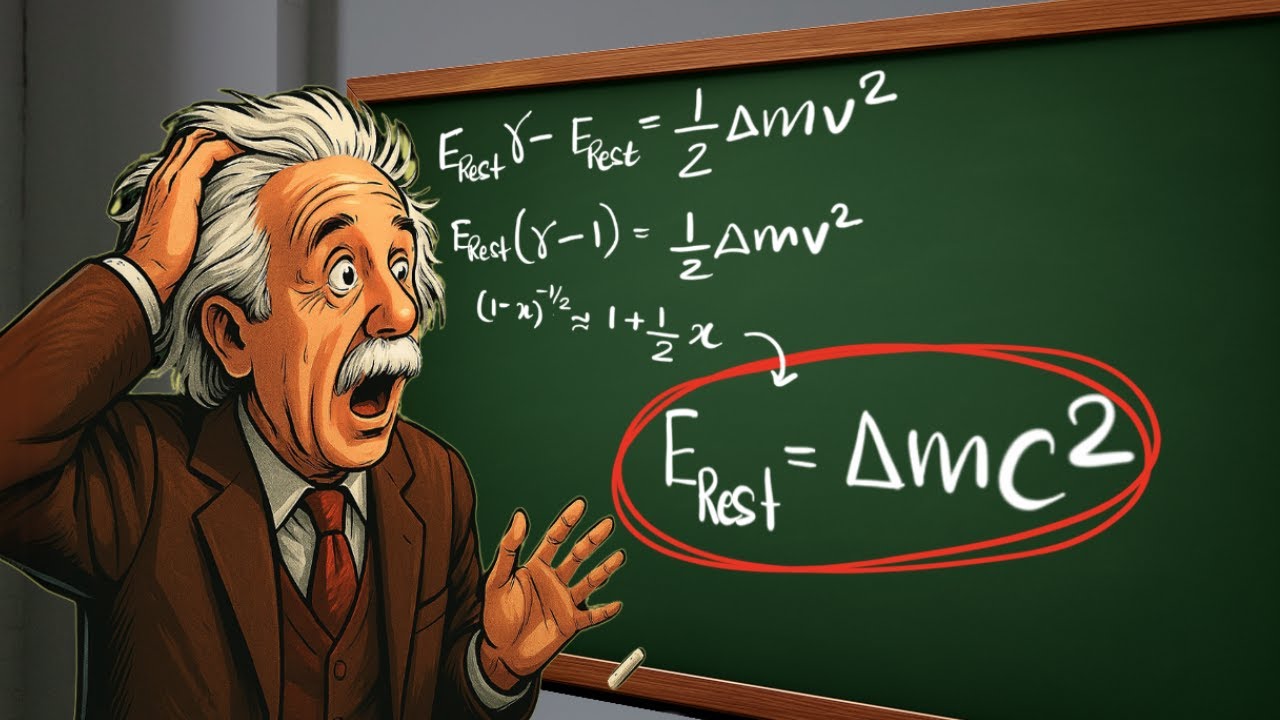
Why speed of light results in E = mc^2 ? [Einstein's original proof]

How can a photon have momentum?

Lecture 1 | New Revolutions in Particle Physics: Basic Concepts

Brian Greene Explains That Whole General Relativity Thing
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: