Fission and Fusion
TLDRThis script delves into the fundamental concepts of nuclear fusion and fission, explaining their historical roots in alchemy and their modern applications. It describes how fusion, the process of combining atomic nuclei, powers stars and creates elements, while fission involves splitting heavy nuclei, releasing energy. The script highlights the challenges of harnessing fusion for energy production due to the extreme temperatures required and control issues. In contrast, fission is more manageable and is used in nuclear reactors to generate electricity. It also touches on the darker side of these technologies, their use in nuclear weapons, including fission bombs and thermonuclear devices, which are significantly more destructive.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Fusion and fission have been conceptualized for centuries, with early forms known as Alchemy.
- 🌟 Fusion involves combining two or more atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, which powers stars and creates elements up to lead.
- 🔥 High temperatures over 40 million degrees Celsius are required for fusion to occur, as seen in our Sun.
- 💥 The Sun's fusion process involves isotopes of hydrogen, deuterium and tritium, combining to form helium and releasing energy and a neutron.
- ⚡ Harnessing fusion for energy is challenging due to the extremely high temperatures needed and the difficulty in controlling the reaction.
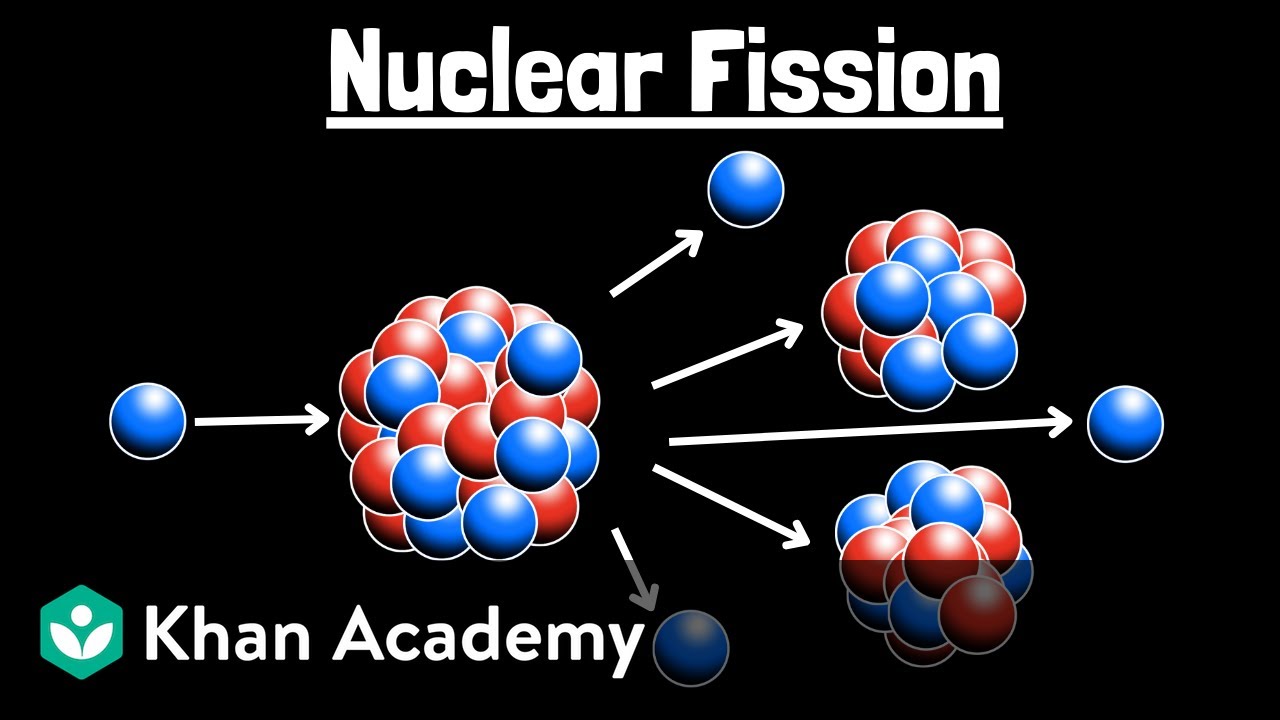
- 💣 Fission is the splitting of an atomic nucleus into smaller fragments, releasing energy and neutrons, primarily occurring in uranium-235 or plutonium-239.
- ⛓ A chain reaction in fission occurs when neutrons released split more fissile atoms, creating a self-sustaining series of fission events.
- 🌐 Nuclear reactors use controlled fission in fuel rods to generate heat for steam production, which then drives turbines to create electricity.
- 💧 Spent fuel rods from reactors remain radioactive and are stored in water to cool and shield from radiation, sometimes for recycling or permanent storage.
- 🚫 Both fusion and fission can be utilized in nuclear weapons, with fission bombs causing radioactive fallout and thermonuclear bombs combining fission and fusion for massive destructive power.
- 👋 The video concludes with a reminder to like, subscribe, and follow the channel on social media for more educational content.
Q & A
What were the historical concepts of fusion and fission known as?
-The historical concepts of fusion and fission were known as Alchemy.
What is the fundamental difference between fusion and fission?
-Fusion involves combining two or more atomic nuclei to create a nucleus of greater mass, while fission involves splitting a nucleus into smaller fragments.
What elements are created through fusion?
-All elements exist because fusion from hydrogen atoms created larger atoms up through lead.
What is the primary source of energy in stars, including our sun?
-Stars, including our sun, are powered by fusion, which creates helium and other elements.
What is the minimum temperature required for fusion to occur?
-Fusion requires very high temperatures, over 40 million degrees Celsius, to occur.
What isotopes of hydrogen are involved in a typical fusion reaction in the Sun?
-Deuterium (an isotope of hydrogen with one neutron) and tritium (an isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons) are involved in a typical fusion reaction in the Sun.
What are the two main challenges in harnessing energy from fusion?
-The two main challenges in harnessing energy from fusion are achieving the extremely high temperatures required to initiate the reaction and controlling the reaction itself.
Which isotopes are necessary for nuclear fission to occur?
-Nuclear fission will only occur when neutrons hit one of two fissionable isotopes: uranium-235 or plutonium-239.
How does a chain reaction in a nuclear reactor work?
-A chain reaction occurs when fission releases neutrons, which hit other fissionable atoms, producing more neutrons that can then act with even more fissionable atoms, and so on.
What is the purpose of the cooling towers in a nuclear power plant?
-The cooling towers in a nuclear power plant are used for cooling down and condensing the water so that it can be reused in the system; they do not contain radioactive material but only steam.
What is the difference between a fission bomb and a thermonuclear bomb?
-A fission bomb, also known as an atom bomb, has an explosive output exclusively from fission reactions. A thermonuclear bomb uses fission to trigger fusion reactions, making it much more powerful and potentially destructive.
How are spent fuel rods in a nuclear power plant handled?
-Spent fuel rods, which are still radioactive, are placed underwater in holding tanks to cool them down and reduce radiation levels. They can be stored for many years and may later be recycled or moved to a more permanent storage location.
Outlines
🔬 Nuclear Fusion and Fission Basics
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of nuclear fusion and fission, which have been considered since the time of alchemy. It explains that fusion is the process where two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, as seen in stars, while fission involves splitting a heavy nucleus into smaller ones, releasing energy and neutrons. The paragraph also discusses the practical challenges of harnessing fusion for energy production, such as the extremely high temperatures required and the difficulty in controlling the reaction. It contrasts this with fission, which is more manageable and is used in nuclear reactors to generate electricity.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Fusion
💡Fission
💡Alchemy
💡Isotopes
💡Neutron
💡Supernova
💡Nuclear Reactor
💡Spent Fuel Rods
💡Chain Reaction
💡Nuclear Weapon
💡Thermodynamics
Highlights
Fusion and fission have been considered for hundreds of years, historically known as Alchemy.
The goal of fusion is not to turn lead into gold, but to combine atomic nuclei to create heavier elements.
Fusion powers stars, creating helium and other elements, with supernovas responsible for heavier elements.
Fusion requires extremely high temperatures, over 40 million degrees Celsius, to occur.
In the Sun, deuterium and tritium, isotopes of hydrogen, fuse under high temperatures to form helium and release energy.
Harnessing fusion energy for electricity is challenging due to the high temperatures and uncontrollable reactions.
Fission is the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments, releasing neutrons and energy.
Nuclear fission occurs with uranium-235 or plutonium-239 when struck by a neutron, leading to a chain reaction.
Nuclear reactors use controlled fission in fuel rods cooled by a coolant fluid, typically water.
The heat from the reactor core is used to generate steam, which drives a turbine to create electricity.
Cooling towers in nuclear power plants are used for cooling down and condensing water, not for radioactive material.
Spent fuel rods are radioactive and must be stored underwater in holding tanks to cool and shield radiation.
Spent fuel rods can glow blue due to Cherenkov radiation and may be stored for years or recycled.
Fission and fusion can be used in nuclear weapons, with fission bombs relying solely on fission reactions.
Only two fission bombs have been used in warfare, causing radioactive contamination known as nuclear fallout.
Thermonuclear bombs use fission to trigger fusion reactions, creating the most powerful and destructive nuclear weapons.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

FISSION vs. FUSION! Which is better?
Difference between Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion

Nuclear Fission: The Basics
Nuclear fission | High school chemistry | Khan Academy

Fusion, Fission, and Energy in Nuclear Equations - IB Physics

Why is nuclear fusion not used to generate electricity? | #aumsum #kids #science
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: