Research Design: Choosing your Data Collection Methods | Scribbr 🎓
TLDRThis video script introduces various data collection methods essential for research, highlighting their importance in obtaining firsthand knowledge and insights. It discusses surveys, including questionnaires and interviews, for gathering opinions and experiences, and differentiates between quantitative and qualitative approaches. The script also covers observations, stressing the value of collecting data on actual behaviors versus self-reported ones. Additionally, it touches on other field-specific methods and the option of using secondary data for analysis, urging researchers to draw inspiration from existing studies when selecting the best methods for their research.
Takeaways
- 📝 Data collection methods are essential for direct measurement and information gathering in research.
- 🔍 Researchers can choose a single method or combine multiple methods for a comprehensive study.
- 📊 Surveys are a popular method to gather data on opinions, behaviors, and demographics through questionnaires or interviews.
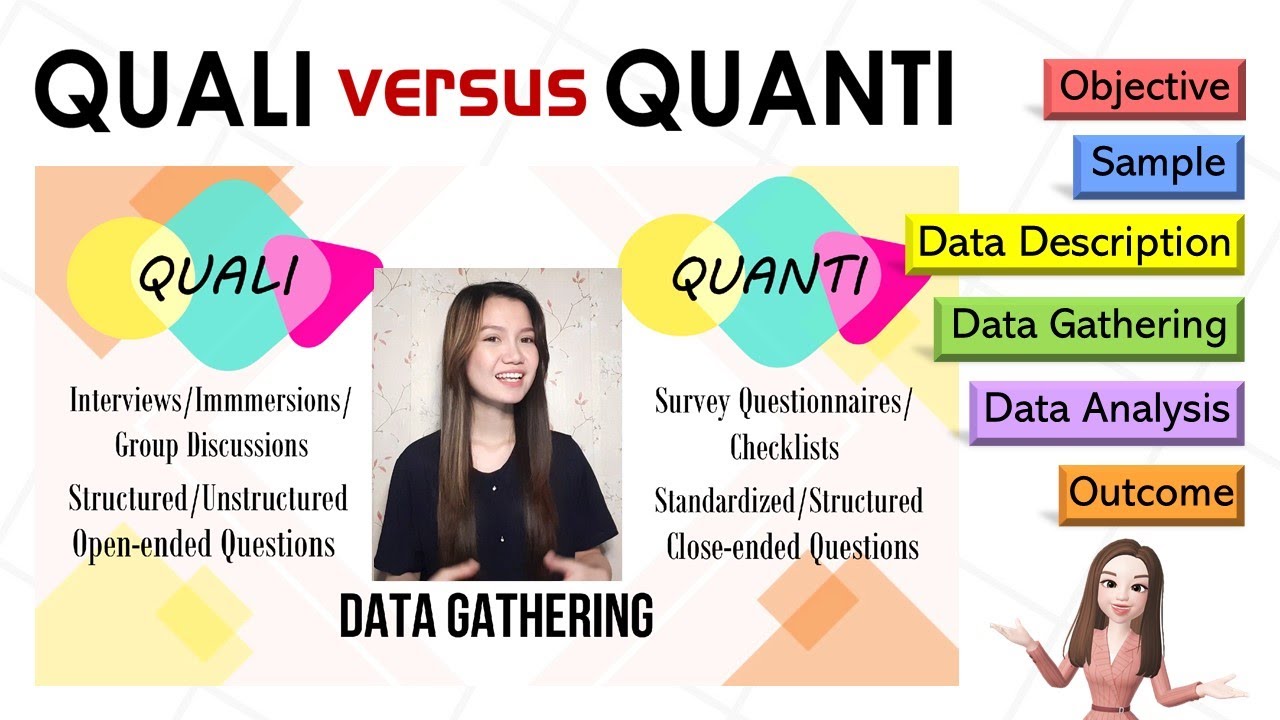
- 📝 Questionnaires are suited for quantitative research, often including closed questions for statistical analysis.
- 🗣️ Interviews are more qualitative, allowing participants to answer in their own words and explore ideas in-depth.
- 👀 Observations enable unobtrusive data collection by watching behaviors or interactions without self-reporting.
- 🔢 Quantitative observation requires systematic counting of specific events with clear, objective rules.
- 📔 Qualitative observation involves detailed note-taking and rich descriptions of observed interactions.
- 🧠 Other fields use specialized data collection methods, such as text analysis in media or neuroimaging in psychology.
- 🔄 Secondary data from previous studies or datasets can be used when original data collection is not feasible.
- 📚 Reviewing relevant studies in your field can guide the selection and application of the most suitable data collection methods.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of data collection methods?
-The primary purpose of data collection methods is to directly measure variables and gather information, allowing researchers to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into their research problems.
What are the two main survey methods mentioned in the script?
-The two main survey methods are self-administered questionnaires and interviews.
How do questionnaires and interviews differ in terms of research type?
-Questionnaires are more common in quantitative research and involve closed questions with standardized answers, while interviews are more common in qualitative research, allowing participants to answer in their own words.
What is the advantage of using questionnaires in research?
-Questionnaires allow for the collection of consistent data from many people, which can be statistically analyzed, and are less time-consuming compared to interviews.
Why might a researcher choose to conduct interviews over questionnaires?
-Interviews allow researchers to explore ideas in more depth through follow-up questions and to understand participants' responses in their own words, providing richer, more nuanced data.
How does observation as a data collection method work?
-Observation involves collecting data by watching characteristics, behaviors, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting, either in real-time or through audiovisual recordings.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative observation?
-Quantitative observation involves systematically measuring or counting specific events or behaviors, while qualitative observation involves taking detailed notes and writing rich descriptions of what is observed without pre-defined categories.
What are some limitations of using secondary data in research?
-Using secondary data limits the researcher's control over which variables are measured and how they are measured, potentially limiting the conclusions that can be drawn from the analysis.
How can researchers ensure consistency in their observations?
-To ensure consistency in observations, researchers must establish clear, objective rules for what to count or measure and define the categories and criteria of their observation in advance.
What are some examples of data collection methods in different fields?
-Examples include collecting texts for media analysis, using neuroimaging in psychology, employing tests or assignments in education, and utilizing scientific instruments to measure physical properties in the physical sciences.
What should researchers do if they are unsure about the best methods for their research?
-Researchers can read relevant studies in their field to see how others have approached similar research problems and decide on the methods they want to use based on those examples.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to Data Collection Methods
This paragraph introduces the concept of data collection methods, emphasizing their importance in gaining first-hand knowledge and insights for research. It explains that researchers can choose from a variety of methods, either using one or combining several in a single study. The paragraph outlines the most common data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations, providing examples of how they can be applied in different research contexts. It also touches on the use of secondary data as an alternative when time or resources are limited.
📋 Surveys and Interviews: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches
This section delves into the specifics of two common data collection methods: surveys and interviews. Surveys are described as a way to gather data on opinions, behaviors, experiences, and demographics through questionnaires or interviews. The paragraph highlights the quantitative nature of questionnaires, which often include closed questions suitable for statistical analysis, and the qualitative aspect of interviews, which allow for in-depth exploration of participants' thoughts. The example of measuring student satisfaction with online classes illustrates the use of questionnaires, while the exploration of teachers' preparation for online classes exemplifies interviews.
👀 The Role of Observations in Data Collection
Observations are introduced as a method for collecting data unobtrusively, focusing on behaviors, characteristics, or social interactions without self-reporting. The paragraph distinguishes between quantitative and qualitative observations, with the former involving systematic measurement or counting of specific events and the latter involving detailed note-taking and rich descriptions. The importance of clear, objective rules for consistent counting in quantitative observation is emphasized, as well as the flexibility of qualitative observation in capturing the nuances of behavior. The paragraph also cautions that being observed may influence participants' behavior.
📚 Exploring Various Data Collection Methods by Field
This paragraph discusses the diversity of data collection methods employed across different fields. It provides examples of how these methods are tailored to the specific needs of various disciplines, such as media and communication, psychology, education, and physical sciences. The paragraph illustrates how these methods can be used to analyze texts, measure cognitive functions, assess knowledge and skills, and determine physical properties like weight or blood pressure.
🔄 Utilizing Secondary Data for Research
The final part of the script addresses the use of secondary data when primary data collection is not feasible. It explains that secondary data, derived from previous studies or government surveys, can be analyzed to answer new research questions. While this approach provides access to larger and more diverse samples, it also comes with limitations, as the researcher has no control over the variables measured or the methodology used in the original study. The paragraph concludes by encouraging researchers to consult relevant studies in their field to inform their choice of data collection methods and to plan the details of their implementation.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Data collection methods
💡Surveys
💡Questionnaires
💡Interviews
💡Observations
💡Quantitative observation
💡Qualitative observation
💡Secondary data
💡Data analysis
💡Research methodology
Highlights
Data collection methods are essential for directly measuring variables and gathering information for research.
Using multiple data collection methods in a single study can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Surveys are an effective way to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and demographic characteristics.
Questionnaires are commonly used in quantitative research and include closed questions with multiple-choice answers or rating scales.
Interviews are more common in qualitative research, allowing participants to answer questions in their own words and explore ideas in-depth.
Observations can be conducted unobtrusively, observing behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Quantitative observation involves systematically measuring or counting specific events or behaviors with clear, objective rules.
Qualitative observation involves taking detailed notes and writing rich descriptions of what is observed, without pre-defined categorization.
Observations can capture data on how people really behave, but being observed may influence participants' behavior.
Secondary data from other researchers can be used for analysis when time or resources are limited.
Using secondary data provides access to larger and more varied samples but may limit the conclusions that can be drawn.
Reading relevant studies in your field can help in choosing the best methods for your research.
Planning the details of data collection methods is crucial for effective research.
Join the next video to learn more about the application and specifics of using different data collection methods.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Research - EP.5 (Research Simplified)

Empirical Research - Qualitative vs. Quantitative

Qualitative research methods

Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research (Practical Research 2)

Qualitative vs Quantitative vs Mixed Methods Research: How To Choose Research Methodology

Qualitative and Quantitative Research
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: