Newton's Second Law of Motion | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
TLDRThe video script delves into Newton's Second Law of Motion, illustrating the principle through a hypothetical scenario involving a royal king, a grand science festival, and the comparison between the forces exerted by a human and a horse on a rock. It emphasizes that force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration, a concept central to understanding motion. The narrative uses the analogy of Newton and a horse applying different magnitudes of force to move a rock, demonstrating that greater force results in greater acceleration. This engaging overview not only explains the law's mathematical expression (F = ma) but also highlights the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration in a relatable way, sparking interest in the fundamental principles of physics.
Takeaways
- 📚 Newton's Second Law of Motion is the focus of the Grand Science Festival.
- 🔵 The rate of change of an object's momentum is directly proportional to the force applied.
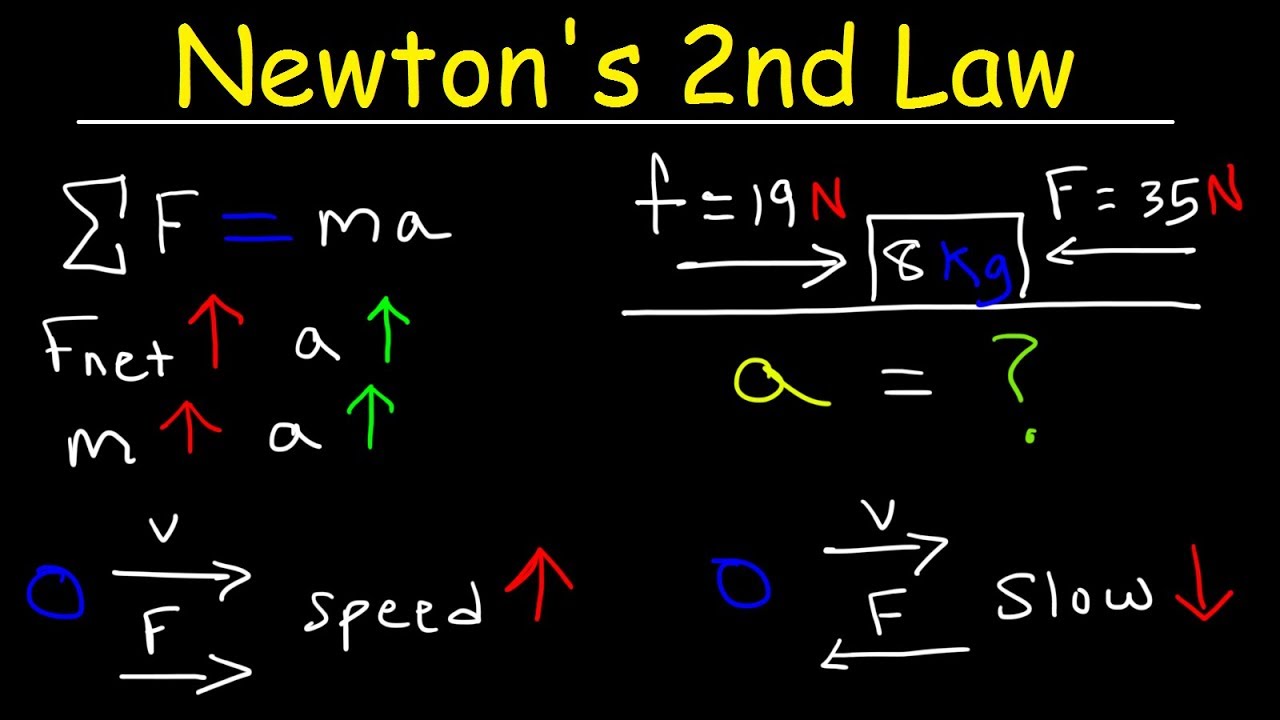
- ⚖️ Force (F) is directly proportional to mass (m) times acceleration (a), as expressed by the formula F = ma.
- 🪨 A small force applied by Newton causes a rock to move slightly, indicating a low acceleration.
- 🐎 A greater force applied by a horse results in a larger movement of the rock, indicating higher acceleration.
- 🤜 Less force results in less acceleration, as seen when Newton applies force.
- 💪 More force results in more acceleration, as seen when the horse applies force.
- 🏋️♂️ The mass of the horse is greater, leading to a greater force being applied.
- 🧍♂️ Newton's mass is less, resulting in a smaller force being applied.
- ⚖️ Force is shown to be directly proportional to mass, with greater mass leading to greater force.
- ⏱️ Force is also directly proportional to acceleration, with greater force leading to greater acceleration.
- 🔧 Combining these relationships, force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration.
Q & A
What is Newton's Second Law of Motion?
-Newton's Second Law of Motion states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the unbalanced force acting on it, and the force acts in the direction of the force applied.
What is the relationship between force and mass according to Newton's Second Law?
-Force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration (F = ma), meaning that for a given mass, the greater the force applied, the greater the acceleration produced.
Why does the rock move only slightly when Newton applies force?
-The rock moves only slightly because Newton, having less mass, applies less force, resulting in less acceleration according to Newton's Second Law.
How does the horse's force application compare to Newton's in terms of moving the rock?
-The horse applies more force because it has more mass, which results in greater acceleration and a greater distance moved by the rock.
What does it imply if force is proportional to acceleration?
-It implies that for a constant mass, an increase in the force applied to an object will result in an increase in its acceleration, and vice versa.
What is the implication of Newton having less mass in the context of force application?
-With less mass, Newton is able to exert less force, which in turn produces less acceleration and movement of the rock.
How does the mass of the horse affect the force it can apply?
-The greater mass of the horse allows it to apply more force, which according to Newton's Second Law, results in a higher acceleration when the same force is applied to the rock.
What is the significance of the statement 'force is directly proportional to mass' in the script?
-This statement highlights that the amount of force an object can exert is related to its mass; larger masses can exert greater forces.
How does the script illustrate the concept that force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration?
-The script uses the examples of Newton and the horse to show that the force exerted on the rock results from the product of their respective masses and the accelerations they produce.
What is the Grand Science Festival mentioned in the script?
-While the script does not provide specific details, the Grand Science Festival is likely an event where scientific principles and discoveries are celebrated and explored, possibly including demonstrations of Newton's laws.
Why might someone try to move the rock as suggested in the script?
-The suggestion to try moving the rock is likely an invitation to experiment with and observe the effects of force and mass on acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law.
What additional factors could influence the movement of the rock other than force, mass, and acceleration?
-Factors such as the friction between the rock and the surface it's on, the angle at which the force is applied, and the rock's initial velocity could also influence its movement.
Outlines
📚 Newton's Second Law of Motion
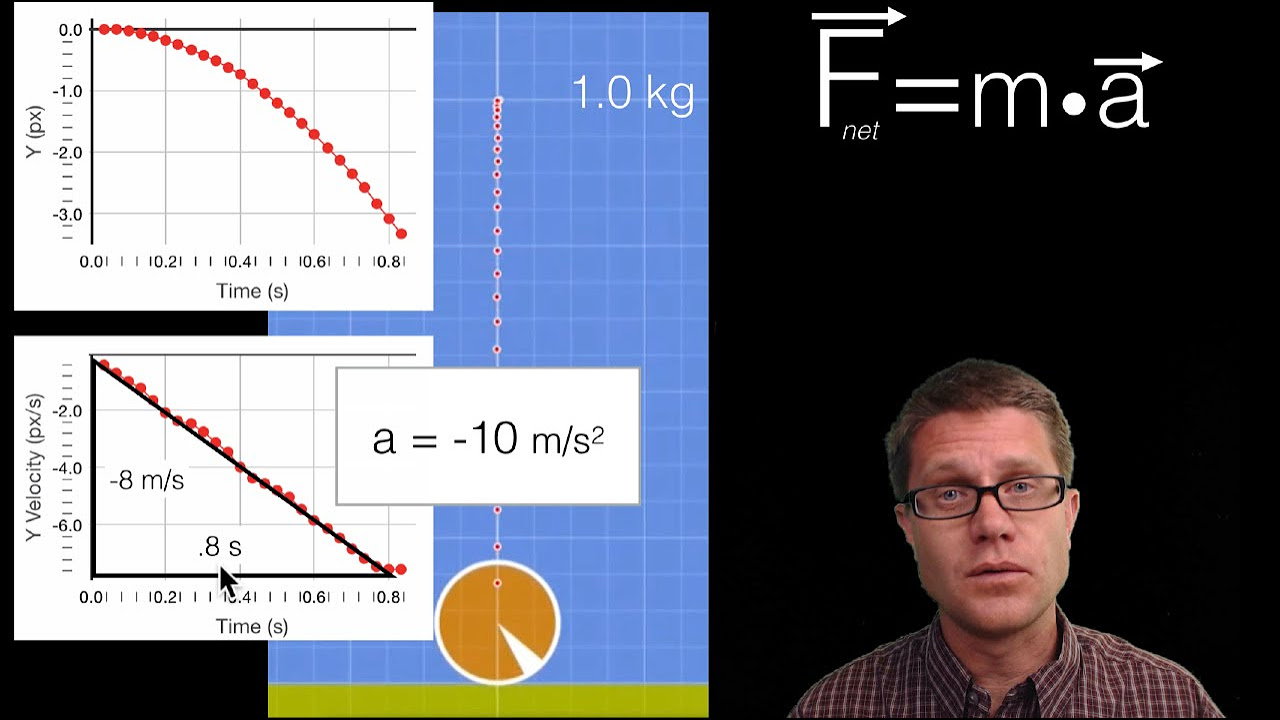
This paragraph introduces Newton's Second Law of Motion, which explains the relationship between the force applied to an object and the resulting acceleration. The law is articulated as F = ma, where F is the force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration. The script uses an analogy of Newton and a horse applying different amounts of force to move a rock, illustrating that greater force results in greater acceleration. It concludes by emphasizing that force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Newton's Second Law of Motion
💡Grand Science Festival
💡Rate of Change of Momentum
💡Unbalanced Force
💡Direct Proportionality
💡Acceleration
💡Mass
💡Force
💡Rock
💡Horse
💡Product of Mass and Acceleration
Highlights
Newton's Second Law of Motion is introduced
The law states that the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the unbalanced force
Force (F) is directly proportional to mass (m) times acceleration (a)
Newton's force causes the rock to move only slightly
The horse's force causes the rock to move a greater distance
Newton applies less force, resulting in less acceleration
The horse applies more force, resulting in more acceleration
Force is directly proportional to acceleration
Newton's mass is less, so he applies less force
The horse's mass is more, so it applies more force
Force is directly proportional to mass
Force is directly proportional to both mass and acceleration
Newton's Second Law can be expressed as F = m*a
The law helps explain how force affects an object's motion
The law is a fundamental principle in classical mechanics
The law has practical applications in engineering and physics
The law has been validated through numerous experiments
The law is a major theoretical contribution by Isaac Newton
The law is a cornerstone of our understanding of motion
The law is a key concept in the Grand Science Festival
The law has had a significant impact on the development of science
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Newton's second law of motion | Forces and Newton's laws of motion | Physics | Khan Academy
Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force, Mass, & Acceleration

Newton's Second Law of Motion | Physics | Infinity Learn NEET
Newton's Laws of Motion and Forces
Newton's Second Law

Newton's 2nd Law of Motion in Physics Explained - [1-5-6]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: