Wearing Glasses - What's the Power? | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-03
TLDRThis script explains the concept of lens power in eyeglasses and contact lenses, measured in diopters. It clarifies that a plus number indicates a converging lens with a focal length of one over the given number in meters, while a minus number signifies a diverging lens. The human eye's typical power is about 40 diopters, due to the cornea's curvature. The script illustrates how additional lens power from glasses is a small adjustment to the eye's natural power, emphasizing the relationship between lens curvature and focal length.
Takeaways
- 👓 Glasses and contact prescriptions include a power value, which is related to the lens' ability to bend light.
- 🔍 The lens power is calculated as 1 divided by the focal length (f), and it's measured in diopters.
- 📏 Diopters are a unit of measurement where 1 diopter equals the reciprocal of the focal length in meters.
- 🌟 A plus (+) prescription indicates a converging lens, while a minus (-) indicates a diverging lens.
- 👁️ The human eye has a natural lens power of approximately 40 diopters, due to the cornea's curvature.
- 📐 The focal length of the eye is about 25 millimeters, which is derived from the size of the eye.
- 👓 When you wear glasses, the additional power is added on top of the eye's natural 40 diopters.
- 🤓 The prescription values like +2.5 or +3.0 are fractional changes to the eye's natural power.
- 🔬 The curvature of the glasses can be observed; they are not very curved compared to the highly curved human eyeball.
- 💡 The more curved a lens is, the shorter its focal length and the higher its lens power.
- 🧐 Understanding your prescription helps you know if you need a strong converging lens or a more relaxed one.
Q & A
What does the number on an eye prescription represent?
-The number on an eye prescription represents the lens power, which is the refractive power of the lens measured in diopters.
What is the significance of the term 'diopters' in the context of eye prescriptions?
-Diopters is a unit of measurement for lens power, defined as the reciprocal of the focal length in meters.
How is the refractive power of a lens calculated?
-The refractive power of a lens is calculated as 1 over the focal length (1/f).
What does a positive lens power indicate on an eye prescription?
-A positive lens power indicates a converging lens, meaning the lens brings light rays together to focus at a point.
What does a negative lens power signify?
-A negative lens power signifies a diverging lens, which spreads out light rays instead of converging them.
What is the typical focal length of the human eye?
-The typical focal length of the human eye is about 25 millimeters, which equates to a refractive power of approximately 40 diopters.
Why are the lenses in glasses not very curved compared to the human eye?
-The lenses in glasses are not very curved because they are designed to provide only a small fractional change to the already powerful curvature of the human eye.
How does the curvature of the cornea relate to its refractive power?
-The more curved the cornea is, the shorter its focal length, and the greater its refractive power.
What is the purpose of adding additional lens power when wearing glasses for reading?
-Adding additional lens power when wearing glasses for reading helps to adjust the focal point to accommodate for the natural decline in the eye's ability to focus on close objects.
How can you determine if your eyes require a lot of converging power from your glasses?
-You can determine if your eyes require a lot of converging power by looking at the prescription number; a higher positive number indicates a stronger converging lens is needed.
What does the difference in lens power between the left and right eye on a prescription indicate?
-The difference in lens power between the left and right eye indicates that each eye has a different level of refractive error and requires a lens with a specific power to correct it.
Outlines
👓 Understanding Lens Prescriptions
This paragraph explains the concept of lens power as indicated on eye prescriptions. It discusses how prescriptions are denoted with plus or minus numbers, which represent the refractive power of the lens measured in diopters. The focal length of the lens is inversely related to its power, with plus lenses converging light and minus lenses diverging it. The script uses the example of a plus three lens for the left eye and a plus 2.5 for the right eye, illustrating the focal lengths in meters. It also contrasts the curvature and power of glasses lenses with that of the human eye, emphasizing the high power of the cornea at about 40 diopters.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Prescription
💡Lens Power
💡Refractive Power
💡Diopters
💡Focal Length
💡Plus Lenses
💡Negative Lenses
💡Cornea
💡Farsightedness
💡Nearsightedness
💡Curvature
Highlights
Prescription at the eye doctor includes lens power measured in diopters.
Lens power is defined as 1 over the focal length of the lens.
Diopter measurement is one over meters.
A plus one lens indicates a focal length of one meter.
A plus two lens has a focal length of half a meter.
The left eye prescription of plus three indicates a focal length of about a third of a meter.
Negative numbers on a prescription indicate diverging lenses.
A negative two power lens has a focal length of negative 0.5 meters.
Prescription helps determine the need for converging or diverging lens power.
The typical focal length of the human eye is about 25 millimeters.
The cornea's power is approximately 40 diopters due to its curvature.
Adding power to the eye's natural 40 diopters is a small fractional change.
Glasses for reading have a slight curvature, indicating a small additional lens power.
The human eyeball is very curved, resembling a marble, indicating high lens power.
Greater curvature of the eye results in a shorter focal length and higher lens power.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (2 of 5) Nearsighted

Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (4 of 5) Farsighted
Physics - Optics: Lenses (3 of 5) Lens Combinations - Converging & Diverging Lenses
Contact Lenses | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-21
Multiple Two Lens System with Diverging and Converging Lens
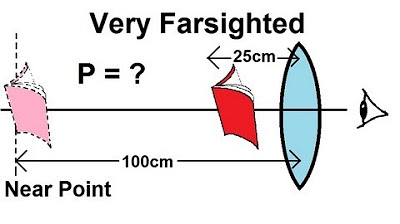
Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (5 of 5) Very Farsighted
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: