Electromagnetism 101 | National Geographic
TLDRElectromagnetism, one of the four fundamental forces of nature, is the subject of a captivating video that delves into its multifaceted role in the universe. The video explains how all matter possesses an electric charge, leading to the formation of atoms through attractive and repulsive forces. When atoms become charged, they generate an electric field, which can transform into a magnetic field when the particles move, creating a flowing electric current. This interaction between electric and magnetic fields can produce a self-sustaining electromagnetic field that radiates energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma radiation. The video also highlights the geodynamo effect, where the Earth's core of liquid metals generates electric currents, producing magnetic fields that turn the planet into a giant electromagnet, providing a protective shield against harmful space radiation. This fundamental force not only drives daily applications but also maintains the cohesion of the world we live in.
Takeaways
- 🧲 Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature that generates light and energy and holds atoms and matter together.
- 🔋 All matter has an electric charge, which can be positive, negative, or neutral, and opposite charges attract while like charges repel.
- 💡 When atoms gain a charge through electron transfer, an electric field forms, leading to the potential for a magnetic field if the charged particles move.
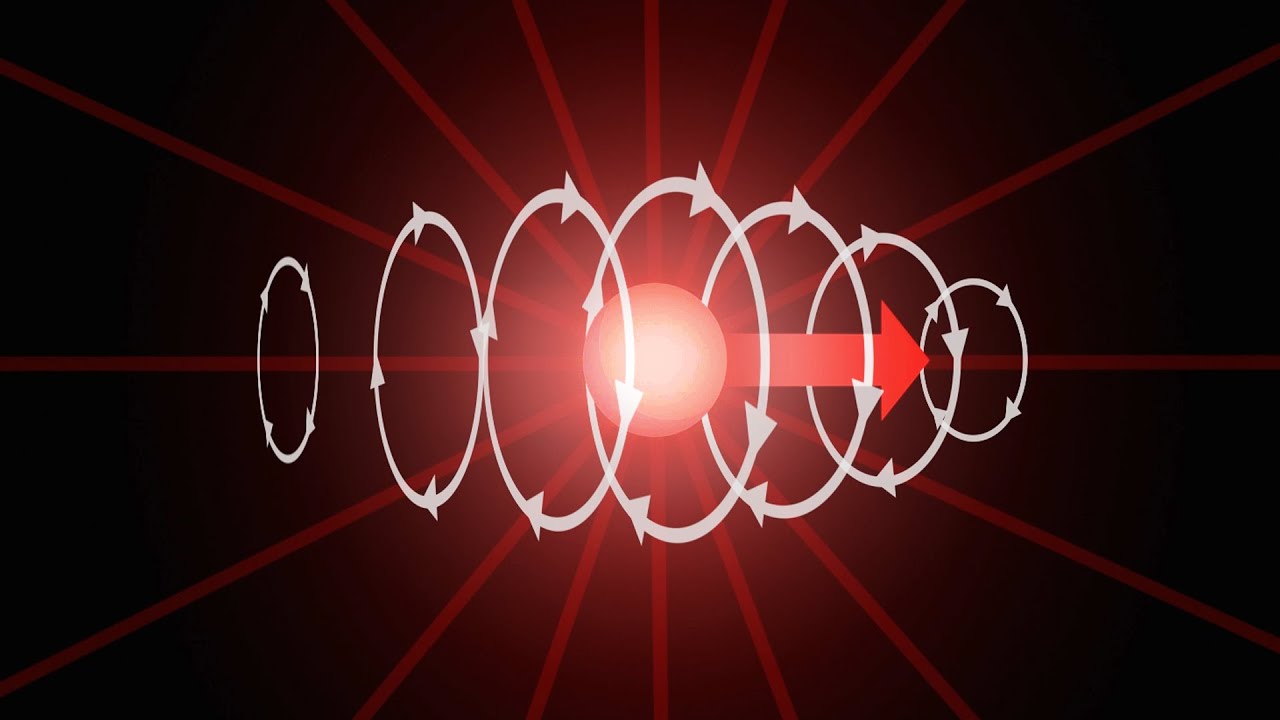
- 🔄 Interacting electric and magnetic fields can produce and sustain each other, creating an electromagnetic field that transmits energy as electromagnetic waves.
- 🌈 The intensity of electromagnetic radiation is determined by its frequency, which makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
- 👀 Visible light is located in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum, with invisible waves on either side, including radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
- 🌌 High-frequency waves like ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma radiation can pass through the human body, making them useful for medical applications.
- ⚙️ Electromagnetism has practical applications in daily life and is the driving force behind the planet's geodynamo, which generates Earth's magnetic field.
- 🌍 The geodynamo is caused by the movement of liquid metals within Earth's core, creating electric currents and magnetic fields that protect the planet from harmful space radiation.
- 🛡️ Earth's magnetic field acts as a shield against harmful radiation, allowing life on Earth to thrive under the influence of electromagnetism.
- ✨ The study of electromagnetism is crucial for understanding the interactions between electric and magnetic fields and their role in the universe.
Q & A
What is one of the four fundamental forces of nature?
-Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
What is the role of electromagnetism in the formation and maintenance of atoms and matter?
-Electromagnetism generates light and energy, and it holds atoms, matter, and the world together through the interactions between electric and magnetic fields.
What are the three possible states of an electric charge in all matter?
-The three possible states of an electric charge in all matter are positive, negative, or zero.
How do opposite and like charges interact in terms of attraction and repulsion?
-Opposite charges attract each other, while like charges repel each other.
What occurs when atoms gain a positive or negative charge through the transfer of electrons?
-When atoms gain a positive or negative charge through the transfer of electrons, a measurable electric field is formed.
What happens when electrically charged particles move?
-When electrically charged particles move, the electric field becomes a flowing electric current, forming a magnetic field around it.
Under what circumstances can electric and magnetic fields produce and sustain each other?
-Under the right circumstances, interacting electric and magnetic fields can continuously produce and sustain one another, generating an electromagnetic field.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum and how is it related to the intensity of radiation?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies that make up different types of electromagnetic radiation. The intensity of this radiation is determined by its frequency.
Where is visible light located in the electromagnetic spectrum?
-Visible light is located near the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What are some examples of low-frequency and high-frequency electromagnetic waves?
-Low-frequency waves include radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves. High-frequency waves include ultraviolet, X, and gamma radiation.
How do high-frequency electromagnetic waves differ from low-frequency waves in terms of their interaction with the human body?
-High-frequency electromagnetic waves can pass through the human body, making them useful for medical applications, unlike low-frequency waves.
What is a geodynamo and how does it relate to Earth's magnetic field?
-A geodynamo is a process involving the churning and flow of liquid metals within Earth's core, generating electric currents that produce magnetic fields encompassing the entire planet, thus turning the planet into a giant electromagnet.
What protective layer is created by Earth's electromagnetism that shields us from harmful space radiation?
-Earth's electromagnetism creates a protective layer around the planet that shields us from the most harmful radiation in space.
Outlines
🧲 Fundamentals of Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, responsible for creating light and energy, and maintaining the structure of atoms and matter. It is a branch of physics that explores the interactions between electric and magnetic fields. All matter possesses an electric charge, which can be positive, negative, or neutral. Charges of different signs attract each other, while like charges repel. This interaction is crucial for the formation and stability of atoms. When atoms become charged through electron transfer, an electric field is generated. Movement of these charged particles results in an electric current and a magnetic field. Under certain conditions, electric and magnetic fields can sustain each other, creating an electromagnetic field that radiates energy waves across the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum includes visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, and higher frequency waves like ultraviolet, X, and gamma radiation. Electromagnetism is not only essential for everyday technology but also powers the Earth's geodynamo, a process that involves the movement of liquid metals beneath the Earth's surface, generating electric currents and magnetic fields, effectively turning the planet into a giant electromagnet. This also results in a protective shield against harmful space radiation.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electromagnetism
💡Electric charge
💡Electric field
💡Magnetic field
💡Electromagnetic field
💡Electromagnetic spectrum
💡Visible light
💡Geodynamo
💡Magnetic poles
💡Radiation
💡Medical applications
Highlights
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, responsible for generating light and energy.
It holds atoms, matter, and the world together through its interactions between electric and magnetic fields.
All matter possesses an electric charge, which can be positive, negative, or neutral.
Opposite electric charges attract, while like charges repel each other.
Electric forces are crucial for the formation and cohesion of atoms.
A transfer of electrons between atoms can lead to a measurable electric field.
Movement of electrically charged particles creates a magnetic field around them.
Under certain conditions, electric and magnetic fields can produce and sustain each other, forming an electromagnetic field.
Electromagnetic fields transmit waves of electromagnetic energy or radiation.
The intensity of radiation is determined by its frequency, forming the electromagnetic spectrum.
Visible light is located in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Invisible electromagnetic waves surround visible light, including radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
High-frequency waves like ultraviolet, X, and gamma radiation can penetrate the human body, useful for medical applications.
Electromagnetism powers the planet, with a geodynamo effect deep within the Earth's core.
The geodynamo generates electric currents that produce magnetic fields, creating Earth's magnetic poles.
Earth's magnetic field acts as a protective shield against harmful space radiation.
Electromagnetism is not only fundamental to daily life but also to the structure and protection of our planet.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: