HMS Victory - The Total Guide (All Parts)
TLDRThe video script offers an in-depth exploration of HMS Victory, a first-rate ship-of-the-line during the Napoleonic Wars, and its pivotal role in British naval history. It details the ship's construction, armament, and crew composition, highlighting the strategic and economic impact of the Royal Navy on the war. The narrative delves into the ship's most famous battle at Trafalgar, where Admiral Nelson's leadership secured a legendary victory. The script also describes the daily life and discipline aboard the ship, the intricacies of naval combat, and the eventual conversion of Victory into a museum ship. It emphasizes the importance of the Royal Navy in global power dynamics and the preservation efforts ensuring Victory's legacy as a historical monument.
Takeaways
- ⚓️ Britain's Royal Navy was the dominant naval power during the Napoleonic Wars, playing a crucial role in Napoleon's defeat.
- 🏆 Napoleon Bonaparte was a formidable adversary on land, but at sea, the British Royal Navy held sway, ensuring British strategic superiority.
- 🚢 The HMS Victory, a first-rate ship-of-the-line, was a symbol of British naval power and is now the world's oldest commissioned warship.
- 🌊 The Battle of Trafalgar was a significant naval battle where the Royal Navy secured a lasting strategic advantage against the combined fleets of France and Spain.
- 🔨 HMS Victory was armed with 104 guns and had a crew complement of around 820 men, showcasing the massive scale of naval warfare during the period.
- 🛠️ HMS Victory was constructed with materials from various sources, including British oak and New England pine, reflecting the global nature of Britain's resources.
- 🎖️ Vice Admiral Nelson, who led the British attack at Trafalgar, is closely associated with HMS Victory and is remembered for his heroic sacrifice.
- 🧭 The ship's navigation and operation required a complex hierarchy of officers and crew members, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
- 🌐 The Royal Navy's global reach was facilitated by the navy's ability to protect trade, seize colonies, and project power, which was essential for Britain's economic and military strength.
- 🔥 The ship's magazine held large quantities of gunpowder, which had to be carefully managed to prevent disaster in the event of fire or water ingress.
- ⏳ HMS Victory has been preserved and is now a museum ship, offering visitors a glimpse into the past and the opportunity to understand the era's naval warfare.
Q & A
In which year did Britain fight a significant naval battle off the coast of Spain?
-Britain fought a significant naval battle off the coast of Spain in 1805 at Cape Trafalgar.
What was the name of the ship that played a central role in the Battle of Trafalgar?
-HMS Victory played a central role in the Battle of Trafalgar.
How many men did HMS Victory typically have on board during the Napoleonic Wars?
-During the Napoleonic Wars, HMS Victory typically had around 820 men on board.
What was the primary purpose of copper-sheathing for Victory's hull?
-Copper-sheathing for Victory's hull served to protect the timbers from shipworm, barnacles, and weeds, maintaining the ship's solidity and streamlined profile.
What was the total area of HMS Victory's sails and how was it comparable?
-The total area of HMS Victory's sails was 6,500 square yards, which is about the size of a football pitch.
What was the role of the 'loblolly boys' on HMS Victory?
-The 'loblolly boys' were surgeon's assistants on HMS Victory, known for feeding soup to patients and also slept in the sick bay in their hammocks.
How were the British Royal Navy's signals communicated before the age of electricity?
-The British Royal Navy's signals were communicated using colored flags arranged in various combinations to convey messages, and at night, by pre-agreed combinations of gunfire, colored lanterns, and rockets.
What was the significance of HMS Victory's three largest decks?
-HMS Victory's three largest decks were significant as they were all about her guns, indicating the ship's primary function as a floating gun battery for naval combat.
What was the term used to describe the process of sailing a ship against the wind?
-The process of sailing a ship against the wind was referred to as 'tacking' or 'wearing ship'.
How did the crew of HMS Victory sleep and where were they located?
-The crew of HMS Victory slept in hammocks, which were strung up from the ship’s beams on the middle or lower gun decks, with their hammocks suspended between the guns, just 16 inches apart.
What was the main reason for the Royal Navy mutiny at Spithead in 1797?
-The main reason for the Royal Navy mutiny at Spithead in 1797 was a strike for better pay, as sailors hadn't had a pay rise in more than a century.
What is the current status and purpose of HMS Victory?
-HMS Victory is currently undergoing a major 10-year conservation project and serves as a museum ship, open to the public, and is considered a unique memorial to the age of naval warfare during the Napoleonic era.
Outlines
🏴☠️ Naval Supremacy and the Battle of Trafalgar
The first paragraph introduces the historical context of Britain's naval dominance during the Napoleonic Wars against France. It highlights the significance of the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, where the Royal Navy defeated the combined fleets of France and Spain, ensuring British naval superiority for the remainder of the war. The paragraph also describes the multifaceted role of the Royal Navy in protecting the homeland, projecting power into Europe, and undermining enemy economies. It introduces HMS Victory, a first-rate ship of the line, and its enduring legacy as the world's oldest commissioned warship on display in Portsmouth.
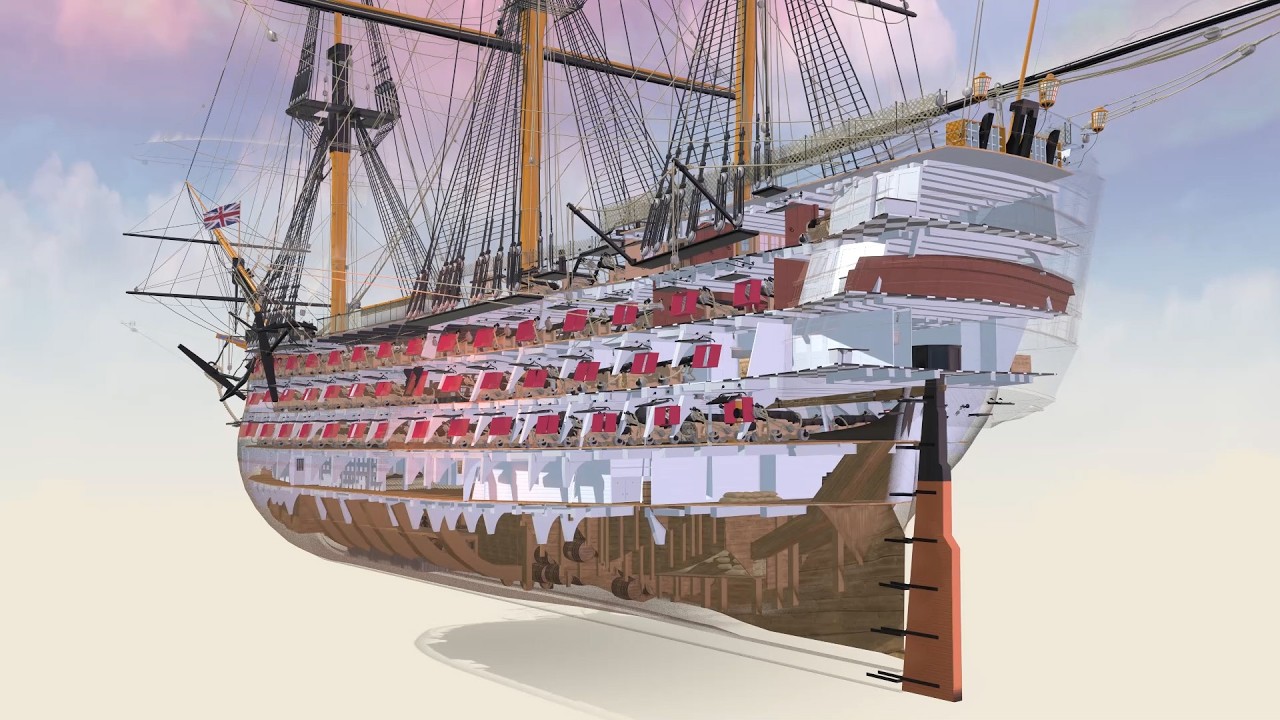
🛥️ Anatomy and Operation of HMS Victory
The second paragraph delves into the intricate details of HMS Victory's structure, operation, and crew. It outlines the ship's vast size, speed, and the technology used to maintain its efficiency, such as copper-sheathing to protect the hull. The paragraph explains the nautical terms for the ship's directions and parts, the composition of the crew, and the various roles each member had to play. It also describes the ship's rigging, masts, sails, and the importance of wind as a propulsion source, painting a picture of the complexity involved in operating a ship of this magnitude.
🏺 The Decks and Functioning of HMS Victory
This paragraph explores the different decks and sections of HMS Victory, detailing their specific uses and the activities that took place on each. It covers the fo'c'sle, waist, quarterdeck, and poop deck, highlighting the ship's bell, guns, boats, and the command center. The paragraph also discusses the ship's navigation and steering mechanisms, the signal system for communication, and the purpose of each gun deck, emphasizing the ship's primary function as a floating gun battery.
🎖️ Admiral's Quarters and Shipboard Life
The fourth paragraph focuses on the quarters and life of the Admiral and crew on HMS Victory. It describes the Admiral's luxurious quarters, the process of clearing the ship for action, and the sleeping arrangements for the crew. The paragraph also provides insight into the crowded and challenging living conditions on the lower decks and the various roles and nationalities present within the crew, offering a glimpse into the social dynamics and daily life aboard the ship.
🍽️ Victualling and Storage on HMS Victory
The fifth paragraph discusses the storage and provisions on HMS Victory, including the ship's hold and its capacity to store supplies for extended periods at sea. It details the types of food stored, the precautions taken to maintain the safety of the gunpowder magazine, and the ship's ballast system. The paragraph also covers the ship's pumping mechanisms for managing water ingress and the anchoring process, revealing the logistical complexities of maintaining a ship of this size.
🏆 The Crew and Their Duties on HMS Victory
The sixth paragraph provides an in-depth look at the composition of HMS Victory's crew, their ranks, and responsibilities. It outlines the hierarchy from commissioned officers to ship's boys, the process of becoming an officer, and the various specialists on board. The paragraph also describes the organization of the crew into watches and divisions, the international nature of the crew, and the methods of recruitment, including volunteering and impressment.
⛵️ Sailing Techniques and Maneuvering
This paragraph examines the techniques and skills required for sailing and maneuvering a ship like HMS Victory. It covers the ship's optimal sailing points, handling of sails, and the effects of wind on the ship's movement. The paragraph explains the methods of tacking and wearing for sailing against the wind, the process of anchoring, and the use of kedging and warping for inshore maneuvering. It also touches on the strategic considerations of wind direction in naval combat.
💥 Naval Combat Tactics and Boarding Actions
The seventh paragraph delves into the tactics and conduct of naval combat, including the importance of wind direction, the process of clearing the ship for battle, and the various types of ammunition used. It describes the different strategies employed by British and French ships, the concept of raking, and the use of boarding tactics to finish a battle. The paragraph also highlights the rarity of major fleet actions and the typical routine and maintenance tasks that filled the time between engagements.
🕰️ Daily Routine and Discipline on a British Warship
The eighth paragraph outlines the daily routine aboard a British warship, from the marking of time by the ship's bell to the sleeping arrangements and meals. It describes the weekly rituals, the types of food consumed, and the strict discipline enforced by the Articles of War. The paragraph also discusses the punishments for various crimes, the infamous navy grog, and the mutinies that occurred within the Royal Navy, providing a comprehensive view of life at sea during the Napoleonic era.
🏛️ HMS Victory's Legacy and Conservation
The ninth paragraph reflects on the legacy of HMS Victory and her role as a museum ship. It discusses the ship's transition to a reserve status post-war, her near escape from being scrapped, and her current status as a flagship and memorial. The paragraph also details the ongoing conservation efforts to preserve the ship for future generations, including structural repairs and public access to the conservation works. It concludes with acknowledgments to various institutions and supporters of the project.
📚 Acknowledgments and Further Maritime History
The final paragraph expresses gratitude to the National Museum of the Royal Navy and other institutions for their contributions to the video series. It invites viewers to visit HMS Victory during her conservation project and learn from the experts on site. The paragraph also recommends a visit to the Royal Museums Greenwich to explore Britain's maritime history further and acknowledges the contributions of artists and patrons who have supported the channel.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Napoleonic Wars
💡HMS Victory
💡Battle of Trafalgar
💡Ship-of-the-line
💡Nelson's flagship
💡Royal Navy
💡Copper-sheathing
💡Rigging
💡Gun deck
💡Press gangs
💡Naval tactics
Highlights
In 1805, Britain's Royal Navy was the world's largest naval power with 136 ships-of-the-line and 110,000 men at sea.
The Battle of Trafalgar off Cape Trafalgar was a strategic naval victory that ensured British naval superiority for the remainder of the war with France.
HMS Victory, a first-rate ship-of-the-line, was the most powerful class of warship afloat, boasting 104 guns and a crew of 820 men.
HMS Victory's construction began in 1759 at Chatham royal dockyard and was designed by Sir Thomas Slade, a leading naval architect.
The ship was built with wood from around 6,000 trees, predominantly British oak, and was launched in 1765.
HMS Victory first saw action in the American War of Independence and later led the British attack at Trafalgar, securing its place in naval history.
The ship's top speed was 10 knots, enhanced by copper-sheathing that protected the hull and kept the ship streamlined.
HMS Victory had 37 sails with a total area of 6,500 square yards, equivalent to the size of a football pitch.
The ship's crew was highly organized, with every man and boy having a designated role, from the admiral to the ship's boys.
HMS Victory's structure included several decks such as the fo'c'sle, waist, quarterdeck, and poop deck, each serving specific functions.
The ship was equipped with the latest naval innovation in 1780, copper-sheathing, which protected the timbers from shipworm and marine growth.
HMS Victory's crew was multinational, with about 10% being foreigners, including Americans and West Indians.
Discipline on board was strict, with severe punishments for crimes such as drunkenness, theft, and mutiny, many punishable by death.
The Battle of Trafalgar in 1805 had 820 men aboard HMS Victory, which was under the command of Admiral Nelson.
HMS Victory is now a museum ship and a famous visitor attraction in Portsmouth, undergoing a major 10-year conservation project.
The ship's bell marked the change of watch and was a central part of the crew's daily routine, with the day beginning at noon.
HMS Victory's crew slept in hammocks strung up between the guns, with about half the crew on duty while the other half rested.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Could You Survive in the Lord Nelson’s Royal Navy?

Horatio Nelson: Britain’s Most Beloved Sailor

How Scharnhorst was Sunk: Battle of the North Cape 1943
How an 18th Century Sailing Warship Works

How America Grew The Most Powerful Navy In The World | War Factories | Timeline

Ghost Ship Mary Celeste: The 150 Year Mystery
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: