The Great Picnic Mix Up: Crash Course Kids #19.1
TLDRThe video script provides an engaging exploration of the concept of mixtures, particularly focusing on solutions. It begins with a relatable scenario of a summer picnic, highlighting the commonality between iced tea and fruit salad as mixtures. The script delves into the science behind these mixtures, explaining the difference between a simple mixture and a solution. It clarifies that in a solution, like sugar in water, the solute (sugar) is evenly distributed among the solvent (water), and this process does not create a new substance. The script also touches on the solubility of substances and the concept of saturation. It uses the example of soda water to illustrate that solutions can be separated back into their original components, emphasizing that mixtures do not always result in new substances. The summary concludes by encouraging viewers to enjoy their picnic while considering the scientific principles at play in their everyday experiences.
Takeaways
- 🍹 A mixture is created by combining two or more different substances.
- 🧪 Iced tea and fruit salad are examples of mixtures, but they differ in how their components are distributed.
- 🍬 Solutions are a type of mixture where the solute (like sugar) is evenly distributed among the solvent (like water).
- 🌬️ The air we breathe is a solution of gases, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
- 🥤 Soda water is a solution of carbon dioxide gas in liquid water, which can separate over time.
- 🔬 Mixing substances in a solution doesn't create a new substance; the components can be separated again.
- 🍓 Fruit salad is a non-uniform mixture where different fruits are combined but not evenly distributed.
- 🍯 The solubility of a substance refers to its ability to dissolve in another, with sugar being highly soluble in water.
- 🏺 Saturation is the point at which no more solute can dissolve in a solvent, leading to undissolved particles settling.
- 🧊 Heating a solution, like iced tea, can cause the solvent (water) to evaporate, leaving the solute (sugar) behind.
- 🧃 Solutions can be made from substances in the same or different states of matter, but they do not always result in new substances.
Q & A
What is a mixture?
-A mixture is created when two or more different substances are combined together.
What are the two main components of a solution?
-The two main components of a solution are the solute, which is the substance that dissolves, and the solvent, which is the substance in which the solute dissolves.
Why is the air we breathe considered a solution?
-The air we breathe is considered a solution because it is a mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, that are evenly distributed.
What happens when a solution is left undisturbed?
-In a solution like soda water, if left undisturbed with the lid off, the dissolved carbon dioxide will slowly float to the top and bubble away, eventually leaving behind plain water and carbon dioxide in the air as separate entities.
What is solubility?
-Solubility is the ability of a substance to be dissolved into another substance.
Why doesn't sand dissolve in water?
-Sand does not dissolve in water because it has low solubility in water, meaning it does not easily mix with water to form a homogeneous solution.
What is the point at which no more solute can dissolve in a solvent called?
-The point at which no more solute can dissolve in a solvent is called saturation.
Why is the fruit salad at the picnic not considered a solution?
-The fruit salad is not considered a solution because the particles that make it up are not equally distributed; you can get a spoonful of only one type of fruit at a time.
How is the sweet tea at the picnic an example of a solution?
-The sweet tea is an example of a solution because the particles of water and sugar are evenly distributed throughout the glass, with every sip containing both sugar and water.
Can the substances that make up a solution be separated again?
-Yes, the substances that make up a solution can be separated again. For instance, heating the iced tea solution can cause the water to evaporate, leaving the sugar behind.
Why do some mixtures not create new substances?
-Some mixtures, including solutions, do not create new substances because they are physical combinations of their constituent parts, which can be separated by physical means without a chemical reaction.
What happens to the carbon dioxide in soda water when you open the bottle?
-When you open a bottle of soda water, the carbon dioxide, which was dissolved under pressure, will slowly escape as bubbles, returning to its gaseous state and leaving the water.
Outlines
🍹 Introduction to Mixtures and Solutions
This paragraph introduces the concept of mixtures, which are created by combining two or more different substances. It distinguishes between mixtures and solutions, explaining that solutions involve the even distribution of solute particles within a solvent. The paragraph uses the examples of iced tea and fruit salad to illustrate these concepts, highlighting that while both are mixtures, only the iced tea is a solution due to the even distribution of its components. It also touches on the idea that solutions do not create new substances and can be separated back into their original components, and introduces the concept of solubility and saturation.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mixture
💡Solution
💡Solute
💡Solvent
💡Solubility
💡Saturation
💡Evaporation
💡
💡Gases in Air
💡Carbon Dioxide
💡Separation
💡Fruit Salad
Highlights
Summertime is associated with picnics and the enjoyment of iced tea and fruit salad, both of which are examples of mixtures.
A mixture is created by combining two or more different substances.
Mixtures can include items such as strawberries and bananas, raspberries and blackberries, or even non-edible combinations like cantaloupe and Legos.
A solution is a type of mixture where the solute (like sugar) is evenly distributed among the solvent (like water).
The solute is the substance that dissolves, while the solvent is the substance in which the solute dissolves.
Air is an example of a solution, composed of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Soda water is a solution of carbon dioxide gas in liquid water.
Mixing substances in solutions does not create a new substance; they can be separated back into their original forms.
The solubility of a substance refers to its ability to dissolve in another substance.
Sand has low solubility in water, whereas sugar has high solubility.
Saturation occurs when no more solute can dissolve into a solution, indicating there is no more room for the solute's particles among the solvent's particles.
Fruit salad is a non-solution mixture because its particles are not equally distributed.
Sweet tea is a solution because the particles of water and sugar are evenly distributed.
The substances in an iced tea solution can be separated by heating and evaporating the water, leaving the sugar behind.
Mixtures can be made of substances in the same or different states of matter.
Not all mixtures result in the creation of new substances, even if it may appear so.
The picnic scenario illustrates the concepts of mixtures, solutions, solubility, and saturation in a relatable way.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

All Mixed Up: Solutions and Mixtures - General Science for Kids!

SOLUTION || SOLUTE AND SOLVENT || MISCIBLE AND IMMISCIBLE LIQUIDS || SCIENCE VIDEO FOR CHILDREN

What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?
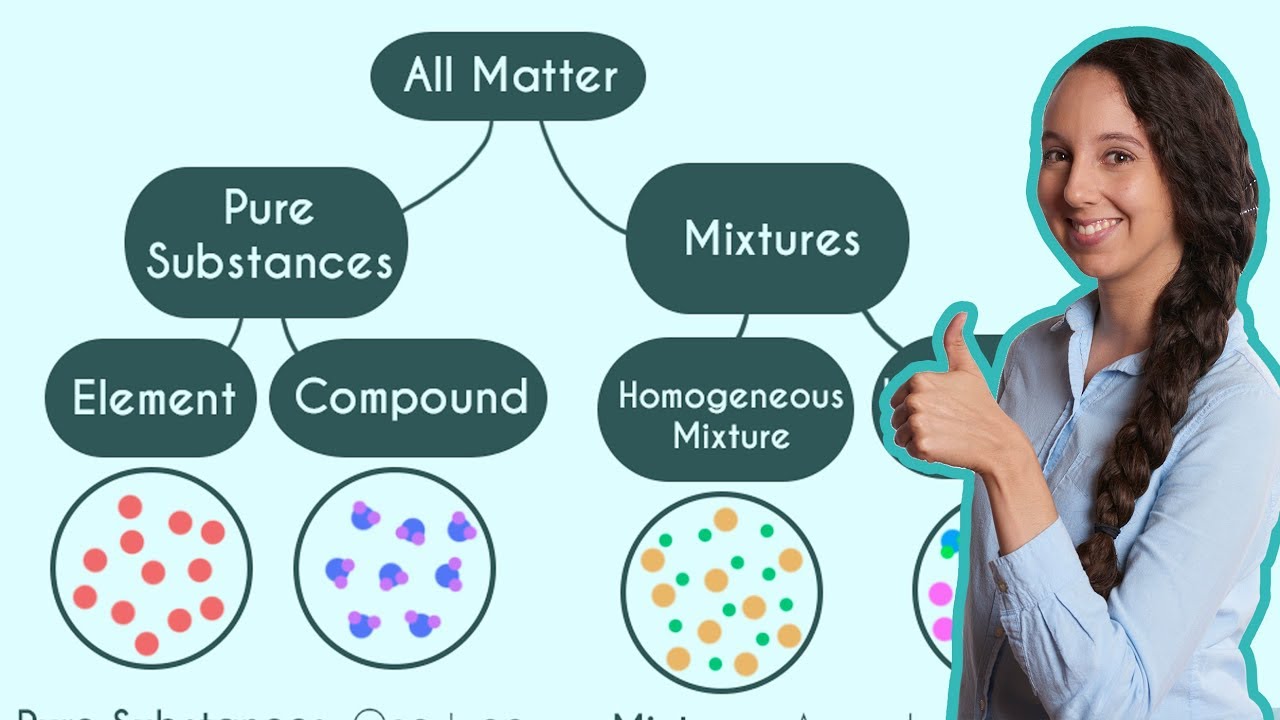
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Solution, Suspension and Colloid | Is Matter around us pure? | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: