Chemistry Lesson: Types of Chemical Reactions
TLDRIn this informative video, Dr. Kent delves into the five primary types of chemical reactions, offering a clear and concise overview. Starting with combination or synthesis reactions, where multiple substances unite to form a new one, such as zinc and chlorine creating zinc chloride. Decomposition reactions are the reverse, where a single substance breaks down into two or more, exemplified by ammonium chloride decomposing into ammonia and hydrogen chloride. Single displacement reactions involve one element replacing another in a compound, as seen with zinc displacing copper in copper(II) chloride. Double displacement reactions feature two elements swapping places, such as in the reaction between silver nitrate and potassium bromide, resulting in the formation of silver bromide and potassium nitrate. Lastly, combustion reactions involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, as demonstrated by the burning of methane and propane. The video provides several examples for each reaction type, simplifying complex chemical concepts for viewers and encouraging further exploration of the subject.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The five main types of chemical reactions discussed are synthesis (combination), decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion.
- 🔬 Synthesis reactions involve two or more substances combining to form a new substance, such as zinc and chlorine combining to make zinc chloride.
- 📉 Decomposition reactions are the reverse of synthesis, where one substance breaks down into two or more substances, like ammonium chloride decomposing into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas.
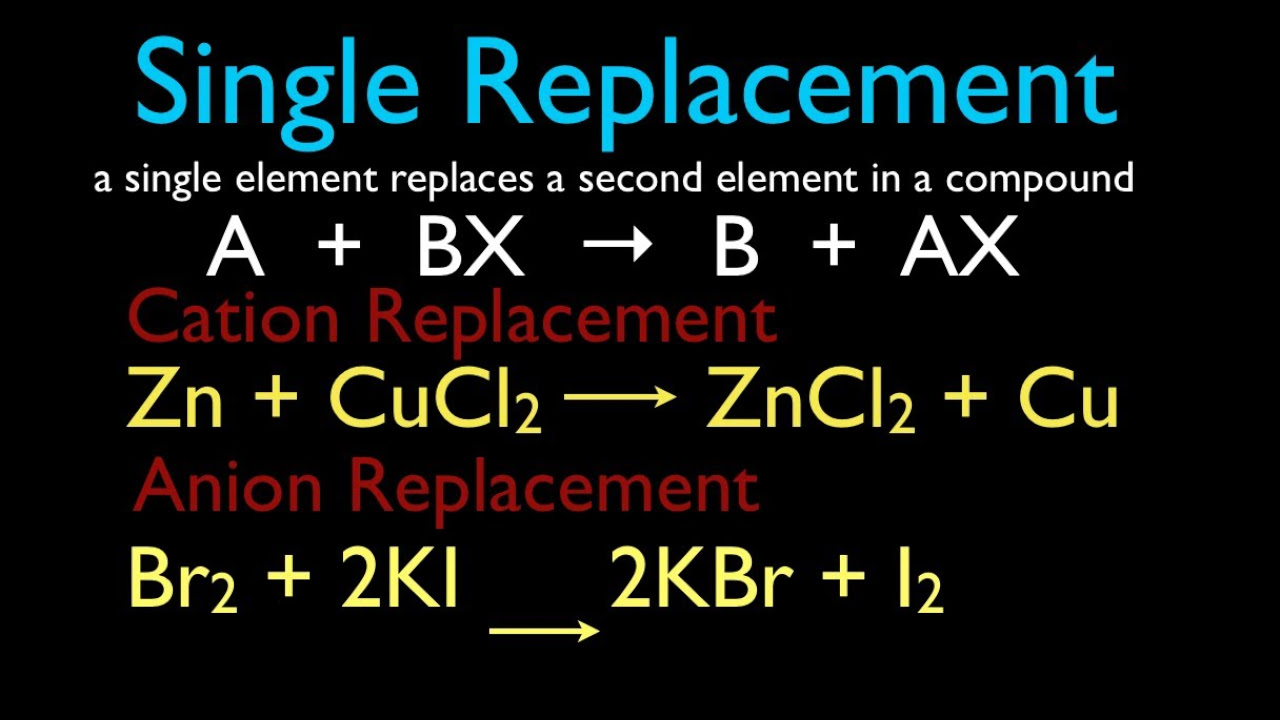
- 🔄 Single displacement reactions occur when one element in a compound is replaced by another, resulting in a new element and compound, such as zinc displacing copper in copper(II) chloride.
- 🔄 Double displacement involves two elements being exchanged between two compounds, forming two new compounds, exemplified by silver nitrate and potassium bromide forming silver bromide and potassium nitrate.
- 🔥 Combustion reactions involve a hydrocarbon (a compound with hydrogen and carbon) reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, like the burning of methane or propane.
- 🌐 To identify the type of reaction, one must look at the reactants and products and determine if they involve combination, decomposition, displacement, or combustion.
- ⚖️ Decomposition is characterized by one substance forming multiple products, which is distinct from combination reactions where multiple reactants form a single product.
- 🛡️ Single displacement is identified by one element moving from one compound to another, while in double displacement, two elements switch places between two compounds.
- 🔍 The script provides examples of each reaction type to illustrate the differences and help in understanding the underlying principles.
- 📚 Further specialized types of reactions will be discussed in future lessons, encouraging viewers to subscribe for updates.
- ✍️ Dr. Kent invites viewers to engage by leaving comments, fostering a community of learners interested in chemistry.
Q & A
What are the five main types of chemical reactions discussed in the video?
-The five main types of chemical reactions discussed are combination (synthesis), decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
What is a combination or synthesis reaction?
-A combination or synthesis reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
How does a decomposition reaction differ from a combination reaction?
-A decomposition reaction is the opposite of a combination reaction. It involves one substance breaking down into two or more substances.
Can you explain a single displacement reaction?
-A single displacement reaction occurs when one element in a compound is replaced by another element. It follows the general form A + BC → AC + B, where element C is displaced from compound BC and combines with A.
What happens in a double displacement reaction?
-In a double displacement reaction, two compounds exchange parts to form two new compounds. The general form is AB + CD → AD + CB, where elements B and D are displaced and form new compounds with A and C, respectively.
What is a combustion reaction and what are its key components?
-A combustion reaction involves a hydrocarbon (a compound containing hydrogen and carbon) burning in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water.
What is the general form of a single displacement reaction?
-The general form of a single displacement reaction is A + BC → AC + B, where element C is displaced from compound BC and forms a new compound AC with A.
What is the general form of a double displacement reaction?
-The general form of a double displacement reaction is AB + CD → AD + CB, where elements B and D are displaced and form new compounds with A and C, respectively.
How does the reaction between zinc and chlorine illustrate a combination reaction?
-The reaction between zinc and chlorine, which produces zinc chloride (Zn + Cl2 → ZnCl2), illustrates a combination reaction because two elements, zinc and chlorine, combine to form a single new compound, zinc chloride.
What is the difference between a combustion reaction and a combination reaction involving carbon and oxygen?
-While both reactions involve carbon and oxygen, a combustion reaction specifically involves a hydrocarbon (a compound with hydrogen and carbon) and oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water. A combination reaction, on the other hand, does not necessarily involve a hydrocarbon and can involve any two substances combining to form a new substance.
What is the role of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide in a double displacement reaction?
-In a double displacement reaction involving hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the hydroxide ion (OH-) from sodium hydroxide combines with the hydrogen ion (H+) from hydrochloric acid to form water (H2O), and the remaining sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions combine to form sodium chloride (NaCl).
How can you identify a decomposition reaction from the given examples?
-A decomposition reaction can be identified by the breakdown of one substance into two or more substances. For example, ammonium chloride decomposing into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas, or water decomposing into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas when electricity is passed through it.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to Chemical Reactions
Dr. Kent introduces the topic of chemical reactions, focusing on five main types: synthesis (combination), decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion. He explains each type with a general form and provides examples, such as zinc combining with chlorine to form zinc chloride for synthesis, ammonium chloride decomposing into ammonia and hydrogen chloride for decomposition, zinc displacing copper in copper(II) chloride for single displacement, silver nitrate reacting with potassium bromide to form silver bromide and potassium nitrate for double displacement, and methane reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water for combustion.
🧪 Examples and Classification of Reactions
The video continues with examples to illustrate each reaction type further. Carbon combining with oxygen to form carbon dioxide is a combination reaction, not combustion, as it lacks hydrogen. Copper(II) chloride reacting with sodium sulfide to form copper(II) sulfide and sodium chloride is a double displacement reaction, as the sulfate and chloride ions switch places. Nickel(II) sulfite decomposing into nickel oxide and sulfur dioxide is a decomposition reaction, as one substance breaks down into two. A carbon and hydrogen containing compound (hydrocarbon) reacting with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water is a combustion reaction. Lastly, calcium reacting with lead(II) chloride to form calcium chloride and lead is a single displacement reaction, as the chloride ion is displaced from lead to calcium.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemical Reactions
💡Combination Reaction
💡Decomposition Reaction
💡Single Displacement Reaction
💡Double Displacement Reaction
💡Combustion Reaction
💡Hydrocarbon
💡Zinc Chloride
💡Ammonium Chloride
💡Magnesium Iodide
💡Sodium Hydroxide
Highlights
Dr. Kent introduces five main types of chemical reactions in the video.
Combination or synthesis reactions involve two or more substances combining to form a new substance.
Decomposition reactions are the reverse of combination, where one substance breaks down into two or more.
Single displacement reactions involve one substance being displaced by another in a compound.
Double displacement reactions occur when two different substances in compounds exchange places.
Combustion reactions involve hydrocarbons burning with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Examples of combination reactions include zinc plus chlorine to form zinc chloride and iron with sulfur to form iron sulfide.
Decomposition is demonstrated by ammonium chloride breaking down into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas.
Water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas through electrolysis.
In single displacement, zinc displaces copper in copper(II) chloride to form copper and zinc chloride.
Magnesium metal reacts with hydroiodic acid in a single displacement to produce magnesium iodide and hydrogen gas.
Double displacement is exemplified by silver nitrate reacting with potassium bromide to form silver bromide and potassium nitrate.
Acid-base reactions are a specialized type of double displacement, such as hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide forming sodium chloride and water.
Combustion is illustrated by methane gas reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Propane gas, another hydrocarbon, also combusts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
Carbon combining with oxygen to form carbon dioxide is a combination reaction, not a combustion reaction.
Copper(II) chloride and sodium sulfide undergo a double displacement reaction to form copper(II) sulfide and sodium chloride.
Nickel(II) sulfite decomposes into nickel oxide and sulfur dioxide gas in a decomposition reaction.
A carbon and hydrogen containing compound reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water is a combustion reaction.
Calcium displaces lead in lead(II) chloride to form calcium chloride and lead in a single displacement reaction.
Dr. Kent encourages viewers to subscribe for future videos on more specialized types of chemical reactions.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

5 Types of Chemical Reactions (Chemistry) + Activity Series, Solubility Rules
Chemical Reactions (2 of 11) Single Replacement Reactions, An Explanation

Types of Chemical Reactions

Classifying Types of Chemical Reactions Practice Problems

Chemical Reaction (5 of 11) Synthesis Reactions, an Explanation

Chemical Reactions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: