02 - Overview of Circuit Components - Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor, Transistor, Diode, Transformer
TLDRThis script introduces fundamental electronic components and their functions in a circuit. It explains the roles of voltage sources, resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, LEDs, transistors, and transformers. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these components for analyzing and designing circuits, highlighting their applications in everyday technology like radios, cameras, and computers. It also touches on the historical significance of these components in advancing electronic technology.
Takeaways
- 🔋 The fundamental components of circuits include power sources (batteries), resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, LEDs, transistors, and transformers.
- 🔌 Power sources, usually depicted as a circle with plus/minus signs, provide the voltage necessary for a circuit to function.
- ⚡ Resistors, symbolized by a zigzag line, limit the flow of current in a circuit and are measured in ohms.
- 🔋 Capacitors store electrical charge and energy in an electric field, using units of farads, commonly microfarads or nanofarads.
- 🌀 Inductors store energy in a magnetic field, typically constructed as coils of wire, and are measured in henries.
- 🔄 Diodes are one-way current devices, allowing electricity to flow in one direction but blocking it in the opposite direction.
- 💡 Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are diodes that emit light when current passes through them, used in various indicator lights and displays.
- 🔩 Transistors function as electronic switches and amplifiers, with the ability to control larger currents and voltages based on smaller input signals.
- 🔄 Transformers are used to increase or decrease AC voltages, working through electromagnetic induction between two or more coils wound around a common core.
- 🔌 The direction of current flow in components like diodes and LEDs is indicated by a band or markings on the component, signifying the anode or positive side.
- 📈 Understanding these basic components is crucial for analyzing and designing circuits, with applications ranging from simple devices to complex computer systems.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a power source in a circuit?
-The primary purpose of a power source in a circuit is to provide energy or electrons, which are necessary for the circuit to function.
How does the size of a battery relate to its ability to deliver current?
-The size of a battery is directly related to its ability to deliver current. A larger battery, like a car battery, is physically larger because it needs to push more current out to provide energy to the motor for starting the car.
What is the symbol for a resistor in an electric circuit?
-The symbol for a resistor in an electric circuit is a zigzag line or squiggly line, which represents resistance to the flow of current.
What is the base unit of resistance and how is it represented?
-The base unit of resistance is the ohm, which is represented by the symbol 'Ω'.
What is a capacitor and how does it function?
-A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge. It functions by allowing electric charge to pile up on its plates, creating an electric field, and storing energy in that field.
What is the symbol for a capacitor in an electric circuit?
-The symbol for a capacitor in an electric circuit consists of two parallel lines that do not touch each other in the middle, representing the two plates of the capacitor.
What is an inductor and how does it store energy?
-An inductor is a coil of wire that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. The energy is stored due to the concentration of the magnetic field within the coil, which is enhanced by the turns of the wire.
What is the unit of measurement for an inductor and how is it represented?
-The unit of measurement for an inductor is the Henry, which is represented by the symbol 'H'.
How does a diode function in an electric circuit?
-A diode functions in an electric circuit by only allowing current to flow in one direction. It acts like a one-way switch, permitting current to pass through in the direction indicated by the band on the diode.
What is the primary function of a transistor in electronic devices?
-The primary function of a transistor in electronic devices is to act as an electronic switch and as an amplifier. It can switch on and off, controlling the flow of current, and it can amplify a signal, making it larger for output.
What is the role of a transformer in an electrical system?
-A transformer in an electrical system steps up or steps down the voltage levels. It allows an AC signal to be transformed from one voltage to another by using the principle of electromagnetic induction across its coils.
Outlines
🔌 Introduction to Circuit Components
The paragraph introduces the viewer to the basics of circuit analysis and the various components that are essential to understanding circuits. It emphasizes the importance of knowing these components to grasp the bigger picture of how circuits function. The speaker intends to discuss common circuit elements without involving complex math or theory, aiming to provide a general overview and motivation for further learning.
🔋 Power Sources and Batteries
This section delves into the first and most crucial component of any circuit: the power source. It explains that power sources, commonly depicted as batteries in diagrams, provide the energy necessary for the circuit to function. The speaker discusses different types of batteries, such as AAA, AA, C, and car batteries, and how their physical size correlates with the amount of current they can deliver. The concept of source voltage is introduced, along with the notation and units of voltage (volts). The paragraph also clarifies the direction of conventional current flow, which is opposite to the actual flow of electrons.
🛠️ The Role of Resistors
The speaker introduces resistors as the second most important circuit component, which are used to limit or control the flow of current in a circuit. Resistors are symbolized by a zigzag line, and their unit of measurement is ohms (Ω). The paragraph explains that resistors can be used to manage the distribution of current in complex circuits with multiple branches. The speaker also describes how resistors are physically small and can have varying resistance values, with color bands on their bodies to indicate their resistance value.
🔋 Capacitors: Energy Storage
Capacitors are introduced as devices that store electric charge, likened to a temporary battery. The speaker explains that capacitors consist of two parallel plates that accumulate charge, creating an electric field and storing energy. Although capacitors come in various shapes and sizes, their function remains the same: to store and release electric charge as needed. The unit of capacitance is the farad (F), but more commonly, microfarads (μF) or picofarads (pF) are used due to the large magnitude of a farad. The speaker also touches on practical applications of capacitors, such as in digital cameras' flash units, where capacitors store charge to produce a brief, intense burst of light.
🔌 Inductors and Magnetic Fields
Inductors are introduced as components that store energy in a magnetic field, which is created when an electric current passes through a coiled wire. The speaker explains that inductors are essentially coils of wire that, when energized, produce a concentrated magnetic field. The unit of measurement for inductance is the henry (H), and like with capacitors, smaller units such as microhenries (μH) and millihenries (mH) are also used. The speaker provides a basic physics lesson on how a magnetic field is generated around a straight wire when current flows through it and how this concept is applied in an inductor to store more energy. The potential applications and importance of inductors in circuits are also briefly mentioned.
🔄 Resonance and Radio Tuning
The speaker continues the discussion on inductors and introduces the concept of resonance, a phenomenon where a capacitor and an inductor work together in a circuit to transmit and receive radio signals. By changing the value of the capacitance, one can tune into different radio frequencies. The speaker explains that at the moment of resonance, the capacitor and inductor exchange energy back and forth, and the frequency of this exchange corresponds to the radio wave being received. This principle is used in older radios and other communication devices to select the desired signal to be amplified and sent to the speaker.
🔧 Diodes and LEDs: One-Way Current and Light Emission
The speaker introduces diodes, which are components that allow current to flow in only one direction, acting as one-way valves for electric current. The symbol for a diode is a triangle with a line, and the direction of the line indicates the allowed direction of current flow. The speaker also introduces light-emitting diodes (LEDs), which are diodes that emit light when current passes through them. LEDs are used in various indicator lights and can be found in numerous electronic devices. The speaker explains the function of diodes and LEDs and their practical applications in electronic circuits.
💡 Transistors: Electronic Switches and Amplifiers
Transistors are introduced as highly versatile components that can function as both electronic switches and amplifiers. The speaker explains that transistors can act like switches, allowing current to flow only when a certain condition is met, and as amplifiers, increasing the strength of an input signal. The symbol for a transistor is depicted with three terminals, and the speaker briefly describes how current flows through a transistor. The importance of transistors in modern technology is highlighted, with their presence in nearly all electronic devices and their role in the advancement of computer and memory technology.
🌀 Transformers: Voltage Regulation
The final component discussed is the transformer, which is used to increase or decrease voltage levels in a circuit, specifically for AC signals. The speaker explains the basic function of a transformer, involving two or more coils of wire wound around a common core. The changing current in the primary coil creates a varying magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil. By adjusting the number of turns in the coils, one can step up or step down the voltage as needed. The speaker mentions the practical application of transformers in power distribution, converting high-voltage power to safer levels for household use.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Circuit Analysis
💡Electrical Source
💡Resistor
💡Capacitor
💡Inductor
💡Diode
💡LED (Light Emitting Diode)
💡Transistor
💡Transformer
💡Electric Field
Highlights
Introduction to circuit analysis and its components without delving into complex math and theory.
Explanation of the necessity of a power source, such as a battery, for every circuit to function.
Differentiation between the physical size of batteries and their ability to deliver current.
Description of source voltage and its representation in circuit diagrams.
Clarification on the direction of current flow and the convention used in circuit diagrams.
Introduction to resistors as components that limit and control the flow of current in a circuit.
Explanation of the symbol and unit (ohms) for resistors, including color coding for different values.
Overview of capacitors as devices that store electric charge and their symbol representation.
Discussion on the practical use of capacitors, such as in digital cameras and their function in flash units.
Introduction to inductors, their basic construction as a coil of wire, and their unit of measurement (Henry).
Explanation of how inductors store energy in a magnetic field and their analogy to capacitors.
Description of the use of inductors and capacitors together in circuits, such as in radio technology.
Overview of diodes as one-way current devices and their symbol representation.
Explanation of LEDs (light-emitting diodes) and their function as both diodes and light sources.
Introduction to transistors, their critical role in modern electronics, and their functions as switches and amplifiers.
Description of the basic symbol and functionality of transistors in electronic circuits.
Discussion on transformers, their use in stepping up or down voltages, and their appearance on utility poles.
Summary of the importance of understanding basic circuit components for further study and practical applications.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
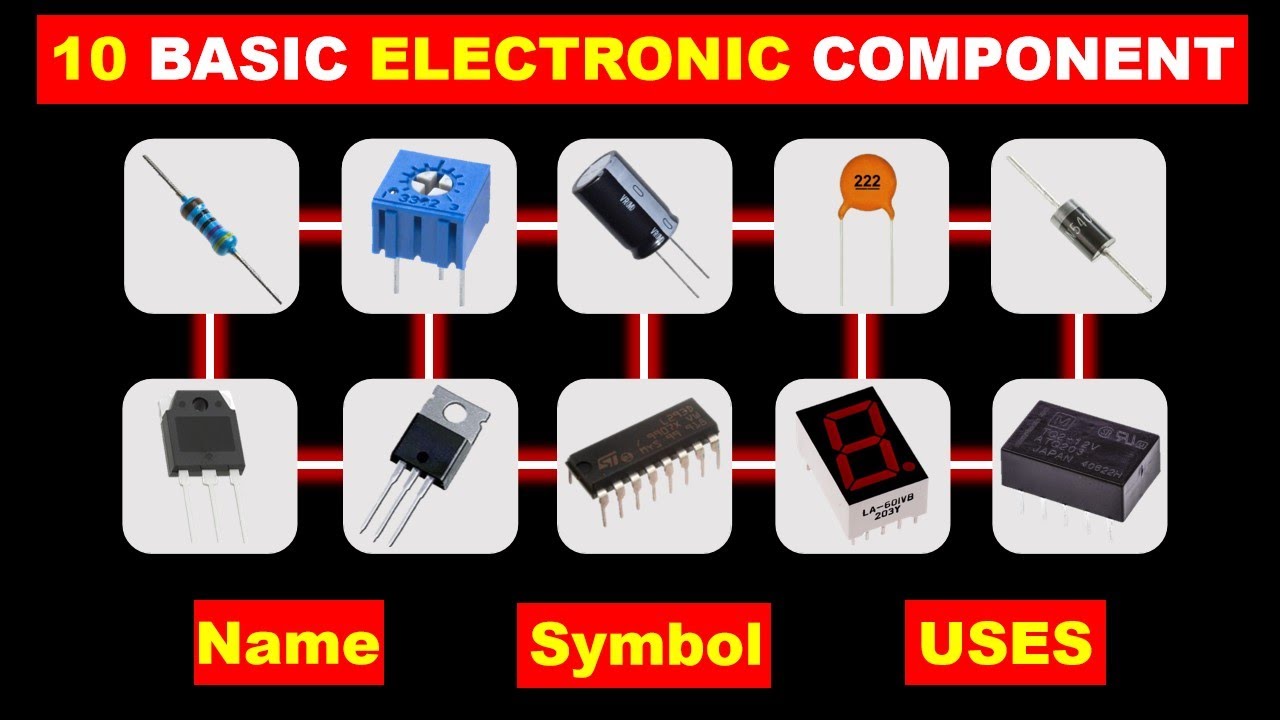
10 Basic Electronics Components and their functions @TheElectricalGuy

Basic Electronic Components With Symbols And Functionality.
12. LCR Circuits—DC Voltage

A simple guide to electronic components.

Circuit symbols

All electronic components names, functions, testing, pictures and symbols - smd components
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: