Physics 15 Torque (10 of 27) When Will A Car Tip Over?
TLDRThis engaging lecture explores the concept of torque and its relationship with the center of gravity and equilibrium in various scenarios. It explains why vehicles, particularly trucks with heavy loads, can tip over when the center of gravity is raised and the forces acting on them during turns cause a torque imbalance. The lecture uses the example of a car's center of gravity and how its position relative to the wheels determines stability. It also discusses the Leaning Tower of Pisa, illustrating how adding weights to one side can shift the center of gravity and prevent collapse. The importance of loading a car with heavy items on the bottom and lighter ones on top is highlighted to avoid raising the center of gravity and increasing the risk of tipping over. The summary concludes with the fundamental principle that the position of the center of gravity in relation to the support structure is crucial for maintaining equilibrium in objects, whether they are vehicles on the road or leaning towers.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The concept of torque and equilibrium are crucial in understanding why certain vehicles or structures do not tip over despite being at a steep angle.
- 🚘 Cars and trucks can remain stable on steep inclines if the center of gravity is positioned in such a way that it creates a counteracting torque, preventing the vehicle from tipping.
- 🚨 Trucks with heavy loads above the road deck can have a higher center of gravity, making them more prone to tipping over during sharp turns or when the forces act upon them in a certain way.
- ⚖️ The center of gravity (center of mass) of a vehicle plays a critical role in its stability; if the weight is distributed unevenly across the tires, it can lead to tipping.
- 📐 The line of action of a vehicle's total weight in relation to the wheel support is essential for determining if a car will tip over or remain stable.
- 🔄 A net torque in a counterclockwise direction on a car can help prevent it from tipping over, which is dependent on the weight distribution and the center of gravity.
- 🚧 If the center of gravity of a car passes through or to the right of the rightmost tire, no weight is being supported by the left tire, and the car is at the brink of tipping over.
- 🏰 The Leaning Tower of Pisa is an example of a structure that has managed to remain standing due to the strategic placement of its center of gravity relative to its support base.
- 🧱 To prevent structures like the Leaning Tower of Pisa from falling, heavy objects such as lead blocks have been used to shift the center of gravity to a more stable position.
- 📦 When loading a car, heavy items should be placed at the bottom and lighter ones on top to avoid raising the center of gravity, which can increase the risk of the vehicle tipping over.
- ⚠️ Placing heavy objects on the roof of a car raises the center of gravity and shifts it towards the unsupported side, making the vehicle more susceptible to tipping.
Q & A
Why do some cars, like trucks with heavy loads, tip over on steep angles?
-Trucks with heavy loads are prone to tipping over because the load raises the center of gravity. When turning, the forces acting on the truck can cause it to tip if the center of gravity shifts beyond the point of support.
How does the center of gravity (CG) relate to the equilibrium of a car on a slope?
-The car remains in equilibrium as long as the line of action of the total weight (from the CG) passes through or to the left of the outer support of the wheel. If this line shifts to the right of the wheel, the car is at risk of tipping over.
What happens when the weight of a car is distributed unevenly across its tires?
-When a car is angled on a slope, more weight is supported by the lower tire. If a pivot point is established and torques are summed, a net torque may develop that prevents the car from tipping over.
Why does placing heavy objects on the roof of a car increase the risk of it tipping over?
-Placing heavy objects on the roof raises the car's center of gravity. This shift makes the car more likely to tip over because it moves the CG relative to the support tire to the right, reducing the margin for stability.
What is the significance of the center of gravity's position in relation to the tower of Pisa's stability?
-The tower of Pisa remains standing as long as its center of gravity is to the left of the outermost support. If the CG shifts to the right of this point, the tower would fall due to the sum of torques causing it to topple.
How have efforts been made to prevent the tower of Pisa from falling over?
-To prevent the tower from falling, heavy lead blocks have been stacked on one side to shift the center of gravity to the left, keeping it within the stability threshold relative to the tower's supports.
What is the concept of equilibrium in the context of the lecture?
-Equilibrium refers to the state where the sum of torques (rotational forces) around a pivot point is zero, preventing an object from tipping over. It's dependent on the location of the center of gravity relative to the object's support.
How does the distribution of weight in a car affect its center of gravity?
-The distribution of weight directly affects the car's center of gravity. Heavier objects placed higher in the car raise the CG, while distributing the weight evenly or placing heavy objects low and light objects high keeps the CG low, enhancing stability.
What is torque in the context of the forces acting on a vehicle?
-Torque, in this context, refers to the rotational force that can cause an object to rotate around an axis. In vehicles, torques act around the pivot point of the wheel's contact with the ground and can cause the vehicle to tip over if unbalanced.
Why is it important to consider the center of gravity when loading a car?
-Considering the center of gravity when loading a car is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing the car from tipping over. A lower CG provides a wider base of support and makes the car less likely to tip when on an incline or during turns.
Can you explain how the concept of torque and center of gravity applies to objects other than vehicles?
-The concept applies to any object that needs to maintain balance or stability. For instance, the leaning tower of Pisa's stability is determined by the position of its center of gravity relative to its base. If the torque caused by the weight of the tower ever exceeds the support provided by its foundation, it would fall.
What would be the outcome if the center of gravity of a car during a turn shifts beyond the outermost point of the tire's support?
-If the center of gravity shifts beyond the outermost point of the tire's support during a turn, the car would experience an unbalanced torque that could cause it to tip over. This is because there would be no counterbalancing force to oppose the torque generated by the car's weight.
Outlines
🚗 Understanding Car Stability and Center of Gravity
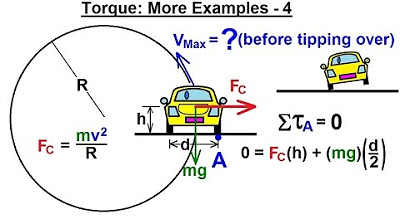
This paragraph discusses the relationship between torque and equilibrium concerning a vehicle's center of gravity. It explains why cars can remain stable on steep inclines without tipping over. The concept is illustrated by showing the center of gravity (represented by a dot) and its line of action relative to the car's wheels. The stability is maintained as long as the line of action of the car's total weight passes to the left of the outer wheel support. If the weight is distributed unevenly across the tires, it is shown that a pivot point can be established to calculate the net torque acting on the car, which in this case prevents it from tipping over. The paragraph also addresses scenarios where vehicles, particularly trucks with high centers of gravity, can tip over and uses the example of the Leaning Tower of Pisa to further explain the importance of the center of gravity's position.
🏗️ Strategies to Prevent Structural Collapse
The second paragraph delves into efforts to prevent the collapse of structures like the Leaning Tower of Pisa. It emphasizes the critical role of the center of gravity's position in relation to the structure's support base. The paragraph describes how adding weight, such as lead blocks, to one side of the tower can shift the center of gravity and maintain its stability. It also touches on the potential future collapse of the tower if its center of gravity shifts too far, causing the sum of torques to topple it. The summary concludes with practical advice on loading a car by placing heavy objects at the bottom and lighter ones on top to keep the center of gravity low and prevent the vehicle from tipping over.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Torque
💡Equilibrium
💡Center of Gravity
💡Stability
💡Base of Support
💡Truck Stability
💡Leaning Tower of Pisa
💡Weight Distribution
💡Tipping Over
💡Heavy Objects
💡Loading a Car
Highlights
Exploring the connection between torque and equilibrium in the center of gravity
Cars can be at a steep angle without tipping over due to the location of the center of gravity
Trucks with heavy loads above the road deck can tip over when turning, raising the center of gravity
The center of gravity of a car is represented by a dot in the lecture
The line of action of the total weight of the car determines if it will tip over
Weight is distributed across the two tires, with more weight on the lower tire at an angle
Net torque causes a counterclockwise force preventing the car from tipping over
If the center of gravity passes through the right tire, the car is at the point of tipping over
No counterbalancing torque if all weight is on one tire
Location of the center of gravity relative to the support determines if an object will fall over
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is kept from falling by stacking lead blocks on one side
If the center of gravity shifts too far, the torque will cause the tower to fall
Heavy objects in a car should be placed on the bottom to avoid raising the center of gravity
Putting a heavy object on the roof raises the center of gravity and increases the risk of tipping over
Equilibrium and center of gravity concepts apply to cars on the road and leaning towers
Understanding the center of gravity is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing accidents
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: