Electromagnetic Forces
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explores the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces in the universe. He explains how electromagnetism operates at all scales but is particularly dominant at the human scale. The video delves into the concepts of electric charges, magnetic forces, and the relationship between them. It demonstrates how moving a charge can generate a magnetic field and vice versa, showing that electricity and magnetism are essentially the same force. Coulomb's Law is introduced to quantify the forces between charges, and examples illustrate how these forces are billions of times stronger than gravity. The video concludes with a practical demonstration of electromagnetism's strength at the human scale, emphasizing its importance in our daily lives.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe, alongside gravity, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force.
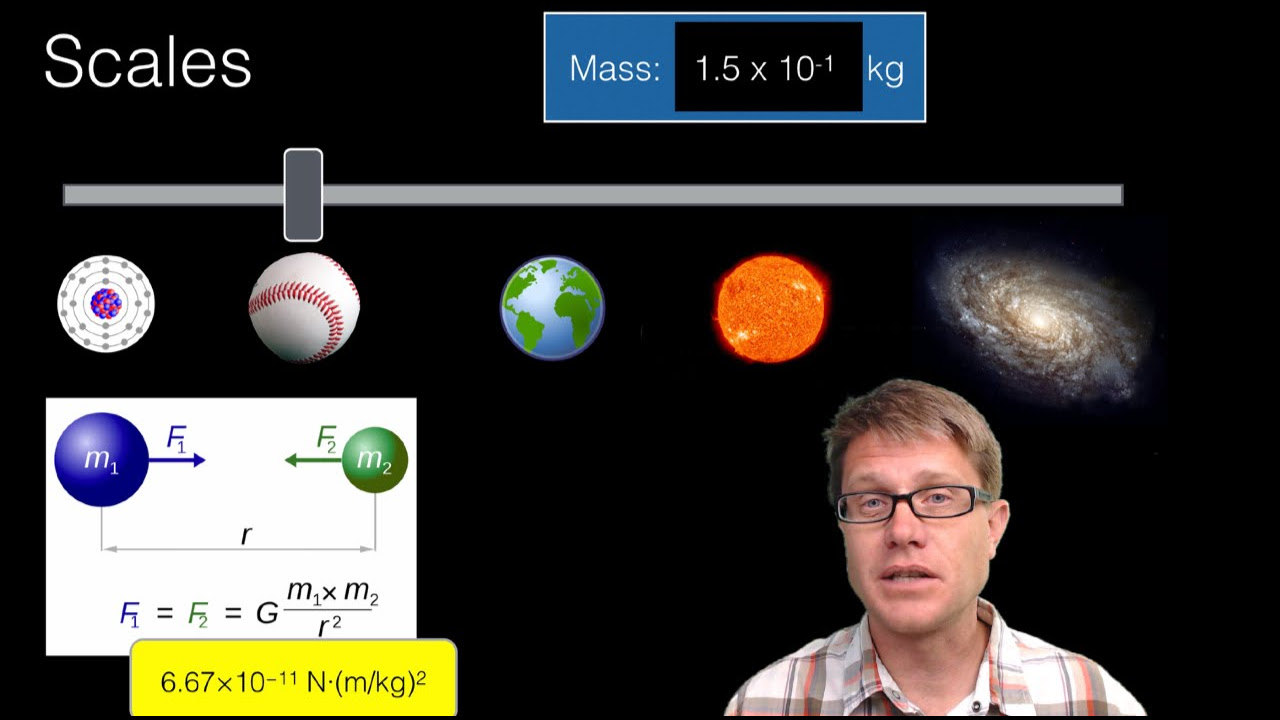
- 🧲 Electromagnetic forces are significant at the human scale, unlike gravity which is more dominant at larger scales.
- 🤝 The presence of opposite electric charges (positive and negative) results in an attractive force, while like charges (both positive or both negative) repel each other.
- 🧲 Magnetic forces involve the attraction between north and south poles of magnetic dipoles, with larger magnets producing stronger forces.
- 🔗 There is a connection between electric charges and magnetic forces: moving a magnet can generate electric charge, and moving an electric charge can generate a magnetic field.
- 🔩 Electromagnetism can be demonstrated through electromagnets, created by running an electric current through a wire wrapped around a non-magnetic metal.
- 🌐 A spinning electromagnet in a generator can generate electric current, showing that moving charges and magnets are essentially the same force.
- ⚡ Electromagnetic forces are billions of times stronger than gravity in terms of their strength as a force.
- ⚖️ Coulomb’s Law quantifies the magnitude of the force between electric charges, indicating that larger charges result in greater attraction or repulsion.
- 🧑🤝🧑 Electromagnetic forces are at play in everyday life, from holding cells together in the human body to enabling industrial magnets to lift objects.
- 🌍 At the human scale, electromagnetic forces are stronger than gravity, which is why we don't fall through the Earth.
Q & A
What are the four fundamental forces in the universe mentioned in the video?
-The four fundamental forces in the universe are gravity, electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force.
How does gravity differ from electromagnetism in terms of the forces between objects?
-Gravity is an attractive force between all matter and operates along all size scales, but it dominates at very large scales. Electromagnetism also operates along all size scales but dominates at human scale and can involve both attractive and repulsive forces depending on the charges involved.
What is the relationship between electric charges and the electromagnetic force?
-Opposite electric charges (positive and negative) attract each other, while like charges (both positive or both negative) repel each other. This interaction is part of the electromagnetic force.
How are magnetic forces related to electromagnetism?
-Magnetic forces are a component of electromagnetism. They involve the attraction between north and south poles of magnetic dipoles, with larger magnets producing a greater force.
Why do magnets not exist as discrete north or south poles?
-Magnets always exist as dipoles because they have both a north and a south pole. They cannot exist with only a single north or south pole in isolation.
How are electric charges and magnets connected?
-Electric charges and magnets are connected because moving a magnet can generate electric charge, and moving an electric charge can generate a magnetic field.
What is an electromagnet and how is it created?
-An electromagnet is a type of magnet that is created when an electric current is run through a wire wrapped around a metal that is not normally magnetic, generating a magnetic field.
How is electromagnetism demonstrated to be a single force in the video?
-Electromagnetism is shown as a single force by demonstrating that moving charges can generate magnetic fields and that spinning an electromagnet in a generator can generate electric current.
What is Coulomb's Law and how is it used to quantify electric charges?
-Coulomb's Law quantifies the electric force between two charges. It states that the force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb's constant is used to calculate the magnitude of this force.
How do electromagnetic forces operate at different scales and why do they dominate at the human scale?
-Electromagnetic forces operate at all scales, but they dominate at the human scale because they are billions of times stronger than gravity in terms of force, making them more noticeable and influential in everyday life.
What is an example of electromagnetic forces at work in the video?
-An example given in the video is using an industrial magnet to attract a person wearing a helmet, demonstrating how electromagnetic forces can hold the person off the ground.
Why doesn't the person in the example fall down through the Earth?
-The person doesn't fall down through the Earth because the electromagnetic forces within the Earth's material are much stronger than gravity, holding the person in place.
Outlines
🧲 Electromagnetism: The Force That Binds Our World
The paragraph introduces the concept of electromagnetism as one of the four fundamental forces in the universe, alongside gravity, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. It emphasizes that electromagnetism operates at all scales but is particularly dominant at the human scale. The paragraph explains the attractive force between opposite electric charges and the repulsive force between like charges. It also covers magnetic forces, the attraction between north and south magnetic poles, and the concept of magnetic dipoles. The connection between electric charges and magnets is highlighted, where movement of either can generate the other. An electromagnet is introduced as an example of how a moving charge can create a magnetic field, and how this relates to the generation of electricity in a large generator. The paragraph concludes with Coulomb's Law as a means to quantify the forces between charges and the dominance of electromagnetic forces at the human scale, illustrated by the example of an industrial magnet lifting a person wearing a helmet.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electromagnetic Force
💡Fundamental Forces
💡Charges
💡Magnetic Dipoles
💡Coulomb's Law
💡Electromagnet
💡Generator
💡Human Scale
💡Gravity
💡Magnetic Field
Highlights
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe, alongside gravity, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force.
Electromagnetic forces operate at all size scales but predominantly affect our human scale.
Opposite electric charges attract each other, while like charges repel.
Magnetic forces involve attraction between north and south poles of magnetic dipoles.
Magnetism and electricity are interconnected; moving a magnet can generate charge, and moving a charge can create a magnetic field.
An electromagnet is created by running current through a wire wrapped around a non-magnetic metal.
A moving charge can generate a magnetic field, demonstrating the unity of electromagnetism.
A large generator can produce electricity by spinning an electromagnet.
Electromagnetic forces are billions of times stronger than gravity in terms of force.
Coulomb’s Law quantifies the force between electric charges, with larger charges resulting in greater attraction or repulsion.
Electromagnetic forces are essential in holding together cells, objects, and even influencing the levitation of a person with an industrial magnet.
Electromagnetic forces are stronger than gravity at the human scale, which is why we don't fall through the Earth.
The strength of electromagnetism is connected to the size of the charge or the magnetic dipole and their movement.
An industrial magnet can lift a person, demonstrating the dominance of electromagnetic forces at the human scale.
Turning off the electromagnet causes the person to fall, illustrating the control over electromagnetic forces.
Electromagnetic forces are what primarily dominate our planet at the human scale, influencing our daily lives.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: